Portal maintenance status: (March 2022)
|

Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar and also rendered Burma (the official English form until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has a population of about 55 million. It is bordered by India to its west, Bangladesh to its southwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon (formerly Rangoon).
Myanmar is a member of the East Asia Summit, Non-Aligned Movement, ASEAN, and BIMSTEC, but it is not a member of the Commonwealth of Nations despite once being part of the British Empire. Myanmar is a Dialogue Partner of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. The country is very rich in natural resources, such as jade, gems, oil, natural gas, teak and other minerals, as well as also endowed with renewable energy, having the highest solar power potential compared to other countries of the Great Mekong Subregion. However, Myanmar has long suffered from instability, factional violence, corruption, poor infrastructure, as well as a long history of colonial exploitation with little regard to human development. In 2013, its GDP (nominal) stood at US$56.7 billion and its GDP (PPP) at US$221.5 billion. The income gap in Myanmar is among the widest in the world, as a large proportion of the economy is controlled by cronies of the military junta. Myanmar is one of the least developed countries; as of 2020, according to the Human Development Index, it ranks 147 out of 189 countries in terms of human development, the lowest in Southeast Asia. Since 2021, more than 600,000 people were displaced across Myanmar due to the surge in violence post-coup, with more than 3 million people in dire need of humanitarian assistance. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1

---- Countries that have officially condemned the events in MyanmarCountries that have offered humanitarian aid to Rohingya MuslimsCountries that have given support for Myanmar's policies regarding Rohingya Muslims
The Rohingya genocide is a term applied to the persecution—including mass killings, mass rapes, village-burnings, deprivations, ethnic cleansing, and internments—of the Rohingya people of western Myanmar (particularly northern Rakhine state).
International reaction focused on pressuring Aung San Suu Kyi to condemn the atrocities and address human-rights issues. Suu Kyi's power was restricted under the 2008 Constitution of Myanmar, which placed key ministries like home, border affairs and defense under military control and reserved 25% of seats in the legislature for serving military officers. Military chief Min Aung Hlaing is regarded as the most powerful person in the country, and in 2021 he launched a military coup, seizing control of the government. (Full article...) -
Image 2Severe flooding in Myanmar began in July 2015 and continued into September, affecting 12 of the country's 14 states, resulting in about 103 deaths and affecting up to 1,000,000 people. Most of the casualties were reported from the Irrawaddy Delta. Torrential rains that began on 16 July destroyed farmland, roads, rail tracks, bridges and houses, leading the government to declare a state of emergency on 30 July in the four worst-hit regions in the west—Magway Division, Sagaing Division, Chin State and Rakhine State.
Myanmar's Ministry of Agriculture reported that more than 1.29 million acres of farm land have been inundated and 687,200 acres damaged. Moreover, 15,239 houses were destroyed, according to OCHA figures. (Full article...) -
Image 3Myint Myint Khin FRCP (Burmese: မြင့်မြင့်ခင်, pronounced [mjɪ̰ɰ̃ mjɪ̰ɰ̃ kʰɪ̀ɰ̃]; 15 December 1923 – 19 June 2014) was a Burmese medical professor and writer. An English major at the University of Rangoon, she was the chair of the Department of Medicine of the Institute of Medicine, Mandalay from 1965 to 1984, and served as a consultant at the World Health Organization from 1985 to 1991. Her literary career began in 1996, spurred on by the HIV/AIDS crisis in the country. She published 11 books in Burmese and two in English. At the time of her death, the former professor was collaborating on an English language book on the history of medical education in the country.
Most of her books dealt with public health and medicine. One notable exception was her last published book in 2013, Poetry for Me, a collection of her English language poetry, which she began working on after the death of her husband Dr. San Baw, a hip replacement pioneer, in 1984. Through her books and interviews, she advocated for more openness and transparency in the country, and spoke out about the regression of women's rights in Myanmar. In 2012, she founded a daycare center for elderly physicians in Yangon. (Full article...) -
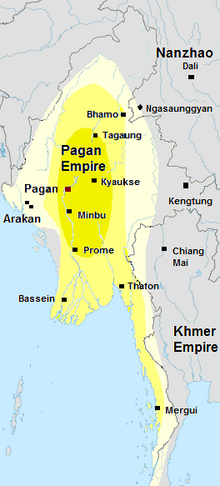
Image 4Pagan empire, c. 1210.
