 Tesseract |
 Truncated tesseract |
 Rectified tesseract |
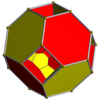 Bitruncated tesseract |
| Schlegel diagrams centered on [4,3] (cells visible at [3,3]) | |||
 16-cell |
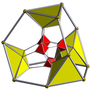 Truncated 16-cell |
 Rectified 16-cell (24-cell) |
 Bitruncated tesseract |
| Schlegel diagrams centered on [3,3] (cells visible at [4,3]) | |||
In geometry, a truncated tesseract is a uniform 4-polytope formed as the truncation of the regular tesseract.
There are three truncations, including a bitruncation, and a tritruncation, which creates the truncated 16-cell.
Truncated tesseract
edit| Truncated tesseract | ||
|---|---|---|
| Schlegel diagram (tetrahedron cells visible) | ||
| Type | Uniform 4-polytope | |
| Schläfli symbol | t{4,3,3} | |
| Coxeter diagrams | ||
| Cells | 24 | 8 3.8.8 16 3.3.3 |
| Faces | 88 | 64 {3} 24 {8} |
| Edges | 128 | |
| Vertices | 64 | |
| Vertex figure | ( )v{3} | |
| Dual | Tetrakis 16-cell | |
| Symmetry group | B4, [4,3,3], order 384 | |
| Properties | convex | |
| Uniform index | 12 13 14 | |
The truncated tesseract is bounded by 24 cells: 8 truncated cubes, and 16 tetrahedra.
Alternate names
edit- Truncated tesseract (Norman W. Johnson)
- Truncated tesseract (Acronym tat) (George Olshevsky, and Jonathan Bowers)[1]
Construction
editThe truncated tesseract may be constructed by truncating the vertices of the tesseract at of the edge length. A regular tetrahedron is formed at each truncated vertex.
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of a truncated tesseract having edge length 2 is given by all permutations of:
Projections
editIn the truncated cube first parallel projection of the truncated tesseract into 3-dimensional space, the image is laid out as follows:
- The projection envelope is a cube.
- Two of the truncated cube cells project onto a truncated cube inscribed in the cubical envelope.
- The other 6 truncated cubes project onto the square faces of the envelope.
- The 8 tetrahedral volumes between the envelope and the triangular faces of the central truncated cube are the images of the 16 tetrahedra, a pair of cells to each image.
Images
edit| Coxeter plane | B4 | B3 / D4 / A2 | B2 / D3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graph | |||
| Dihedral symmetry | [8] | [6] | [4] |
| Coxeter plane | F4 | A3 | |
| Graph | |||
| Dihedral symmetry | [12/3] | [4] |
| A polyhedral net |
Truncated tesseract projected onto the 3-sphere with a stereographic projection into 3-space. |
Related polytopes
editThe truncated tesseract, is third in a sequence of truncated hypercubes:
| Image | ... | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Octagon | Truncated cube | Truncated tesseract | Truncated 5-cube | Truncated 6-cube | Truncated 7-cube | Truncated 8-cube | |
| Coxeter diagram | ||||||||
| Vertex figure | ( )v( ) | ( )v{ } |
( )v{3} |
( )v{3,3} |
( )v{3,3,3} | ( )v{3,3,3,3} | ( )v{3,3,3,3,3} |
Bitruncated tesseract
edit| Bitruncated tesseract | ||
|---|---|---|
| Two Schlegel diagrams, centered on truncated tetrahedral or truncated octahedral cells, with alternate cell types hidden. | ||
| Type | Uniform 4-polytope | |
| Schläfli symbol | 2t{4,3,3} 2t{3,31,1} h2,3{4,3,3} | |
| Coxeter diagrams | = | |
| Cells | 24 | 8 4.6.6 16 3.6.6 |
| Faces | 120 | 32 {3} 24 {4} 64 {6} |
| Edges | 192 | |
| Vertices | 96 | |
| Vertex figure | Digonal disphenoid | |
| Symmetry group | B4, [3,3,4], order 384 D4, [31,1,1], order 192 | |
| Properties | convex, vertex-transitive | |
| Uniform index | 15 16 17 | |
The bitruncated tesseract, bitruncated 16-cell, or tesseractihexadecachoron is constructed by a bitruncation operation applied to the tesseract. It can also be called a runcicantic tesseract with half the vertices of a runcicantellated tesseract with a construction.
Alternate names
edit- Bitruncated tesseract/Runcicantic tesseract (Norman W. Johnson)
- Tesseractihexadecachoron (Acronym tah) (George Olshevsky, and Jonathan Bowers)[2]
Construction
editA tesseract is bitruncated by truncating its cells beyond their midpoints, turning the eight cubes into eight truncated octahedra. These still share their square faces, but the hexagonal faces form truncated tetrahedra which share their triangular faces with each other.
