Ptolemaiida is a taxon of wolf-sized afrothere mammals that lived in northern and eastern Africa during the Paleogene. The oldest fossils are from the latest Eocene strata of the Jebel Qatrani Formation, near the Fayum oasis in Egypt.[1] A tooth is known from an Oligocene-aged stratum in Angola,[2] and Miocene specimens (of Kelba) are known from Kenya and Uganda. [3]
| Ptolemaiida | |
|---|---|
| |
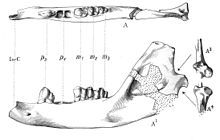
| Lower jaw of Ptolemaia lyonsi | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Superorder: | Afrotheria |
| Grandorder: | Afroinsectiphilia |
| Order: | †Ptolemaiida Simons & Bown, 1995 |
| Families and genera | |
| |
The origin of the Ptolemaiida is obscure, and debated. The type species was originally thought to be a primate, but, later, when elongated skulls with long canines of Ptolemaia and Qarunavus were found, they were then thought to be hyaenodontids, or giant, carnivorous relatives of the pantolestids Palaeosinopa, and of modern shrews[4] The family Ptolemaiidae was elevated to order level in 1995,[1] although some experts later placed the Ptolemaiidae within the pantolestids.[5]
Recently, Ptolemaiida has been placed within Afrotheria[6] on the basis of paleobiology, as the taxon was endemic to Africa, and because of some similarities in the anatomical features of the skull in common with aardvarks.[7][8] It is currently unclear if they form a sister taxon to Tubulidentata or are a paraphyletic sequence leading to them. Regardless, their close relation may offer the possibility for true dental synapomorphies in Afroinsectiphilia.[7][8] A posterior study on ptolemaiidan dentitions further reinforces these results.[9]
As mentioned earlier, there has been much confusion about the origins and even identities of the ptolemaiidans. The first specimen, a set of isolated molar teeth, of the type species, Ptolemaia lyonsi, was originally identified as being a primate, as they were flat and nearly identical to those of primates. Later, when the first skull was found, it was then thought to be a monstrous, wolf-sized shrew, as the skull had long canine fangs, and was very gracile. However, recently, there has been a reconsideration of the ptolemaiidan diet, and possible behavior, as wear on the teeth suggest that it crushed hard or abrasive food, and that the teeth had little or no shearing ability. Even so, some sources still refer to them as being gigantic, carnivorous shrews.[10]
References
edit- ^ a b Simons, E. L.; Bown, T. M. (April 1995). "Ptolemaiida, a new order of Mammalia—with description of the cranium of Ptolemaia grangeri". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 92 (8): 3269–73. Bibcode:1995PNAS...92.3269S. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.8.3269. PMC 42147. PMID 11607526.
- ^ Jacobs, L. L.; Myers, T. S.; Goncalves, A. O.; Graf, J. F.; Jacobs, B. F.; Kappelman, J. W.; Mateus, O.; Polcyn, M. J.; Rasbury, E. T.; Vineyard, D. P. (2013). "Cabinda revisited: Age and environment of new Cenozoic vertebrate fossils from northern Angola". Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs. 45 (7): 0.
- ^ Savage (1965). "Fossil Mammals of Africa: 19. The Miocene Carnivora of East Africa". Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Geology. 10 (8): 241–316.
- ^ Simon; et al. (1974). "New Carnivorous Mammals from the Oligocene of Egypt" (PDF). Annals of the Geological Survey of Egypt. IV: 157–166.
- ^ McKenna, Malcolm C.; Bell, Susan Groag (1997). Classification of Mammals above the Species Level. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-11013-8.
- ^ Nishihara, H.; Satta, Y.; Nikaido, M.; Thewissen, J. G.; Stanhope, M. J.; Okada, N. (2005). "A retroposon analysis of Afrotherian phylogeny". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 22 (9): 1823–33. doi:10.1093/molbev/msi179. PMID 15930154.
- ^ a b Cote, S; Werdelin, L.; Seiffert, E. R.; Barry, J. C. (March 2007). "Additional material of the enigmatic Early Miocene mammal Kelba and its relationship to the order Ptolemaiida". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (13): 5510–5. Bibcode:2007PNAS..104.5510C. doi:10.1073/pnas.0700441104. PMC 1838468. PMID 17372202.
- ^ a b Seiffert, Erik R. (2007). "A new estimate of afrotherian phylogeny based on simultaneous analysis of genomic, morphological, and fossil evidence". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 7 (1): 224. Bibcode:2007BMCEE...7..224S. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-7-224. PMC 2248600. PMID 17999766.
- ^ Kampouridis, Panagiotis; Hartung, Josephina; Augustin, Felix J.; El Atfy, Haytham; Ferreira, Gabriel S. (2023). "Dental eruption and adult dentition of the enigmatic ptolemaiid Qarunavus meyeri from the Oligocene of the Fayum Depression (Egypt) revealed by micro-computed tomography clarifies its phylogenetic position". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 199 (4): 1078–1091. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlad065.
- ^ Prothero, Donald R. (2006). After the Dinosaurs: The Age of Mammals. Indiana University Press. p. 168. ISBN 0253000556.
In addition to these large mammals, the small mammal fauna of the Fayûm beds of Africa include many different insectivores (including one, Ptolemaia, that became a wolf-sized predator) ....