The Viruses Portal
Welcome!
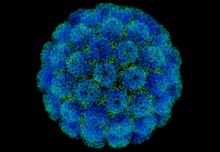
Viruses are small infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all forms of life, including animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and archaea. They are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most abundant type of biological entity, with millions of different types, although only about 6,000 viruses have been described in detail. Some viruses cause disease in humans, and others are responsible for economically important diseases of livestock and crops.
Virus particles (known as virions) consist of genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA, wrapped in a protein coat called the capsid; some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope. The capsid can take simple helical or icosahedral forms, or more complex structures. The average virus is about 1/100 the size of the average bacterium, and most are too small to be seen directly with an optical microscope.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids, others from bacteria. Viruses are sometimes considered to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce and evolve through natural selection. However they lack key characteristics (such as cell structure) that are generally considered necessary to count as life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life".
Selected disease
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting mainly the liver, caused by hepatitis C virus (HCV), an RNA virus of the Flaviviridae family which only infects humans and chimpanzees. A "non-A non-B hepatitis" was postulated in the 1970s, and HCV was demonstrated in 1989. HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with intravenous drug use in the developed world, and with improperly sterilised medical equipment and blood transfusions in the developing world. In about 80% of those infected, the virus establishes a chronic infection in the liver, and around 10–30% of those infected will develop cirrhosis over 30 years. Some people with cirrhosis go on to develop liver failure, liver cancer or other serious complications.
An estimated 143 million people worldwide (2%) have chronic HCV infections as of 2015. The prevalence is highest in Central and East Asia, North Africa and the Middle East. The virus causes around a quarter of cases of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, and is a major reason for liver transplantation. The recommended therapy is an appropriate combination of protease inhibitors. Although 95% of people treated in this way are cured, the treatments are expensive and older therapies are less effective. No vaccine against hepatitis C is available.
Selected image
Bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, are among the most common entities on Earth.
Credit: Graham Beards (21 October 2008)
In the news
26 February: In the ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), more than 110 million confirmed cases, including 2.5 million deaths, have been documented globally since the outbreak began in December 2019. WHO
18 February: Seven asymptomatic cases of avian influenza A subtype H5N8, the first documented H5N8 cases in humans, are reported in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia, after more than 100,0000 hens died on a poultry farm in December. WHO
14 February: Seven cases of Ebola virus disease are reported in Gouécké, south-east Guinea. WHO
7 February: A case of Ebola virus disease is detected in North Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. WHO
4 February: An outbreak of Rift Valley fever is ongoing in Kenya, with 32 human cases, including 11 deaths, since the outbreak started in November. WHO
21 November: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gives emergency-use authorisation to casirivimab/imdevimab, a combination monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy for non-hospitalised people twelve years and over with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, after granting emergency-use authorisation to the single mAb bamlanivimab earlier in the month. FDA 1, 2
18 November: The outbreak of Ebola virus disease in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, which started in June, has been declared over; a total of 130 cases were recorded, with 55 deaths. UN
Selected article
The history of virology is usually considered to begin in the late 19th century, when the first evidence for the existence of viruses came from experiments using filters with pores small enough to retain bacteria. Dmitry Ivanovsky showed in 1892 that sap from a diseased tobacco plant remained infectious despite having been filtered; this agent, later known as tobacco mosaic virus, was the first virus to be demonstrated. In 1898, Friedrich Loeffler and Paul Frosch showed that foot-and-mouth, an animal disease, was caused by a filterable agent. That year, Martinus Beijerinck (pictured) called the filtered infectious substance a "virus" – often considered to mark the beginning of virology.
Bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, were characterised by Frederick Twort and Félix d'Herelle in the early 20th century. In 1926, Thomas Milton Rivers defined viruses as obligate parasites. Viruses were demonstrated to be particles, rather than a fluid, by Wendell Meredith Stanley, and the invention of the electron microscope in 1931 allowed them to be visualised.
