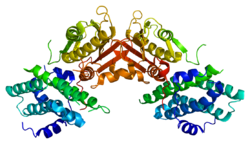
Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 2 (PDK2) also known as pyruvate dehydrogenase lipoamide kinase isozyme 2, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDK2 gene.[5][6] PDK2 is an isozyme of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase.
Structure
editThe protein encoded by the PDK2 gene has two sites, an active site and an allosteric site that allow for the activity and regulation of this enzyme. There are many structural motifs that are important to the regulation of this enzyme. Nov3r and AZ12 inhibitors bind at the lipoamide binding site that is located at one end of the R domain. Pfz3 binds in an extended site at the other end of the R domain. One inhibitor, dicholoroacetate (DCA), binds at the center of the R domain.[7] Within the active site, there are three amino acid residues, R250, T302, and Y320, that make the kinase resistant to the inhibitor dichloroacetate, which uncouples the active site from the allosteric site. This supports the theory that R250, T302, and Y320 stabilize the "open" and "closed" conformations of the built-in lid that controls the access of a nucleotide into the nucleotide-binding cavity. This strongly suggests that the mobility of ATP lid is central to the allosteric regulation of PDHK2 activity serving as a conformational switch required for communication between the active site and allosteric sites in the kinase molecule.[8] There is also a DW-motif that is crucial in mediating DCA, nucleotide, and lipoyl domain binding site communication. This network is responsible for rendering PDK2 locked in the closed, or inactive conformation.[9]
Function
editThe Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) complex must be tightly regulated due to its central role in general metabolism. Within the complex, there are three serine residues on the E1 component that are sites for phosphorylation; this phosphorylation inactivates the complex. In humans, there have been four isozymes of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase that have been shown to phosphorylate these three sites: PDK1, PDK2, PDK3, and PDK4.[10] PDK2 has been identified as the most abundant isoform in human tissues. Through many studies, it has been made clear that the activity of this enzyme is essential, even at rest, to regulate glycolysis/carbodydrate oxidation and producing metabolites for oxidative phosphorylation and the electron transport chain. These studies have illustrated that the kinetics of the PDK isoform population, specifically PDK2, is more important in determining PDH activity than measuring PDK activity.[11]
Regulation
editAs the primary regulators of a crucial step in the central metabolic pathway, the pyruvate dehydrogenase family is tightly regulated itself by a myriad of factors. PDK2 activity is modulated by low levels of hydrogen peroxide; this happens because the compound temporarily oxidizes the cysteine residues 45 and 392 on the enzyme, resulting in an inactive PDK2 and greater PDH activity. These conditions also inactivate the TCA cycle, the next step in aerobic respiration. This alludes to the fact that when there is a high level of O2 production in the mitochondria, which may occur because of nutrient excess, the increase in the products serve as a negative feedback that control mitochondria metabolism.[12] PDK2, in conjunction with PDK3 and PDK4, are primary targets of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta or beta, with PDK2 having two elements that respond to these receptors.[13]
Clinical significance
editAll of the pyruvate dehydrogenase isozymes have been associated with various metabolic disorders, including diabetes. This is due to a mechanism by which consistently elevated free fatty acid levels stimulate the PDK enzymes, particularly, PDK2 and PDK4 in the liver. In stimulating this activity, there is less PDH activity, and therefore less glucose uptake.[14]
Cancer
editAs the PDK enzymes are associated with central metabolism and growth, they are often associated with various mechanisms of cancer progression. Enhanced PDK2 activity leads to increased glycolysis and lactic acid production, known as the Warburg effect. In some studies, the wild-type form of tumor protein p53 prevents manifestation of tumorigenesis by regulating PDK2 activity.[15] Additionally, inhibition of PDK2 subsequently inhibits HIF1A in cancer cells by both a prolyl-hydroxylase (PHD)-dependent mechanism and a PHD-independent mechanism. Therefore, mitochondria-targeting metabolic modulators increase pyruvate dehydrogenase activity, and suppress angiogenesis as well, normalizing the pseudo-hypoxic signals that lead to normoxic HIF1A activation in solid tumors.[16]
References
edit- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000005882 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000038967 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Gudi R, Bowker-Kinley MM, Kedishvili NY, Zhao Y, Popov KM (Dec 1995). "Diversity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase gene family in humans". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 270 (48): 28989–94. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.48.28989. PMID 7499431.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: PDK2 pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isozyme 2".