Pagan empire during Sithu II's reign. Kengtung and Chiang Mai are also claimed to be part of the empire according to the Burmese chronicles. Pagan incorporated key ports of lower Burma into its core administration by the 13th century.
The Kingdom of Pagan (Burmese: ပုဂံခေတ်, pronounced [bəɡàɰ̃ kʰɪʔ], lit. 'Pagan Period'; also known as the Pagan dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and culture, the spread of Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.
The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Mranma/Burmans. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, presumably for the first time unifying under one polity the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. By the late 12th century, Anawrahta's successors had extended their influence farther to the south into the upper Malay Peninsula, to the east at least to the Salween river, in the farther north to below the current China border, and to the west, in northern Arakan and the Chin Hills. In the 12th and 13th centuries, Pagan, alongside the Khmer Empire, was one of two main empires in mainland Southeast Asia. (Full article...) -
Image 5

Thura Ma Chit Po (Burmese: သူရ မချစ်ပို; February 1908 – 8 April 1949) was a Burmese woman who was the one and only civilian woman to have received the Thura medal for bravery. She gathered intelligence on the Karen National Defence Organisation (KNDO) on behalf of the Myanmar Military before she was caught and executed by the KNDO insurgents. (Full article...) -
Image 6

Myitkyina (Burmese: မြစ်ကြီးနားမြို့; MLCTS: mrac kri: na: mrui., pronounced [mjɪʔtɕíná]; (Eng; mitchinar) Jinghpaw: Myitkyina, [mjìtkjí̠ná]) is the capital city of Kachin State in Myanmar (Burma), located 1,480 kilometers (920 mi) from Yangon, and 785 kilometers (488 mi) from Mandalay [1]. In Burmese it means "near the big river", and Myitkyina is on the west bank of the Ayeyarwady River, just below 40 kilometers (25 mi) from Myit-son (Burmese for confluence) of its two headstreams (the Mali and N'mai rivers). It is the northernmost river port and railway terminus in Myanmar. The city is served by Myitkyina Airport. (Full article...) -
Image 7
The 2004 Myanmar cyclone was considered the worst to strike the country since 1968. The second tropical cyclone of the 2004 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, it formed as a depression on May 16 in the central Bay of Bengal. With low wind shear and a surge in the monsoon trough, the storm intensified while meandering over open waters. The storm eventually began a steady northeastward motion due to a ridge to the north over India. While approaching land, an eye developed in the center of the storm, indicative of a strong cyclone. On May 19, the cyclone made landfall along northwestern Myanmar near Sittwe, with maximum sustained winds estimated at 165 km/h (105 mph) by the India Meteorological Department. The storm rapidly weakened over land, although its remnants spread rainfall into northern Thailand and Yunnan province in China.
Winds from the cyclone reached 157 km/h (98 mph) in Myanmar, occurring in conjunction with heavy rainfall and a high storm surge. Despite the storm's ferocity, the government did not report about the cyclone for ten days, as they usually under-report on landfalling storms. The cyclone caused heavy damage throughout Rakhine State, destroying or heavily damaging 4,035 homes and leaving 25,000 people homeless. There was widespread crop damage, resulting in food shortages, and damaged roads disrupted subsequent relief efforts. Damage in Myanmar totaled over K621 million kyat ($99.2 million USD), making it the worst storm in the country since 1968, and there were 236 deaths, with an unofficial death toll as high as 1,000. Although damage was heaviest in Myanmar, the cyclone's effects also spread into neighboring Bangladesh, where strong winds knocked over trees and capsized two ships. (Full article...) -
Image 8
The Karen (/kəˈrɛn/ ⓘ kə-REN), also known as the Kayin, Kariang or Kawthoolese, are an ethnolinguistic group of Tibeto-Burman language-speaking people. The group as a whole is heterogeneous and disparate as many Karen ethnic groups do not associate or identify with each other culturally or linguistically. These Karen groups reside primarily in Kayin State, southern and southeastern Myanmar. The Karen account for around 6.69% of the Burmese population. Many Karen have migrated to Thailand, having settled mostly on the Myanmar–Thailand border. A few Karen have settled in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India, and other Southeast Asian and East Asian countries.