Selected outbreak
The 1993 hantavirus outbreak in the Four Corners region of southwest USA was of a novel hantavirus, subsequently named Sin Nombre virus. It caused the previously unrecognised hantavirus pulmonary syndrome – the first time that a hantavirus had been associated with respiratory symptoms. Mild flu-like symptoms were followed by the sudden onset of pulmonary oedema, which was fatal in half of those affected. A total of 24 cases were reported in April–May 1993, with many of those affected being from the Navajo Nation territory. Hantavirus infection of humans generally occurs by inhaling aerosolised urine and faeces of rodents, in this case the deer mouse (Peromyscus; pictured).
Previously documented hantavirus disease had been confined to Asia and Europe, and these were the first human cases to be recognised in the USA. Subsequent investigation revealed undiagnosed cases dating back to 1959, and Navajo people recalled similar outbreaks in 1918, 1933 and 1934.
Selected quotation
| “ | The unusual features of the giant Mimivirus revived the popular, yet unresolved question: "Are viruses alive?" The discovery that some of them can get sick adds a new twist to this old debate. | ” |
—Hiroyuki Ogata & Jean-Michel Claverie on the relationship between Sputnik virophage and mimivirus
Recommended articles
Viruses & Subviral agents: bat virome • elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus • HIV • introduction to viruses![]() • Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus
• Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus![]() • virus
• virus![]()
Diseases: colony collapse disorder • common cold • croup • dengue fever![]() • gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza
• gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza![]() • meningitis
• meningitis![]() • myxomatosis • polio
• myxomatosis • polio![]() • pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
• pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
Epidemiology & Interventions: 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak • Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations • Disease X • 2009 flu pandemic • HIV/AIDS in Malawi • polio vaccine • Spanish flu • West African Ebola virus epidemic
Virus–Host interactions: antibody • host • immune system![]() • parasitism • RNA interference
• parasitism • RNA interference![]()
Methodology: metagenomics
Social & Media: And the Band Played On • Contagion • "Flu Season" • Frank's Cock![]() • Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa
• Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa![]() • social history of viruses
• social history of viruses![]() • "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
• "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
People: Brownie Mary • Macfarlane Burnet![]() • Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C
• Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C![]() • HIV-positive people
• HIV-positive people![]() • Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock
• Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock![]() • poliomyelitis survivors
• poliomyelitis survivors![]() • Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White
• Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White![]()
Selected virus
Hepatitis delta virus or hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a small virusoid, the sole member of the Deltavirus genus. It infects humans. A subviral satellite, it can only replicate in the presence of a hepatitis B (HBV) helper virus. The spherical virion is 36 nm in diameter, with an envelope containing three HBV proteins. The single-stranded, negative-sense, circular RNA genome of 1679 nucleotides is smaller than that of any known animal virus. It has an unusual base composition for an entity that infects animals, and is extensively bound to itself to form a partially double-stranded, rod-shaped structure. These features have led to suggestions that HDV might be related to viroids, small unencapsidated circular RNAs that infect plants. Unlike viroids, HDV encodes a protein, hepatitis D antigen.
Both HDV and HBV enter liver cells using the sodium/bile acid cotransporter as their receptor. They are mainly transmitted via injecting drug use and blood products. More than 15 million people are infected with both viruses, which is associated with a greater risk of liver complications than HBV infection alone. Around one in five jointly infected patients die. The HBV vaccine protects against HDV.
Did you know?
- ...that the stripes on tulips (examples pictured) that caused tulip mania were probably caused by a virus, but this was unknown to science at the time?
- ...that epidemiologist Li Lanjuan was the first to propose a lockdown of Wuhan during the 2019–20 coronavirus outbreak?
- ...that the human bocavirus is the fourth most commonly found virus in samples collected from the respiratory system?
- ...that research by Harold Ginsberg on adenoviruses led to the development of gene therapy, in which modified versions of viruses can be used to implant healthy versions of genes to treat disease?
