This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2018) |
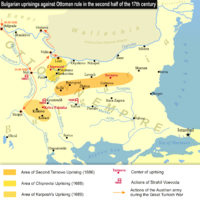
The Second Tarnovo uprising (Bulgarian: Второ търновско въстание, Vtoro tarnovsko vastanie), according to a unique Russian source published in 1847, is thought to be a Bulgarian uprising against Ottoman rule based in the former Bulgarian capital, Tarnovo, that broke out in 1686 and was severely crushed by the Ottoman authorities.
| Second Tarnovo uprising | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Bulgarian Rebels |
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Rostislav Stratimirovic | Unknown | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| about 40,000[1] | 25,000[2] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Heavy[3] | Unknown[4] | ||||||
In 1686 Russia, Saxony, Brandenburg and Bavaria joined the Holy League against the Ottoman Empire. Rostislav Stratimirovic — a descendant of the medieval Shishman dynasty decided to exploit the international situation, established relations with the Russian Patriarch Joachim and visited Moscow in preparation for the uprising. In his absence the uprising burst prematurely and was doomed. He quickly returned to Tarnovo where he was proclaimed Prince of Bulgaria after the city was briefly liberated, with about 40,000 people gathering.
However, the Ottoman authorities reacted immediately and quickly recaptured the city using regular army, brutally suppressing the uprising. Rostislav Stratimirovic fled the Ottoman territory and settled in Russia where he married the niece of the patriarch – Maria Dubrovska.
The only source about the uprising (and the very existence of Rostislav Statimirovic) is the family chronicles of Rostislavich-Dubrovsky clan, now missing. Its legendary character makes many historians doubt its authenticity and consider it "a beautiful legend" which served the political interests in 19th-century Russia. The ostensible owner of the chronicles, the amateur Russian historian Nikolay Savelyev, who called himself Savelyev-Rostislavich (1815–1854), pretended to be a descendant of Rostislav of Bulgaria and the Patriarch's niece. However, no independent sources corroborating such a genealogy of his rather modest family exist, and the whole story is presumed to be concocted by him.[5]
However, the Ottoman archives do indeed speak of insurgent activities in Tarnovo region during this period, centred on Arbanasi village.
See also
edit- First Tarnovo Uprising, 1598
References and notes
edit- ^ Geschichte des Osmanischen Reiches (I-V, Gotha 1908–1913) Nicolae Iorga ,p 188
- ^ Geschichte des Osmanischen Reiches (I-V, Gotha 1908–1913) Nicolae Iorga ,p 188
- ^ Geschichte des Osmanischen Reiches (I-V, Gotha 1908–1913) Nicolae Iorga ,p 188
- ^ Geschichte des Osmanischen Reiches (I-V, Gotha 1908–1913) Nicolae Iorga ,p 188
- ^ Шишманов И. Д. Априлов и Н. В. Савельев-Ростиславич // Сборникъ на БАН. Книга 21: Нови студии изъ областьта на българското възраждане: В. Е. Априлов, Неофит Рилски, Неофит Бозвели. София: Печатница и букволеярница П. Глушков, 1926. С. 5-32.