Jean-Nicolas Servan, also known as Giovanni Niccolò Servandoni (2 May 1695 – 19 January 1766) was an Italian decorator, architect, scene-painter, firework designer and trompe-l'œil specialist.



He was born in Florence, the son of a French carriage driver.
Career
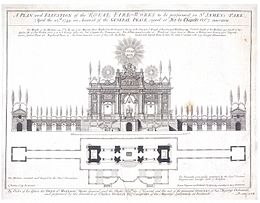
editHe was educated as an artist of perspective in Rome and was a pupil of Giovanni Paolo Panini worked in London as a set designer at the recently founded Royal Academy of Music but moved to Paris in 1724, where he became director of decorations (1724 to 1742) at the Paris Opera, at that time situated in the Théâtre du Palais-Royal. He became a member of the Académie Royale de Peinture et de Sculpture in 1731. His activity was considerable, whether as a painter or as an inventor of scenic contrivances for fêtes at the marriage of royal personages.[2] He decorated public festivals in England,[3] France, and Portugal.
During the years 1738–1743 and 1754–1758, Servandoni produced a series of successful theatrical productions much in the style of seventeenth-century machine plays, with an emphasis on elaborate changes in décor and special effects, often set to music.[4] Unlike the machine plays of the seventeenth century, Servandoni's productions used pantomime rather than dialog, with a description of the story provided in the program. His productions were typically based on well-known stories from literature and mythology such as the "Spectacle de Pandore" (1739) which told the tale of Prometheus and Pandora or "La forêt enchantée" (1754) which was inspired by Torquato Tasso's "Jerusalem Delivered". He died in Paris early in 1766.
French Works
edit- Saint Sulpice, façade and original square and surrounding buildings, although only No. 6 was completed by him, and the fountain was replaced.
Belgian Works
editAuthor
edit- Description abregée de l'eglise Saint Pierre de Rome (Paris, 1738)
- La Relation de la répresentation de la forêt enchantée sur le théâtre des Tuileries, le 31 mars 1754.
References
editNotes
- ^ "Tentoonstelling / Giovanni Niccolò Servandoni (1695-1766). Schilder, decorateur, architect | Centrum Vlaamse Architectuurarchieven". Archived from the original on 2017-02-02. Retrieved 2017-01-25.
- ^ One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Servan, Jean Nicolas". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 24 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 684.
- ^ Melanie Doderer-Winkler, "Magnificent Entertainments: Temporary Architecture for Georgian Festivals" (London and New Haven, Yale University Press for The Paul Mellon Centre for Studies in British Art, 2013). ISBN 0300186428 and ISBN 978-0300186420
- ^ Olivier, Marc (2005). "Jean-Nicolas Servandoni's Spectacles of Nature and Technology". French Forum. 30 (2): 31–47. doi:10.1353/frf.2005.0036. S2CID 194021122.
Sources
- Milizia, Francesco (1797). Dizionario delle Belle Arti del Disegno y Estratto in Gran Parte dalla Enciclopedia Metodica da Francesco Milizia, Seconda Edizione, Tomo Secondo. Bassano, Italy. p. 172.
- Olivier, Marc (2005). "Jean-Nicolas Servandoni's Spectacles of Nature and Technology". French Forum. 30 (2): 31–47. doi:10.1353/frf.2005.0036. S2CID 194021122.
- Guidoboni, Francesco (2016) doctoral thesis Giovanni Niccolò Servandoni (1695-1766) architetto
Bibliography
edit- Melanie Doderer-Winkler, "Magnificent Entertainments: Temporary Architecture for Georgian Festivals" (London and New Haven, Yale University Press for The Paul Mellon Centre for Studies in British Art, 2013). ISBN 0300186428 and ISBN 978-0300186420.
- Cristiano Marchegiani, « Servandoni (Servandon), Giovanni Niccolò Girolamo (Jean-Nicolas-Jérôme) », in Dizionario Biografico degli Italiani, vol. 92, Roma, Istituto dell'Enciclopedia Italiana, 2018, pp. 264–268.
External links
edit- Media related to Giovanni Niccolò Servandoni at Wikimedia Commons