Introduction
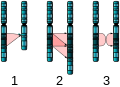
Selected article - Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with artificial selection, which is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Variation of traits, both genotypic and phenotypic, exists within all populations of organisms. However, some traits are more likely to facilitate survival and reproductive success. Thus, these traits are passed onto the next generation. These traits can also become more common within a population if the environment that favours these traits remains fixed. If new traits become more favored due to changes in a specific niche, microevolution occurs. If new traits become more favored due to changes in the broader environment, macroevolution occurs. Sometimes, new species can arise especially if these new traits are radically different from the traits possessed by their predecessors. (Full article...) General images -The following are images from various evolutionary biology-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected picture - The last known Thylacine photographed at Hobart (formerly Beaumaris) Zoo in 1933. A scrotal sac is not visible in this or any other of the photos or film taken, leading to the supposition that "Benjamin" was a female, but the existence of a scrotal pouch in the Thylacine makes it impossible to be certain Did you know... -
CategoriesRelated portalsTasks you can do
Related topicsWikiProjectsWikiProjects connected with biology: A complete list of scientific WikiProjects can be found here. See also Wikispecies, a Wikimedia project dedicated to classification of biological species. Associated WikimediaDiscover Wikipedia using portals |
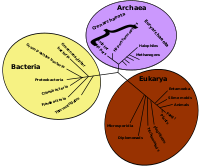

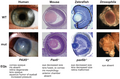









![Image 16A covalent adduct between the metabolite of benzo[a]pyrene, the major mutagen in tobacco smoke, and DNA (from Mutation)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d8/Benzopyrene_DNA_adduct_1JDG.png/87px-Benzopyrene_DNA_adduct_1JDG.png)