The foramen rotundum is a circular hole in the sphenoid bone of the skull. It connects the middle cranial fossa and the pterygopalatine fossa. It allows for the passage of the maxillary nerve (V2), a branch of the trigeminal nerve.
| Foramen rotundum of Sphenoid | |
|---|---|
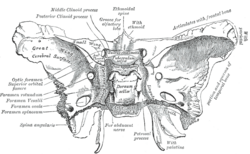 Sphenoid bone. Upper surface. (Foramen rotundum labeled at center left) | |
 Base of the skull. Upper surface. Sphenoid is yellow, and arrows indicate the foramen rotundum.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Sphenoid bone |
| System | Skeletal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen rotundum ossis sphenoidalis |
| TA98 | A02.1.05.035 |
| TA2 | 621 |
| FMA | 53154 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
Structure
editThe foramen rotundum is one of the several circular apertures (the foramina) located in the base of the skull, in the anterior and medial part of the sphenoid bone.
The mean area of the foramina rotunda is not considerable, which may suggest that they play a minor role in the dynamics of blood circulation in the venous system of the head.[1]
Development
editThe foramen rotundum evolves in shape throughout the fetal period, and from birth to adolescence. It achieves a perfect ring-shaped formation in the fetus after the 4th fetal month. It is mostly oval-shaped in the fetal period, and round-shaped after birth (generally speaking). After birth, the rotundum is about 2.5 mm and in 15- to 17-year-olds about 3 mm in length. The average diameter of the foramen rotundum in adults is 3.55 mm.[2][3]
Function
editThe foramen rotundum allows the passage of the maxillary nerve (V2), a branch of the trigeminal nerve.[4] It also allows the passage of the artery of the foramen rotundum and an emissary vein.
History
editEtymology
editForamen is the Latin term designating a hole-like opening. It derives from the Latin forare meaning to bore or perforate. Here, the opening is round as indicated by the Latin rotundum meaning round.
See also
editReferences
editThis article incorporates text in the public domain from page 150 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Reymond J, Charuta A, Wysocki J (2005). "The morphology and morphometry of the foramina of the greater wing of the human sphenoid bone". Folia Morphologica. 64 (3): 188–93. PMID 16228954.
- ^ Yanagi S (1987). "Developmental studies on the foramen rotundum, foramen ovale and foramen spinosum of the human sphenoid bone". The Hokkaido Journal of Medical Science. 62 (3): 485–96. PMID 3610040.
- ^ Lang J, Maier R, Schafhauser O (1984). "Postnatal enlargement of the foramina rotundum, ovale et spinosum and their topographical changes". Anatomischer Anzeiger. 156 (5): 351–87. PMID 6486466.
- ^ Barral, Jean-Pierre; Croibier, Alain (2009-01-01). "16 - Maxillary nerve". Manual Therapy for the Cranial Nerves. Churchill Livingstone. pp. 129–138. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-3100-7.50019-7. ISBN 978-0-7020-3100-7.
External links
edit- Anatomy photo:22:os-0905 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)
- Superior view of the base of the skull at winona.edu