This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. (December 2018) |
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2018) |
The Praetorian Prefecture of Gaul (Latin: praefectura praetorio Galliarum) was one of four large prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided.
| Praetorian prefecture of the Gauls Praefectura praetorio Galliarum | |
|---|---|
| Praet. Prefecture of the Western Roman Empire | |
| 337-477 510-536 | |
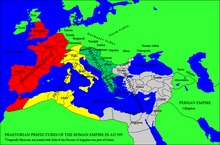 Praetorian Prefectures of the Roman Empire (395) | |
| Capital | Augusta Treverorum (until 395/407) Arelate (from 395/407) |
| Historical era | Late Antiquity |
• Established | 337 |
• Conquest of Provence by the Visigoths | 477 |
• Re-established by the Ostrogoths | 510 |
• Fall of Provence to the Franks | 536 |
| Political subdivisions | Diocese of Gaul Diocese of Britain Diocese of Spain Diocese of the Seven Provinces |
History
editThe prefecture was established after the death of Constantine I in 337, when the empire was split up among his sons and Constantine II received the rule of the western provinces, with a praetorian prefect as his chief aide.[citation needed] The prefecture comprised not only Gaul, but also of Roman Britain, Spain, and Mauretania Tingitana in Africa Proconsulare. Its territory overlapped considerably with what was once controlled by the short-lived Gallic Empire in the 260s.
After the permanent partition of the Empire in 395 into West and East spheres of control, the prefecture of Gaul continued to belong to the Western Roman Empire. Augusta Treverorum (present-day Trier in Germany) served as the prefecture's seat until 407 (or, according to other estimates, in 395), when it was transferred to Arelate (Arles).
The prefecture continued to function until 477, when the last areas under its control were seized by the Visigoths after the abolition of the Western imperial government of Ravenna in the previous year.
In 510, the Ostrogoth king Theodoric the Great re-established the prefecture in the small part of Gaul (the Provence) that he had just conquered, with headquarters again at Arelate. This short lived revival lasted until the area was in turn conquered by the Franks in 536, while the Ostrogoths were occupied by the East Roman invasion of Italy.
List of known praefecti praetorio Galliarum
edit4th century
edit- Junius Bassus (318-331)
- C. Caelius Saturninus (331-335)
- C. Annius Tiberianus (335-337)
- Aurelius Ambrosius (337-340)
- Aconius Catullinus Philomathius (341, uncertain whether he was prefect of Gaul)
- Fabius Titianus (341-350)
- Vulcacius Rufinus (353-354)
- Gaius Ceionius Rufius Volusianus Lampadius (354-355)
- Honoratus (355-357)
- Flavius Florentius (c. 357-360)
- Nebridius (360-361)
- Decimius Germaniacus (361)
- Sallustius (in 363)
- Sextus Claudius Petronius Probus (366)
- Vulcacius Rufinus (2nd term, (366-368)
- Viventius (368-371)
- Maximinus (371-376) [1]
- Flavius Claudius Antonius (376-377)
- Ausonius (377-378, co-prefect from 376)
- Siburius (378-382)
- Mallius Theodorus (382-383)
- Euodius (c. 384-386)
- Constantinianus (389)
- Neoterius (390)
- Hilarius (396)
- Theodorus (396/397)
- Flavius Vincentius (397-400)
5th century
edit- Andromachus (c. 401)
- Claudius Postumus Dardanus (1st term, c. 402)
- Romulianus (404-405)
- Petronius (402-408) - seat of the prefecture moved to Arelate in 407
- Limenius (408) - assassinated at Ticinum (Pavia)
- Apollinaris (408)
- Decimus Rusticus (409-411)
- Claudius Postumus Dardanus (2nd term, 412-413)
- Vicentius (413)
- Iulius (c. 414)
- Agricola (416-418)
- Exuperantius (421-424)
- Amatus (c. 425)
- Flavius Aetius (426-c. 427)
- Auxiliaris (435-437)
- Avitus (c. 439)
- Florentius (439)
- Caecina Decius Aginatius Albinus (440)
- Marcellus (c. 441-445)
- Tonantius Ferreolus (450/451-453)
- Priscus Valerianus (before 456)
- Paeonius (456-458)
- Magnus (459-460)
- Arvandus (461-465, 467-468)
- Magnus (469)
- Magnus Felix (c. 470)
- Eutropius (c. 471)
- Polemius (475-after 477) - the last remnants of the prefecture in the Provence were conquered by the Visigoths
6th century
edit- Petrus Marcellinus Felix Liberius (510-536) - Prefect under Ostrogothic rule
References
edit- ^ Burns (1994), p. 58
Sources
edit- Burns, Thomas S. (1994), Barbarians within the gates of Rome:a study of Roman military policy and the barbarians, ca. 375-425 A.D., Indiana University Press, ISBN 978-0-253-31288-4