Rheobatrachus, whose members are known as the gastric-brooding frogs or platypus frogs, is a genus of extinct ground-dwelling frogs native to Queensland in eastern Australia. The genus consisted of only two species, the southern and northern gastric-brooding frogs, both of which became extinct in the mid-1980s. The genus is unique because it contains the only two known frog species that incubated the prejuvenile stages of their offspring in the stomach of the mother.[3]
| Gastric-brooding frogs | |
|---|---|

| |
| Southern gastric-brooding frog (Rheobatrachus silus) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Myobatrachidae |
| Genus: | †Rheobatrachus Liem, 1973 |
| Species | |
| |
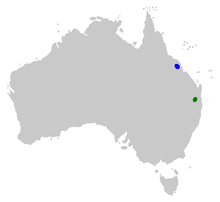
| The former distributions of Rheobatrachus silus (green) and Rheobatrachus vitellinus (blue) | |
The combined ranges of the gastric-brooding frogs comprised less than 2,000 square kilometres (770 sq mi). Both species were associated with creek systems in rainforests at elevations of between 350 and 1,400 metres (1,150 and 4,590 ft). The causes of the gastric-brooding frogs' extinction are not clearly understood, but habitat loss and degradation, pollution, and some diseases may have contributed.
The assignment of the genus to a taxonomic family is hotly debated. Some biologists class them within Myobatrachidae under the subfamily Rheobatrachinae, but others place them in their own family, Rheobatrachidae.[4] Molecular genetics finds it sister to Mixophyes.[5]
Scientists at the University of Newcastle and University of New South Wales announced in March 2013 that the frog would be the subject of a cloning attempt, referred to as the "Lazarus Project", to resurrect the species. Embryos were successfully cloned, and the project eventually hopes to produce a living frog.[6][7]
The southern gastric brooding frog has been listed as Extinct by the IUCN because it has not been recorded in the wild since 1981, and extensive searches over the last 35 years have failed to locate this species.
Taxonomy
editThe genus Rheobatrachus was first described in 1973 by David Liem[8] and since has not undergone any scientific classification changes; however its placement has been controversial. It has been placed in a distinct subfamily of Myobatrachidae, Rheobatrachinae; in a separate family, Rheobatrachidae; placed as the sister taxon of Limnodynastinae; and synonymized with Limnodynastinae. In 2006, D. R. Frost and colleagues found Rheobatrachus, on the basis of molecular evidence, to be the sister taxon of Mixophyes and placed it within Myobatrachidae.[9][5]
Both species of gastric-brooding frogs were very different in appearance and behaviour from other Australian frog species. Their large protruding eyes and short, blunt snout along with complete webbing and slimy bodies differentiated them from all other Australian frogs. The largely aquatic behaviour exhibited by both species was only shared (in Australia) with the Dahl's aquatic frog and their ability to raise their young in the mother's stomach was unique among all frogs.
Common names
editThe common names, "gastric-brooding frog" and "platypus frog", are used to describe the two species. "Gastric-brooding" describes the unique way the female raised the young and "platypus" describes their largely aquatic nature.
Reproduction
editWhat makes these frogs unique among all frog species is their form of parental care. Following external fertilization by the male, the female would take the eggs or embryos into her mouth and swallow them.[10] It is not clear whether the eggs were laid on the land or in the water, as it was never observed before their extinction. Interestingly, Darwin's frog, another species of frog, has been observed to exhibit similar mouth-brooding characteristics. This feature still remains extremely rare in nature.
Eggs found in females measured up to 5.1 mm in diameter and had large yolk supplies. These large supplies are common among species that live entirely off yolk during their development. Most female frogs had around 40 ripe eggs, almost double that of the number of juveniles ever found in the stomach (21–26). This means one of two things, that the female fails to swallow all the eggs or the first few eggs to be swallowed are digested.
At the time the female swallowed the fertilized eggs her stomach was no different from that of any other frog species. In the jelly around each egg was a substance called prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), which could turn off production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. This source of PGE2 was enough to cease the production of acid during the embryonic stages of the developing eggs. When the eggs had hatched the tadpoles created PGE2. The mucus excreted from the tadpoles' gills contained the PGE2 necessary to keep the stomach in a non-functional state. These mucus excretions do not occur in tadpoles of most other species. Tadpoles that do not live entirely off a yolk supply still produce mucus cord, but the mucus along with small food particles travels down the oesophagus into the gut. With Rheobatrachus (and several other species) there is no opening to the gut and the mucus cords are excreted. During the period that the offspring were present in the stomach the frog would not eat.
