The praetorian prefecture of Italy (Latin: Praefectura praetorio Italiae, in its full form (until 356) praefectura praetorio Italiae, Illyrici et Africae) was one of four praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided. It comprised the Italian peninsula, the western Balkans, the Danubian provinces and parts of North Africa. The Prefecture's seat moved from Rome to Milan and finally, Ravenna.
| Praetorian prefecture of Italy Praefectura praetorio Italiae | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Praetorian prefecture of the Roman Empire | |||||||||||||
| 324–584 | |||||||||||||
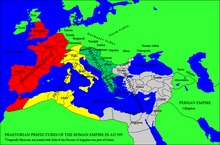 Praetorian prefectures of the Roman Empire in 395 AD. | |||||||||||||
| Capital | Ravenna from 476[citation needed] | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Late antiquity | ||||||||||||
• Established | 324 | ||||||||||||
| 476 | |||||||||||||
| 493 | |||||||||||||
• Start of Gothic War | 535 | ||||||||||||
| 568 | |||||||||||||
• Foundation of Exarchate of Ravenna | 584 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Structure and history
editThe prefecture was established in the division of the Empire after the death of Constantine the Great in 337, and was made up of dioceses. Initially these were the Diocese of Africa, the Diocese of Italy, the Diocese of Pannonia, the Diocese of Dacia and the Diocese of Macedonia (the last two were until c. 327 united in the Diocese of Moesia). Eventually the Diocese of Italy was split in two, the Diocese of Suburbicarian Italy (Italia suburbicaria: "Italy under the City", also referred to as "Diocese of the City of Rome") and the Diocese of Annonarian Italy (Italia annonaria: "provisioning Italy").
In 347, the praetorian prefecture of Illyricum was established, comprising the dioceses of Pannonia, Dacia and Macedonia. Vulcacius Rufinus was the prefect, 347–352. The new prefecture was abolished in 361 by Julian and reestablished in 375 by Gratian. Its territory was contested between the two halves of the Empire, until the final partition in 395, when the Diocese of Pannonia was split off from the Illyricum and joined to the Western Empire and the prefecture of Italy as the Diocese of Illyricum.
Despite the end of the Western Empire in 476, the Germanic successor states under Odoacer and Theodoric the Great continued to use the Roman administrative machinery, as well as being nominal subjects of the Eastern emperor at Constantinople. The Prefecture thus survived, and came again into Roman hands after Justinian's Gothic War. However, with the Lombard invasion in 568, Roman rule became reduced to fragmented and isolated territories, and the Prefecture gave its place to the Exarchate of Ravenna, established by the emperor Maurice.
Prefects continue however to be attested until well into the 7th century. The last attested holder occurs in 639, and a couple of seals bearing the title eparchos ("prefect" in Greek) survive from the late 7th century, although it has been suggested that they are a misprint for exarchos ("exarch").[1]
List of known praefecti praetorio Italiae et Africae
edit- Aemilianus (328)
- Lucius Papius Pacatianus (334-335)
- Aconius Catullinus Philomathius (341)
- Marcus Maecius Memmius Furius Baburius Caecilianus Placidus (342-344)
- Vulcacius Rufinus (first time, 344–347)
- Gaius Ceionius Rufius Volusianus Lampadius (355)
- Taurus (356-361)
- Claudius Mamertinus (361-365)
- Vulcacius Rufinus (second time, 365–368)
- Sextus Claudius Petronius Probus (first time, c. 368–375)
- Decimius Hilarianus Hesperius (378-380)
- Afranius Syagrius (382)
- Flavius Hypatius (382-383)
- Sextus Claudius Petronius Probus (second time, 383)
- Nonius Atticus (383-384)
- Vettius Agorius Praetextatus (384)
- Neoterius (385)
- Sextus Claudius Petronius Probus (third time, 387)
- Virius Nicomachus Flavianus (390-392)
Western Empire
edit- Nummius Aemilianus Dexter (395)
- Eusebius (395-396)
- Mallius Theodorus (397-399)
- Valerius Messala Avienus (399-400)
- Rufus Synesius Hadrianus (400-405)
- Flavius Macrobius Longinianus (1st time, 406)
- Curtius (407-408)
- Flavius Macrobius Longinianus (2nd time, 408)
- Mallius Theodorus (408-409)
- Caecilianus (409)
- Jovius (409)
- Melitius (410-412)
- Seleucus (prefect for Africa, 412)
- Ioannes (412-413)
- Rufus Synesius Hadrianus (413-414)
- Seleucus (414-415)
- Junius Quartus Palladius (416-421)
- Anicius Auchenius Bassus (possibly, 426)
- Anicius Auchenius Bassus (435)
- Anicius Acilius Glabrio Faustus (c. 438)
- Petronius Maximus (439)
- Caecina Decius Aginatius Albinus (443-448)
- Caecina Decius Basilius (458)
- Caelius Aconius Probianus (461-463)
- Caecina Decius Basilius (463-465)
- Felix Himelco (473)
Germanic rule
editUnder Odoacer:
- Nar. Manlius Boethius (between 480 and 486) (he served as consul in 487)
- Caecina Decius Maximus Basilius (483) (he had served as consul in 480)
- Caecina Mavortius Basilius Decius (486-493) (he served as consul in 486)
Under the Ostrogoths:
- Liberius (494-500)
- Flavius Albinus (?500-503)[2] (he had served as consul in 493)
- Cassiodorus the Elder (500-?)
- Anicius Probus Faustus iunior (509-512) (he had served as consul in 490)
- Rufius Magnus Faustus Avienus (527-528) (he had served as consul in 502)
- Faustus (521/522) or 529[3]
- Cassiodorus the Younger (533-537) (he had served as consul in 514)
- Fidelis (537-538)
- Reparatus (538-539)
East Roman rule
edit- Athanasius (539-542)
- Maximinus (c. 542)
- Narses (554-568)
- Longinus (568-575)
References
edit- ^ Nesbitt, John; Oikonomides, Nicolas, eds. (1994). Catalogue of Byzantine Seals at Dumbarton Oaks and in the Fogg Museum of Art, Volume 2: South of the Balkans, the Islands, South of Asia Minor. Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection. p. 16. ISBN 0-88402-226-9.
- ^ Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire, II, 51-2
- ^ Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire, II, P452