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of a bitruncated tesseract having edge length 2 is given by all permutations of:
Structure
editThe truncated octahedra are connected to each other via their square faces, and to the truncated tetrahedra via their hexagonal faces. The truncated tetrahedra are connected to each other via their triangular faces.
Projections
edit| Coxeter plane | B4 | B3 / D4 / A2 | B2 / D3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graph | |||
| Dihedral symmetry | [8] | [6] | [4] |
| Coxeter plane | F4 | A3 | |
| Graph | |||
| Dihedral symmetry | [12/3] | [4] |
Stereographic projections
editThe truncated-octahedron-first projection of the bitruncated tesseract into 3D space has a truncated cubical envelope. Two of the truncated octahedral cells project onto a truncated octahedron inscribed in this envelope, with the square faces touching the centers of the octahedral faces. The 6 octahedral faces are the images of the remaining 6 truncated octahedral cells. The remaining gap between the inscribed truncated octahedron and the envelope are filled by 8 flattened truncated tetrahedra, each of which is the image of a pair of truncated tetrahedral cells.
| Colored transparently with pink triangles, blue squares, and gray hexagons |
Related polytopes
editThe bitruncated tesseract is second in a sequence of bitruncated hypercubes:
| Image | ... | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Bitruncated cube | Bitruncated tesseract | Bitruncated 5-cube | Bitruncated 6-cube | Bitruncated 7-cube | Bitruncated 8-cube | |
| Coxeter | |||||||
| Vertex figure | ( )v{ } |
{ }v{ } |
{ }v{3} |
{ }v{3,3} |
{ }v{3,3,3} | { }v{3,3,3,3} |
Truncated 16-cell
edit| Truncated 16-cell Cantic tesseract | ||
|---|---|---|
| Schlegel diagram (octahedron cells visible) | ||
| Type | Uniform 4-polytope | |
| Schläfli symbol | t{4,3,3} t{3,31,1} h2{4,3,3} | |
| Coxeter diagrams | = | |
| Cells | 24 | 8 3.3.3.3 16 3.6.6 |
| Faces | 96 | 64 {3} 32 {6} |
| Edges | 120 | |
| Vertices | 48 | |
| Vertex figure | square pyramid | |
| Dual | Hexakis tesseract | |
| Coxeter groups | B4 [3,3,4], order 384 D4 [31,1,1], order 192 | |
| Properties | convex | |
| Uniform index | 16 17 18 | |
The truncated 16-cell, truncated hexadecachoron, cantic tesseract which is bounded by 24 cells: 8 regular octahedra, and 16 truncated tetrahedra. It has half the vertices of a cantellated tesseract with construction .
It is related to, but not to be confused with, the 24-cell, which is a regular 4-polytope bounded by 24 regular octahedra.
Alternate names
edit- Truncated 16-cell/Cantic tesseract (Norman W. Johnson)
- Truncated hexadecachoron (Acronym thex) (George Olshevsky, and Jonathan Bowers)[3]
Construction
editThe truncated 16-cell may be constructed from the 16-cell by truncating its vertices at 1/3 of the edge length. This results in the 16 truncated tetrahedral cells, and introduces the 8 octahedra (vertex figures).
(Truncating a 16-cell at 1/2 of the edge length results in the 24-cell, which has a greater degree of symmetry because the truncated cells become identical with the vertex figures.)
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of a truncated 16-cell having edge length √2 are given by all permutations, and sign combinations of
- (0,0,1,2)
An alternate construction begins with a demitesseract with vertex coordinates (±3,±3,±3,±3), having an even number of each sign, and truncates it to obtain the permutations of
- (1,1,3,3), with an even number of each sign.
Structure
editThe truncated tetrahedra are joined to each other via their hexagonal faces. The octahedra are joined to the truncated tetrahedra via their triangular faces.
Projections
editCentered on octahedron
editThe octahedron-first parallel projection of the truncated 16-cell into 3-dimensional space has the following structure:
- The projection envelope is a truncated octahedron.
- The 6 square faces of the envelope are the images of 6 of the octahedral cells.
- An octahedron lies at the center of the envelope, joined to the center of the 6 square faces by 6 edges. This is the image of the other 2 octahedral cells.
- The remaining space between the envelope and the central octahedron is filled by 8 truncated tetrahedra (distorted by projection). These are the images of the 16 truncated tetrahedral cells, a pair of cells to each image.
This layout of cells in projection is analogous to the layout of faces in the projection of the truncated octahedron into 2-dimensional space. Hence, the truncated 16-cell may be thought of as the 4-dimensional analogue of the truncated octahedron.
Centered on truncated tetrahedron
editThe truncated tetrahedron first parallel projection of the truncated 16-cell into 3-dimensional space has the following structure:
- The projection envelope is a truncated cube.
- The nearest truncated tetrahedron to the 4D viewpoint projects to the center of the envelope, with its triangular faces joined to 4 octahedral volumes that connect it to 4 of the triangular faces of the envelope.
- The remaining space in the envelope is filled by 4 other truncated tetrahedra.