Information on tadpole development was observed from a group that was regurgitated by the mother and successfully raised in shallow water. During the early stages of development tadpoles lacked pigmentation, but as they aged they progressively develop adult colouration. Tadpole development took at least six weeks, during which time the size of the mother's stomach continued to increase until it largely filled the body cavity. The lungs deflated and breathing relied more upon gas exchange through the skin. Despite the mother's increasing size she still remained active.
The birth process was widely spaced and may have occurred over a period of as long as a week. However, if disturbed the female may regurgitate all the young frogs in a single act of propulsive vomiting. The offspring were completely developed when expelled and there was little variation in colour and length of a single clutch.[11]
Cause of extinction
editThe cause for the gastric-brooding frogs' extinction is speculated to be due to human introduction of pathogenic fungi into their native range. Populations of southern gastric-brooding frogs were present in logged catchments between 1972 and 1979. The effects of such logging activities upon southern gastric-brooding frogs was not investigated but the species did continue to inhabit streams in the logged catchments. The habitat that the southern gastric-brooding frog once inhabited is now threatened by feral pigs, the invasion of weeds, altered flow and water quality problems caused by upstream disturbances.[12] Despite intensive searching, the species has not been located since 1976 or 1981 (depending on the source).
The Eungella National Park, where the northern gastric-brooding frog was once found, was under threat from bushfires and weed invasion. Continual fires may have destroyed or fragmented sections of the forest.[13] The outskirts of the park are still subject to weed invasion and chytrid fungus has been located within several rainforest creeks within the park. It was thought that the declines of the northern gastric-brooding frog during 1984 and 1985 were possibly normal population fluctuations.[14] Eight months after the initial discovery of the northern gastric-brooding frog, sick and dead Eungella torrent frogs, which cohabitat the streams with gastric brooding frogs, were observed in streams in Pelion State Forest.[15] Given the more recent understanding of the role of the amphibian disease in the decline and disappearance of amphibians, combined with the temporal and spatial pattern of the spread of the pathogen in Australia, it appears most likely that the disease was responsible for the decline and disappearance of the gastric-brooding frogs. Despite continued efforts to locate the northern gastric-brooding frog it has not been found. The last reported wild specimen was seen in the 1980s. In August 2010 a search organised by the Amphibian Specialist Group of the International Union for Conservation of Nature set out to look for various species of frogs thought to be extinct in the wild, including the gastric-brooding frog.[16]
Conservation status
editBoth species are listed as Extinct under both the IUCN Red List and under Australia's Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999; however, they are still listed as Endangered under Queensland's Nature Conservation Act 1992.
De-extinction attempt
editScientists are making progress in their efforts to bring the gastric-brooding frog species back to life using somatic-cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), a method of cloning.[17]
In March 2013, Australian scientists successfully created a living embryo from non-living preserved genetic material. These scientists from the University of Newcastle Australia led by Prof Michael Mahony, who was the scientist who first discovered the northern gastric-brooding frog, Simon Clulow and Prof Mike Archer from the University of New South Wales hope to continue using somatic-cell nuclear transfer methods to produce an embryo that can survive to the tadpole stage. "We do expect to get this guy hopping again," says UNSW researcher Mike Archer.[18]
The scientists from the University of Newcastle have also reported successful freezing and thawing (cryopreservation) of totipotent amphibian embryonic cells,[19] which along with sperm cryopreservation[20] provides the essential "proof of concept" for the use of cryostorage as a genome bank for threatened amphibians and also other animals.
References
edit- ^ IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group (2022). "Rheobatrachus silus". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2022. IUCN: e.T19475A78430533.
- ^ IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group (2022). "Rheobatrachus vitellinus". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2022. IUCN: e.T19476A78430385.
- ^ Barker, J.; Grigg, G. C.; Tyler, M. J. (1995). A Field Guide to Australian Frogs. Surrey Beatty & Sons. p. 350. ISBN 0-949324-61-2.
- ^ Heyer, W. Ronald; Liem, David S. (1976). "Analysis of the inter-generic relationships of the Australian frog family Myobatrachidae" (PDF). Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology. 233 (233): 1–29. doi:10.5479/si.00810282.233.