- ...that the Tiverton fire of 1731 resulted in an increased incidence of smallpox?
Selected biography
Randy Shilts (8 August 1951 – 17 February 1994) was an American journalist, author and AIDS activist. The first openly gay reporter for a mainstream US newspaper, Shilts covered the unfolding story of AIDS and its medical, social, and political ramifications from the first reports of the disease in 1981. New York University's journalism department later ranked his 1981–85 AIDS reporting in the top fifty works of American journalism of the 20th century. His extensively researched account of the early days of the epidemic in the US, And the Band Played On Politics, People, and the AIDS Epidemic, first published in 1987, brought him national fame. The book won the Stonewall Book Award and was made into an award-winning film. Shilts saw himself as a literary journalist in the tradition of Truman Capote and Norman Mailer. His writing has a powerful narrative drive and interweaves personal stories with political and social reporting.
He received the 1988 Outstanding Author award from the American Society of Journalists and Authors, the 1990 Mather Lectureship at Harvard University, and the 1993 Lifetime Achievement Award from the National Lesbian and Gay Journalists' Association. He died of AIDS in 1994.
In this month
7 November 1991: Magic Johnson announced his retirement from basketball because of his infection with HIV
14 November 1957: Kuru, the first human prion disease, described by Daniel Gajdusek and Vincent Zigas
16 November 2002: The first case of severe acute respiratory syndrome (virus pictured) recorded in Guangdong, China
17 November 1995: Lamivudine approved for treatment of HIV
22 November 2013: Simeprevir approved for treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection
23 November 1978: Structure of tomato bushy stunt virus solved by Stephen Harrison and colleagues, the first atomic-level structure of a virus
24 November 2007: Outbreak of new Ebola species, Bundibugyo virus
26 November 1898: Martinus Beijerinck coined the term contagium vivum fluidum to describe the agent causing tobacco mosaic disease
Selected intervention
Several human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines, including Cervarix and Gardasil, have been approved to protect against infections with particular types of HPV, associated with cervical and other cancers. All vaccines protect against the high-risk HPV types 16 and 18. Gardasil is a quadrivalent vaccine that additionally protects against low-risk HPV-6 and -11, which are associated with most cases of genital warts. A second-generation nine-valent Gardasil vaccine protects against five additional high-risk HPV types. It is estimated that the vaccines may prevent 70% of cervical cancer, 80% of anal cancer, 60% of vaginal cancer, 40% of vulvar cancer and possibly some oropharyngeal cancers. Protection lasts for at least 8–9 years. Some advocate giving Gardasil to men and boys with the primary aim of protecting their female sexual partners; others consider vaccinating only women and girls to be more cost effective. The licensed vaccines are subunit vaccines, containing only the L1 capsid protein of the virus, which self-assembles into virus-like particles. They are not effective in people already infected with HPV. Research is ongoing into therapeutic HPV vaccines including the viral oncoproteins, E6 and E7, but none has yet been licensed.
Subcategories
Subcategories of virology:
Topics
Things to do
- Comment on what you like and dislike about this portal
- Join the Viruses WikiProject
- Tag articles on viruses and virology with the project banner by adding {{WikiProject Viruses}} to the talk page
- Assess unassessed articles against the project standards
- Create requested pages: red-linked viruses | red-linked virus genera
- Expand a virus stub into a full article, adding images, citations, references and taxoboxes, following the project guidelines
- Create a new article (or expand an old one 5-fold) and nominate it for the main page Did You Know? section
- Improve a B-class article and nominate it for Good Article
 or Featured Article
or Featured Article status
status - Suggest articles, pictures, interesting facts, events and news to be featured here on the portal
WikiProjects & Portals
 WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
Medicine • Microbiology • Molecular & Cellular Biology • Veterinary Medicine
Related PortalsAssociated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus

