The Karen consist of two subgroups, the White Karen and the Red Karen. The Karen groups as a whole are often confused with the Padaung tribe, best known for the neck rings worn by their women, but they are just one sub-group of Red Karens (Karenni), one of the tribes of Kayah in Kayah State, Myanmar. (Full article...) -
Image 9The Thirty Comrades (Burmese: ရဲဘော်သုံးကျိပ်) constituted the embryo of the modern Burmese army called the Burma Independence Army (BIA) which was formed to fight for independence from Britain. This was accomplished just before the majority of the Thirty Comrades returned with the invading Japanese Army initially through Southern Burma in December 1941.
In April 1941, small groups of Burmese youth left Burma secretly to obtain military training to fight the British colonists in the struggle for independence. Their leader was Thakin Aung San and they were sent by the Dobama Asiayone ("We Burmans Association") with the intention to get assistance from Guangzhou. By a quirk of fate, however, they ran into the Japanese instead in Amoy and arrived in Japan later to be flown to occupied parts of Sanya, in order to receive military training from the Japanese Army. They were later moved to Formosa for security reasons and subsequently returned to Burma via Vietnam and
Thailand with the Japanese. On 26 December 1941, in a house (owned by a Burmese doctor) in Bangkok, about 25 of the Thirty Comrades had their blood drawn from their arms in syringes, then poured into a silver bowl from which each of them drank – thway thauk in time-honoured Burmese military tradition – pledging "eternal loyalty" among themselves and to the cause of Burmese independence. Their average age was just 24 years. A Japanese officer called Suzuki Keiji, better known among the Burmese by his nom de guerre Bo Mogyo (Commander Thunderbolt) and head of a special intelligence unit called Minami Kikan (南機関) formed in order to support a national uprising in Burma, was the mentor and principal trainer of the Thirty Comrades. The British were driven out of Burma to India during World War II. (Full article...) -
Image 10
The State Peace and Development Council (Burmese: နိုင်ငံတော် အေးချမ်းသာယာရေး နှင့် ဖွံ့ဖြိုးရေး ကောင်စီ [nàɪɰ̃ŋàɰ̃dɔ̀ ʔédʑáɰ̃θàjajé n̥ḭɰ̃ pʰʊ̰ɰ̃bjó jé kaʊ̀ɰ̃sì]; abbreviated SPDC or နအဖ, [na̰ʔa̰pʰa̰]) was the official name of the military government of Burma (Myanmar) which, in 1997, succeeded the State Law and Order Restoration Council (Burmese: နိုင်ငံတော် ငြိမ်ဝပ်ပိပြားမှု တည်ဆောက်ရေးအဖွဲ့; abbreviated SLORC or နဝတ) that had seized power under the rule of Saw Maung in 1988. On 30 March 2011, Senior General and Council Chairman Than Shwe signed a decree that officially dissolved the council.
SLORC succeeded the Pyithu Hluttaw as a legislature and the Council of State as a ruling council, after dissolving the state organs of the Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma. In 1997, SLORC was abolished and reconstituted as the State Peace and Development Council (SPDC). The powerful regional military commanders, who were members of SLORC, were promoted to new positions and transferred to the capital of Rangoon (now Yangon). The new regional military commanders were not included in the membership of the SPDC. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) - load new batch

- ... that Molly Burman resumed releasing music three years later after finding that "Happy Things" had accrued a million streams on Spotify?
- ... that former Burmese actress Honey Nway Oo turned rebel and took up arms against the military junta following the 2021 Myanmar coup d'état?
- ... that the talabaw soup, which consists primarily of bamboo shoots, is the essential dish of Myanmar's Karen people, who use it to supplement rice?