- ^ Knoechel TR, Tucker AD, Robinson CM, Phillips C, Taylor W, Bungay PJ, Kasten SA, Roche TE, Brown DG (Jan 2006). "Regulatory roles of the N-terminal domain based on crystal structures of human pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 2 containing physiological and synthetic ligands". Biochemistry. 45 (2): 402–15. doi:10.1021/bi051402s. PMID 16401071.
- ^ Klyuyeva A, Tuganova A, Popov KM (Aug 2008). "Allosteric coupling in pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 2". Biochemistry. 47 (32): 8358–66. doi:10.1021/bi800631h. PMC 2568900. PMID 18627174.
- ^ Li J, Kato M, Chuang DT (Dec 2009). "Pivotal role of the C-terminal DW-motif in mediating inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 2 by dichloroacetate". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (49): 34458–67. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.065557. PMC 2797213. PMID 19833728.
- ^ Kolobova E, Tuganova A, Boulatnikov I, Popov KM (Aug 2001). "Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity through phosphorylation at multiple sites". The Biochemical Journal. 358 (Pt 1): 69–77. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3580069. PMC 1222033. PMID 11485553.
- ^ Dunford EC, Herbst EA, Jeoung NH, Gittings W, Inglis JG, Vandenboom R, LeBlanc PJ, Harris RA, Peters SJ (Jun 2011). "PDH activation during in vitro muscle contractions in PDH kinase 2 knockout mice: effect of PDH kinase 1 compensation". American Journal of Physiology. Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 300 (6): R1487-93. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00498.2010. PMID 21411764.
- ^ Hurd TR, Collins Y, Abakumova I, Chouchani ET, Baranowski B, Fearnley IM, Prime TA, Murphy MP, James AM (12 October 2012). "Inactivation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 2 by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287 (42): 35153–60. doi:10.1074/jbc.m112.400002. PMC 3471752. PMID 22910903.
- ^ Degenhardt T, Saramäki A, Malinen M, Rieck M, Väisänen S, Huotari A, Herzig KH, Müller R, Carlberg C (14 September 2007). "Three members of the human pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase gene family are direct targets of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta". Journal of Molecular Biology. 372 (2): 341–55. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.06.091. PMID 17669420.
- ^ Bajotto G, Murakami T, Nagasaki M, Qin B, Matsuo Y, Maeda K, Ohashi M, Oshida Y, Sato Y, Shimomura Y (March 2006). "Increased expression of hepatic pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases 2 and 4 in young and middle-aged Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats: induction by elevated levels of free fatty acids". Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental. 55 (3): 317–23. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2005.09.014. PMID 16483874.
- ^ Contractor T, Harris CR (15 January 2012). "p53 negatively regulates transcription of the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase Pdk2". Cancer Research. 72 (2): 560–7. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-11-1215. PMID 22123926.
- ^ Sutendra G, Dromparis P, Kinnaird A, Stenson TH, Haromy A, Parker JM, McMurtry MS, Michelakis ED (28 March 2013). "Mitochondrial activation by inhibition of PDKII suppresses HIF1a signaling and angiogenesis in cancer". Oncogene. 32 (13): 1638–50. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.198. PMID 22614004.
Further reading
edit- Sugden MC, Holness MJ (May 2003). "Recent advances in mechanisms regulating glucose oxidation at the level of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by PDKs". American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism. 284 (5): E855–62. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00526.2002. PMID 12676647.
