The quadrangular space, also known as the quadrilateral space (of Velpeau) and the foramen humerotricipitale, is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: triangular space and triangular interval.[1]
| Quadrangular space | |
|---|---|
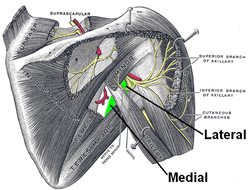 Suprascapular and axillary nerves of right side, seen from behind. Quadrangular space is the lateral space, labeled in green at center right. Axillary nerve is visible entering it. | |
 The scapular and circumflex arteries. (Quadrangular space is visible but not labeled. Posterior humeral circumflex artery is visible entering quadrangular space at center right.) | |
| Anatomical terminology |
Structure
editThe quadrangular space is one of the three spaces in the axillary space.
Boundaries
editThe quadrangular space is defined by:[2]
- above/superior: teres minor muscle.[3][4]
- below/inferior: teres major muscle.[3]
- medially: long head of the triceps brachii muscle (lateral margin).[3]
- laterally: surgical neck of the humerus.[3]
- anteriorly: subscapularis muscle.
Contents
editThe quadrangular space transmits the axillary nerve, the posterior humeral circumflex artery and the posterior circumflex humeral vein.[3]
Clinical significance
editThe quadrangular space is a clinically important anatomic space in the arm as it provides the anterior regions of the axilla a passageway to the posterior regions. In the quadrangular space, the axillary nerve and the posterior humeral circumflex artery can be compressed or damaged due to space-occupying lesions or disruption in the anatomy due to trauma. Other common causes of axillary nerve compression at the quadrangular space include local compression due to osteophytes which are common in osteoarthritis, shoulder dislocations, fractures of the humeral neck, repetitive use, and external pressure (such as from crutches). Symptoms of axillary nerve compression include axillary nerve related weakness of the deltoid muscle (shoulder abduction) and teres minor (external rotation of the arm) as well as numbness of the lateral shoulder. The quadrangular space is the most common site of axillary nerve compression.[5][6]
History
editThe quadrangular space is so named because the three skeletal muscles and one long bone that form its boundaries leave a space in the shape of a complete quadrangle.
The quadrangular space is also known as the quadrilateral space,[4] the quadrilateral space of Velpeau, and the foramen humerotricipitale.
See also
editAdditional images
edit-
Muscles on the dorsum of the scapula, and the triceps brachii.
References
editThis article incorporates text in the public domain from page 589 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Krishna, Garg (2010). "7 - Scapula". BD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy (Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical) Volume 1 - Upper limb and thorax (Fifth ed.). India: CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd. p. 81. ISBN 978-81-239-1863-1.
- ^ Anatomy photo:03:04-0101 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Scapular Region: Quadrangular Space of Scapular Region"
- ^ a b c d e Pinkas, D.; Wiater, J. M. (2017-01-01). "37 - Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder". Orthopaedic Physical Therapy Secrets (3rd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 318–326. doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-28683-1.00037-0. ISBN 978-0-323-28683-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ a b Adam Mitchell; Drake, Richard; Gray, Henry David; Wayne Vogl (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. p. 649. ISBN 0-443-06612-4.
- ^ Silver, S; Ledford, CC; Vogel, KJ; Arnold, JJ (1 March 2021). "Peripheral Nerve Entrapment and Injury in the Upper Extremity". American Family Physician. 103 (5): 275–285. PMID 33630556.
- ^ Mangi, Mohammad Danish; Zadow, Steven; Lim, WanYin (12 October 2022). "Nerve entrapment syndromes of the upper limb: a pictorial review". Insights into Imaging. 13 (1): 166. doi:10.1186/s13244-022-01305-5. PMC 9556688. PMID 36224295.
External links
edit- Quadrangular space at the Duke University Health System's Orthopedics program
- Photo at umich.edu
- Diagram at wustl.edu
- Photo at tufts.edu
- Photo at ithaca.edu