- ... that Maung O, Prince of Salin, and his sister Nanmadaw Me Nu became de facto rulers of Burma when King Bagyidaw was suffering from depression?
- ... that the Burmese Buddhist monk Sagyo Thu-Myat successfully lobbied for the recalibration of the Burmese calendar?
- ... that one academic described the introduction of femboys to Myanmar as a tactic to achieve an "ideological revolution"?
- ... that Thinzar Shunlei Yi hid in the Burmese jungle for a month and joined a rebel militia following the 2021 Myanmar coup d'état?
- ... that the mission of the United Nations special envoy on Myanmar has been called a "diplomatic graveyard"?
Related portals and projects
General images - load new batch
-
Image 1Aung San Suu Kyi addresses crowds at the NLD headquarters shortly after her release. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 2Salween river at Mae Sam Laep on the Thai-Myanmar border (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 3A bull fight, 19th-century watercolour (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 4The restored Taungoo or Nyaungyan dynasty c. 1650 CE. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 5Vegetable stall on the roadside at the Madras Lancer Lines, Mandalay, January 1886. Photographer: Hooper, Willoughby Wallace (1837–1912). (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 6Aerial view of a burned Rohingya village in Rakhine state, September 2017 (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 7Recorder's Court on Sule Pagoda Road, with the Sule Pagoda at the far end, Rangoon, 1868. Photographer: J. Jackson. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 8Political Map of Burma (Myanmar) c. 1450 CE. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 9Temples at Mrauk U, was the capital of the Mrauk U Kingdom, which ruled over what is now Rakhine State. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 10The paddle steamer Ramapoora (right) of the British India Steam Navigation Company on the Rangoon river having just arrived from Moulmein. 1895. Photographers: Watts and Skeen (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 13Portuguese ruler and soldiers mounting an Elephant. Philips, Jan Caspar (draughtsman and engraver) (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 14Saint Mary's Cathedral in Downtown Yangon is the largest Roman Catholic cathedral in Burma. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 15The shores of Irrawaddy River at Nyaung-U, Bagan (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 16A wedding procession, with the groom and bride dressed in traditional Burmese wedding clothes, reminiscent of royal attire (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 17British soldiers dismantling cannons belonging to King Thibaw's forces, Third Anglo-Burmese War, Ava, 27 November 1885. Photographer: Hooper, Willoughby Wallace (1837–1912). (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 18Hlei pyaingbwè - a Burmese regatta (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 19Myinhkin thabin - equestrian sport (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 20Sculpture of Myanmar mythical lion (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 21Protesters in Yangon carrying signs reading "Free Daw Aung San Suu Kyi" on 8 February 2021. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 23A large fracture on the Mingun Pahtodawgyi caused by the 1839 Ava earthquake. (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 24Myanmar (Burma) map of Köppen climate classification (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 2519th-century funeral cart and spire, which would form part of the procession from the home to the place of cremation (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 26A theatrical performance of the Mon dance (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 27Protesters in Yangon with a banner that reads non-violence: national movement in Burmese, in the background is Shwedagon Pagoda. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 28British soldiers on patrol in the ruins of the Burmese town of Bahe during the advance on Mandalay, January 1945. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 31A group of Buddhist worshipers at Shwedagon Pagoda, an important religious site for Burmese Buddhists (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 32Pagan Kingdom during Narapatisithu's reign. Burmese chronicles also claim Kengtung and Chiang Mai. Core areas shown in darker yellow. Peripheral areas in light yellow. Pagan incorporated key ports of Lower Burma into its core administration by the 13th century. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 33Grandfather Island, Dawei (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 35British soldiers remove their shoes at the entrance of Shwedagon Pagoda. To the left, a sign reads "Foot wearing is strictly prohibited" in Burmese, English, Tamil, and Urdu. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 37Former US President Barack Obama poses barefoot on the grounds of Shwedagon Pagoda, one of Myanmar's major Buddhist pilgrimage sites. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 38Boxing match, 19th-century watercolour (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 39Two female musicians play the saung at a performance in Mandalay. (from Culture of Myanmar)
Major topics
Categories
More topics
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus