The bare-throated bellbird (Procnias nudicollis) is a species of bird in the family Cotingidae. It is found in moist subtropical and tropical forests in Argentina, Brazil, and Paraguay. The male has white plumage and bristly bluish-black bare skin around its eye, beak and throat. The female is more drab, being olive-brown above with streaked yellow underparts. The male has one of the loudest known bird calls, producing a metallic sound similar to a hammer striking an anvil. This bird feeds strictly on fruit and plays a part in dispersing the seeds of forest trees. It is considered Near Threatened because of loss of its forest habitat and collection for the pet bird trade
| Bare-throated bellbird | |
|---|---|

| |
| In Paraná, Brazil. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Cotingidae |
| Genus: | Procnias |
| Species: | P. nudicollis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Procnias nudicollis (Vieillot, 1817)
| |
| |
The male bird has striking white plumage and a bare bluish-black patch of skin around its eyes and beak and on its throat. The female is duller in colour with a black crown, olive-brown upper parts and yellowish underparts streaked with olive green. This bird is about 27 cm (11 in) long.[2]
Like other bellbirds (Procnias), the bill of P. nudicollis has a short bill with a very wide gape.[3]
Voice
editThe male has one of the loudest calls of any bird—a sharp sound like that of a hammer striking an anvil or a bell.[2] Before making such a call, an individual must take a sharp inhale to increase air pressure in the interclavicular air-sacs surrounding its syrinx. It takes a long time for young males to learn the call, as one such male living in captivity next to an adult P. nudicollis that frequently called could not perfect it within 10 months of practice.[3]
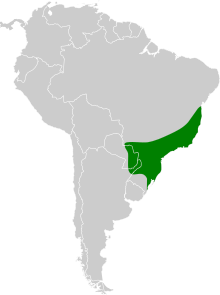
Distribution
editThe bare-throated bellbird is native to Brazil, Paraguay and Argentina.[1] Whereas it is common in the former two countries, it is rare in Argentina. In 2017, less than 250 mature individuals were estimated to exist in Argentina.[4]
Unlike many other cotingids, they migrate seasonally to different altitudes in Paraguay and east Brazil based on fruit production and the age class of the migrating individuals. Some evidence suggests they are also migratory in south-east Brazil and nearby parts of Paraguay, and that they only visit Argentina.[1][4][3]
Their natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest and subtropical or tropical moist montane forest. The bare-throated bellbird prefers primary forests, but may also be present in secondary forests with fruit trees, as well as abandoned rubber groves.[1][4]
Despite its vulnerable status, a juvenile male has been photographed in 2007 foraging in one of the campuses of the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, an unusual urban setting located on an artificial island in the vicinity of the heavily polluted Guanabara Bay.[5] Another specimen was previously spotted in 2005 at the Ibirapuera Park in São Paulo.[6]
Behaviour
editCotingids like P. nudicollis spend a relatively short time foraging due to their frugivory, or fruit-based, diet since fruits do not move as insects do, and so spend plenty of their time preening and idling, as well as singing during their reproductive period.[3]
Diet
editAs a frugivory species, P. nudicollis disperses seeds for the plants it consumes in the Atlantic rainforest ecosystem, such as the Euterpe edulis.[7]
It consumes fruits from plants of the Arecaceae, Myrtaceae, Myrcinaceae, Moraceae, Myristicaceae, Apocynaceae, Sapindaceae, Lauraceae, Leguminosae, Burseraceae, Malpighiaceae, Celastraceae, Elaeocarpaceae, Araliaceae and Liliaceae families.[4] The width of their gape enables them to swallow fruits whole, then regurgitate large seeds.[3]
Although adult members of the bellbird species have only been observed eating fruit, snails have also been recorded in the stomach of a P. nudicollis specimen of unknown sex. These are theorized to have been consumed as a source of calcium for egg-laying females, as snails are consumed for this reason by the scaled fruiteater, also of the Cotingidae family.[3]
Mating
editAlthough P. nudicollis' mating practices have not been observed as closely as its relative, the bearded bellbird, they are likely similar.[3]
The male P. nudicollis produces its loud call while it perches on a high branch in order to attract a mate.[2][3] Their breeding season lasts from September to February.[4]
Conservation status
editP. nudicollis is listed in Brazil as Near Endangered, where it has been found in the protected areas of Intervales State Park, Pico do Marumbi State Park, Irati National Forest, Capão Bonito National Forest and Guapiaçu Private Ecological Reserve. Reforestation efforts of a Reserva Ecologica Michelin abandoned rubber plantation in Bahia may expand their territory.
Furthermore, it is listed in Argentina and Paraguay as Endangered. P. nudicollis has been found in the Paraguayan protected area of Reserva Natural del Bosque Mbaracayú, around which it is featured in high school student outreach campaigns. It has also been found in Argentinian protected areas of Iguazú National Park, Reserva de Biosfera Yaboty, Reserva de uso Multiple Guarani and Reserva Natural Cultural Papel Misionero, although it may only be present in Argentina during migration.[4]
Habitat loss
editP. nudicollis is threatened by habitat loss through agricultural conversion and deforestation. Only 10% of its historical range within six Brazilian coastal states, from Bahia to Paraná, remaining after deforestation. Other emergent threats involve urbanization, industrialization, and road-building.[4]
Poaching
editP. nudicollis is also threatened by heavy poaching for cagebirds.[1] It is the only cotingid widely kept as a cagebird, popular in Brazil.[3]
Trapping pressure has been most significant in Brazil's southern Bahia, São Paulo and Santa Catarina, as well as in Paraguay for sale in its capital city of Asunción.[4]
References
edit- ^ a b c d e BirdLife International (2020). "Procnias nudicollis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22700968A177705453. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22700968A177705453.en. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
- ^ a b c "Bare-throated bellbird fact file". ARKive. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 12 January 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Snow, David W. (2004). "Family Cotingidae (Cotingas)". In del Hoyo, J.; Elliott, A.; Christie, D.A. (eds.). Handbook of the Birds of the World. Vol. 9: Cotingas to Pipits and Wagtails. Barcelona, Spain: Lynx Edicions. pp. 32–108 [104–105]. ISBN 978-84-87334-69-6.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Wheatley, H. (2023). "BirdLife International (2023) Species factsheet: Procnias nudicollis". BirdLife International. BirdLife International. Retrieved 18 January 2023.
- ^ Guiserpa.com - Brazilian birdwatcher's photographic site Archived July 14, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Estudo revela 120 espécies de ave no Ibirapuera" ["Study uncovers 120 bird species at Ibirapuera"]Folha de S.Paulo, 12 October 2005
- ^ dos Santo, Jaqueline; Varassin, Isabela Galarda; Muschner, Valéria Cunha; Ovaskainen, Otso (22 October 2018). "Estimating seed and pollen dispersal kernels from genetic data demonstrates a high pollen dispersal capacity for an endangered palm species". American Journal of Botany. 105 (11): 1802–1812. doi:10.1002/ajb2.1176. Retrieved 19 January 2023.
Further reading
edit- Snow, D.W. (1982). The Cotingas: Bellbirds, Umbrella birds and their allies. British Museum Press. ISBN 0-19-858511-X
