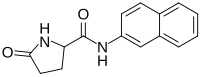
Pyrrolidonyl-β-naphthylamide (PYR) is a molecule used in microbiology to detect the presence of pyrrolidonyl peptidase.[1] In the presence of bacteria with pyrrolidonyl peptidase, it is broken down to pyroglutamic acid and 2-naphthylamine. To detect this process, p-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde is added and a change to a pink color can then be detected.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N1-(Naphthalen-2-yl)-5-oxo-L-prolinamide
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S)-N-(Naphthalen-2-yl)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxamide | |
| Other names
Pyrrolidonyl-beta-naphthylamide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.721 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H14N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 254.289 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ Oberhofer, Thomas R. (1986). "Value of the l-pyrrolidonyl-β-naphthylamide hydrolysis test for identification of select gram-positive cocci". Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease. 4: 43–47. doi:10.1016/0732-8893(86)90055-6.