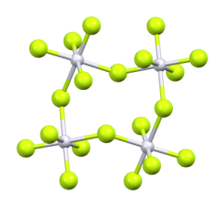
Ruthenium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula RuF5. This green volatile solid has rarely been studied but is of interest as a binary fluoride of ruthenium, i.e. a compound containing only Ru and F. It is sensitive toward hydrolysis. Its structure consists of Ru4F20 tetramers, as seen in the isostructural platinum pentafluoride. Within the tetramers, each Ru adopts octahedral molecular geometry, with two bridging fluoride ligands.[1]
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
ruthenium(V) fluoride
| |
| Other names
Ruthenium(V) fluoride, Ruthenium(5+) pentafluoride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.015 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| F5Ru | |
| Molar mass | 196.06 g/mol |
| Appearance | green solid |
| Density | 3.82 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 86.5 °C (187.7 °F; 359.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 227 °C (441 °F; 500 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ruthenium pentafluoride reacts with iodine to give ruthenium(III) fluoride.[2][3]
References
edit- ^ J. H. Holloway, R. D. Peacock, R. W. H. Small "The crystal structure of ruthenium pentafluoride" J. Chem. Soc., 1964, 644-648. doi:10.1039/JR9640000644
- ^ A. F. Holleman (2019), Lehrbuch der anorganischen Chemie (in German), Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG, p. 1418, ISBN 978-3-11-083817-6
- ^ E.A. Seddon, K.R. Seddon (2013), The Chemistry of Ruthenium (in German), Elsevier, p. 155, ISBN 978-1-4832-8990-8