- Kobayashi T, Cohen P (Apr 1999). "Activation of serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated protein kinase by agonists that activate phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase is mediated by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) and PDK2". The Biochemical Journal. 339 (2): 319–28. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3390319. PMC 1220160. PMID 10191262.
- Gold MR, Scheid MP, Santos L, Dang-Lawson M, Roth RA, Matsuuchi L, Duronio V, Krebs DL (Aug 1999). "The B cell antigen receptor activates the Akt (protein kinase B)/glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling pathway via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase". Journal of Immunology. 163 (4): 1894–905. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.163.4.1894. PMID 10438924.
- Baker JC, Yan X, Peng T, Kasten S, Roche TE (May 2000). "Marked differences between two isoforms of human pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (21): 15773–81. doi:10.1074/jbc.M909488199. PMID 10748134.
- Steussy CN, Popov KM, Bowker-Kinley MM, Sloan RB, Harris RA, Hamilton JA (Oct 2001). "Structure of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. Novel folding pattern for a serine protein kinase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (40): 37443–50. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104285200. PMC 2147663. PMID 11483605.
- Kolobova E, Tuganova A, Boulatnikov I, Popov KM (Aug 2001). "Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity through phosphorylation at multiple sites". The Biochemical Journal. 358 (Pt 1): 69–77. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3580069. PMC 1222033. PMID 11485553.
- Korotchkina LG, Patel MS (Oct 2001). "Site specificity of four pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoenzymes toward the three phosphorylation sites of human pyruvate dehydrogenase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (40): 37223–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103069200. PMID 11486000.
- Peters SJ, Harris RA, Wu P, Pehleman TL, Heigenhauser GJ, Spriet LL (Dec 2001). "Human skeletal muscle PDH kinase activity and isoform expression during a 3-day high-fat/low-carbohydrate diet". American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism. 281 (6): E1151–8. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.2001.281.6.e1151. PMID 11701428. S2CID 22798857.
- Tuganova A, Boulatnikov I, Popov KM (Aug 2002). "Interaction between the individual isoenzymes of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase and the inner lipoyl-bearing domain of transacetylase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex". The Biochemical Journal. 366 (Pt 1): 129–36. doi:10.1042/BJ20020301. PMC 1222743. PMID 11978179.
- Boulatnikov I, Popov KM (Feb 2003). "Formation of functional heterodimers by isozymes 1 and 2 of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics. 1645 (2): 183–92. doi:10.1016/S1570-9639(02)00542-3. PMID 12573248.
- Hiromasa Y, Roche TE (Sep 2003). "Facilitated interaction between the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 2 and the dihydrolipoyl acetyltransferase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (36): 33681–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212733200. PMID 12816949.
- Watt MJ, Heigenhauser GJ, LeBlanc PJ, Inglis JG, Spriet LL, Peters SJ (Oct 2004). "Rapid upregulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase activity in human skeletal muscle during prolonged exercise". Journal of Applied Physiology. 97 (4): 1261–7. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00132.2004. PMID 15169745.
- Bao H, Kasten SA, Yan X, Roche TE (Oct 2004). "Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 2 activity limited and further inhibited by slowing down the rate of dissociation of ADP". Biochemistry. 43 (42): 13432–41. doi:10.1021/bi049488x. PMID 15491150.
- Bao H, Kasten SA, Yan X, Hiromasa Y, Roche TE (Oct 2004). "Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 2 activity stimulated by speeding up the rate of dissociation of ADP". Biochemistry. 43 (42): 13442–51. doi:10.1021/bi0494875. PMID 15491151.
- Abbot EL, McCormack JG, Reynet C, Hassall DG, Buchan KW, Yeaman SJ (Jun 2005). "Diverging regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform gene expression in cultured human muscle cells". The FEBS Journal. 272 (12): 3004–14. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04713.x. PMID 15955060. S2CID 21366281.