- ^ a b Frost, Darrel R.; Grant, Taran; Faivovich, Julián; Bain, Raoul H.; Haas, Alexander; Haddad, Célio F.B.; De Sá, Rafael O.; Channing, Alan; Wilkinson, Mark; Donnellan, Stephen C.; Raxworthy, Christopher J.; Campbell, Jonathan A.; Blotto, Boris L.; Moler, Paul; Drewes, Robert C.; Nussbaum, Ronald A.; Lynch, John D.; Green, David M.; Wheeler, Ward C. (2006). "The amphibian tree of life". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 297: 1–370. doi:10.1206/0003-0090(2006)297[0001:TATOL]2.0.CO;2. hdl:2246/5781. S2CID 86140137.
- ^ Yong, Ed (15 March 2013). "Resurrecting the Extinct Frog with a Stomach for a Womb". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 18 March 2013. Retrieved 15 March 2013.
- ^ Dolak, Kevin (20 March 2013). "Frog That Gives Birth Through Mouth to be Brought Back From Extinction". ABC News.
- ^ Liem, David S. (1973). "A new genus of frog of the family Leptodactylidae from S. E. Queensland, Australia". Memoirs of the Queensland Museum. 16 (3): 459–470.
- ^ Amphibian Species of the World – Rheobatrahus (under "Comments"). research.amnh.org
- ^ "Rheobatrachus vitellinus – Northern Gastric-brooding Frog, Eungella Gastric-brooding Frog". Department of the Environment, Canberra. 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2015.
- ^ Tyler, M. J. (1994). Chapter 12, "Gastric Brooding Frogs", pp. 135–140 in Australian Frogs A Natural History. Reed Books
- ^ Hines, H., Mahony, M. and McDonald, K. 1999. An assessment of frog declines in Wet Subtropical Australia. In: A. Campbell (ed.), Declines and Disappearances of Australian Frogs. Environment Australia.
- ^ Winter, J.; McDonald, K. (1986). "Eungella, the land of cloud". Australian Natural History. 22 (1): 39–43.
- ^ McDonald, K.R. (1990). "Rheobatrachus Liem and Taudactylus Straughan & Lee (Anura: Leptodactylidae) in Eungella National Park, Queensland: distribution and decline". Transactions of the Royal Society of South Australia. 114 (4): 187–194.
- ^ Mahony, Michael. "Report to Queensland National Park on status of stream frogs in Pelion State Forest".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Black, Richard (9 August 2010). "Global hunt begins for 'extinct' species of frogs". BBC. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ^ Nosowitz, Dan (15 March 2013) Scientists Resurrect Bonkers Extinct Frog That Gives Birth Through Its Mouth. popsci.com
- ^ Messenger, Stephen (15 March 2013) Scientists successfully create living embryo of an extinct species. treehugger.com
- ^ Moreira, Nei; Lawson, Bianca; Clulow, Simon; Mahony, Michael J.; Clulow, John (2013). "Towards gene banking amphibian maternal germ lines: short-term incubation, cryoprotectant tolerance and cryopreservation of embryonic cells of the frog, Limnodynastes peronii". PLOS ONE. 8 (4): e60760. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...860760L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0060760. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3618038. PMID 23577155.
- ^ Browne, Robert; Mahony, Clulow (2002). "A comparison of sucrose, saline, and saline with egg-yolk diluents on the cryopreservation of cane toad (Bufo marinus) sperm". Cryobiology. 44 (251–157): 251–7. doi:10.1016/S0011-2240(02)00031-7. PMID 12237090.
Further reading
edit- Barker, J.; Grigg, G. C.; Tyler, M. J. (1995): A Field Guide to Australian Frogs. Surrey Beatty & Sons.
- Pough, F. H.; Andrews, R. M.; Cadle, J. E.; Crump, M.; Savitsky, A. H. & Wells, K. D. (2003): Herpetology (3rd ed.). Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey.
- Ryan, M. (ed.) (2003): Wildlife of Greater Brisbane. Queensland Museum, Brisbane.
- Ryan, M. & Burwell, C. (eds.) (2003): Wildlife of Tropical North Queensland. Queensland Museum, Brisbane.
- Tyler, M. J. (1984): There's a frog in my throat/stomach. William Collins Pty Ltd, Sydney. ISBN 0-00-217321-2
- Tyler, M. J. (1994): Australian Frogs – A Natural History. Reed Books.
- Zug, G. E.; Vitt, L. J. & Caldwell, J. P. (2001): Herpetology (2nd ed.). Academic Press, San Diego, California.
External links
edit- "Gastric-brooding frog" at the Encyclopedia of Life
- Animal Diversity Web – Rheobatrachus silus (Accessed 2006/08/19)
- American Museum of Natural History – Rheobatrachus (Accessed 2006/08/19)