- These volumes are the images of the cells lying on the near side of the truncated 16-cell; the other cells project onto the same layout except in the dual configuration.
- The six octagonal faces of the projection envelope are the images of the remaining 6 truncated tetrahedral cells.
Images
edit| Coxeter plane | B4 | B3 / D4 / A2 | B2 / D3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graph | |||
| Dihedral symmetry | [8] | [6] | [4] |
| Coxeter plane | F4 | A3 | |
| Graph | |||
| Dihedral symmetry | [12/3] | [4] |
| Net |
Stereographic projection (centered on truncated tetrahedron) |
Related polytopes
editA truncated 16-cell, as a cantic 4-cube, is related to the dimensional family of cantic n-cubes:
| n | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry [1+,4,3n-2] |
[1+,4,3] = [3,3] |
[1+,4,32] = [3,31,1] |
[1+,4,33] = [3,32,1] |
[1+,4,34] = [3,33,1] |
[1+,4,35] = [3,34,1] |
[1+,4,36] = [3,35,1] |
| Cantic figure |
||||||
| Coxeter | = |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
| Schläfli | h2{4,3} | h2{4,32} | h2{4,33} | h2{4,34} | h2{4,35} | h2{4,36} |
Related uniform polytopes
editRelated uniform polytopes in demitesseract symmetry
edit| D4 uniform polychora | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| {3,31,1} h{4,3,3} |
2r{3,31,1} h3{4,3,3} |
t{3,31,1} h2{4,3,3} |
2t{3,31,1} h2,3{4,3,3} |
r{3,31,1} {31,1,1}={3,4,3} |
rr{3,31,1} r{31,1,1}=r{3,4,3} |
tr{3,31,1} t{31,1,1}=t{3,4,3} |
sr{3,31,1} s{31,1,1}=s{3,4,3} | ||||
Related uniform polytopes in tesseract symmetry
edit| B4 symmetry polytopes | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | tesseract | rectified tesseract |
truncated tesseract |
cantellated tesseract |
runcinated tesseract |
bitruncated tesseract |
cantitruncated tesseract |
runcitruncated tesseract |
omnitruncated tesseract | ||
| Coxeter diagram |
= |
= |
|||||||||
| Schläfli symbol |
{4,3,3} | t1{4,3,3} r{4,3,3} |
t0,1{4,3,3} t{4,3,3} |
t0,2{4,3,3} rr{4,3,3} |
t0,3{4,3,3} | t1,2{4,3,3} 2t{4,3,3} |
t0,1,2{4,3,3} tr{4,3,3} |
t0,1,3{4,3,3} | t0,1,2,3{4,3,3} | ||
| Schlegel diagram |
|||||||||||
| B4 | |||||||||||
| Name | 16-cell | rectified 16-cell |
truncated 16-cell |
cantellated 16-cell |
runcinated 16-cell |
bitruncated 16-cell |
cantitruncated 16-cell |
runcitruncated 16-cell |
omnitruncated 16-cell | ||
| Coxeter diagram |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
|||||
| Schläfli symbol |
{3,3,4} | t1{3,3,4} r{3,3,4} |
t0,1{3,3,4} t{3,3,4} |
t0,2{3,3,4} rr{3,3,4} |
t0,3{3,3,4} | t1,2{3,3,4} 2t{3,3,4} |
t0,1,2{3,3,4} tr{3,3,4} |
t0,1,3{3,3,4} | t0,1,2,3{3,3,4} | ||
| Schlegel diagram |
|||||||||||
| B4 | |||||||||||
Notes
editReferences
edit- T. Gosset: On the Regular and Semi-Regular Figures in Space of n Dimensions, Messenger of Mathematics, Macmillan, 1900
- H.S.M. Coxeter:
- Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, (3rd edition, 1973), Dover edition, ISBN 0-486-61480-8, p. 296, Table I (iii): Regular Polytopes, three regular polytopes in n-dimensions (n≥5)
- H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd Edition, Dover New York, 1973, p. 296, Table I (iii): Regular Polytopes, three regular polytopes in n-dimensions (n≥5)
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6 [1]
- (Paper 22) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi Regular Polytopes I, [Math. Zeit. 46 (1940) 380-407, MR 2,10]
- (Paper 23) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes II, [Math. Zeit. 188 (1985) 559-591]
- (Paper 24) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III, [Math. Zeit. 200 (1988) 3-45]
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 26. pp. 409: Hemicubes: 1n1)
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript (1991)
- N.W. Johnson: The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs, Ph.D. (1966)
- 2. Convex uniform polychora based on the tesseract (8-cell) and hexadecachoron (16-cell) - Models 13, 16, 17, George Olshevsky.
- Klitzing, Richard. "4D uniform polytopes (polychora)". o3o3o4o - tat, o3x3x4o - tah, x3x3o4o - thex
External links
edit- Paper model of truncated tesseract created using nets generated by Stella4D software