The Southern Cameroons was the southern part of the British League of Nations mandate territory of the British Cameroons in West Africa. Since 1961, it has been part of the Republic of Cameroon, where it makes up the Northwest Region and Southwest Region.
| Southern Cameroons | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the British Cameroons | |||||||||||
| 1916–1961 | |||||||||||
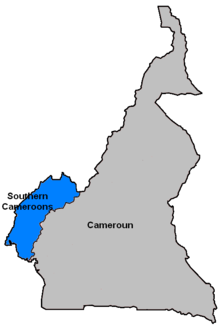 The Southern Cameroons now constitute the Southwest Region and Northwest Region. | |||||||||||
| Capital | Buea | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
• 1987 | 42,710 km2 (16,490 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
• 1987 | 2,100,000 | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
| 1916 | |||||||||||
• Federated with French Cameroons | 1 October 1961 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Cameroon | ||||||||||
Since 1994, pressure groups in the territory claim there was no legal document (treaty of union) in accordance to UNGA RES 1608(XV) paragraph 5, and are seeking to restore statehood and independence from the Cameroon. They renamed the British Southern Cameroons as Ambazonia (from Ambas Bay).
History
editLeague of Nations mandate
editFollowing the Treaty of Versailles, the German territory of Kamerun was divided on 28 June 1919, between a French and a British League of Nations Mandate, the French, who had previously administered the whole occupied territory, getting the larger. The French mandate was known as Cameroun. The British mandate comprised two adjacent territories, Northern Cameroons and Southern Cameroons. They were administered from, but not joined to, the British territory of Nigeria through the British Resident (although some incumbents had the rank of District Officer, Senior Resident or Deputy Resident) with headquarters in Buea.
Applying the principle of indirect rule, the British allowed native authorities to administer populations according to their own traditions. These also collected taxes, which were then paid over to the British. The British devoted themselves to trade and to exploiting mining resources of the territory. South Cameroons students, including Emmanuel Mbela Lifafa Endeley, created the Cameroons Youth League (CYL) on 27 March 1940, to oppose what they saw as the exploitation of their country.
-
Delegates to the Bamenda conference on the future constitution of Southern Cameroons in front of the Bamenda social centre in May 1956.
United Nations Trust territory
editWhen the League of Nations ceased to exist in 1946, most of the mandate territories were reclassified as UN trust territories, henceforth administered through the UN Trusteeship Council. The object of trusteeship was to prepare the lands for eventual independence. The United Nations approved the Trusteeship Agreements for British Cameroons to be governed by Britain on 6 December 1946.
Southern Cameroons was divided in 1949 into two provinces: Bamenda (capital Bamenda, hence also thus named) and Southern (capital Buea). Yet the residential type of administration was continued with a single British Resident at Buea, but in 1949 Edward John Gibbons was appointed Special Resident, and on 1 October 1954, when political power shifted to the elected government, succeeded himself as first of only two commissioners.
Following the Ibadan General Conference of 1950, a new constitution for Nigeria devolved more power to the regions. In the subsequent election thirteen Southern Cameroonian representatives were elected to the Eastern Nigerian House of Assembly in Enugu. In 1953, however, the Southern Cameroons representatives, unhappy with the domineering attitude of Nigerian politicians and lack of unity among the ethnic groups in the Eastern Region, declared a "benevolent neutrality" and withdrew from the assembly. At a conference in London from 30 July to 22 August 1953, the Southern Cameroons delegation asked for a separate region of its own. The British agreed, and Southern Cameroons became an autonomous region with its capital still at Buea. Elections were held in 1954 and the parliament met on 1 October 1954, with E.M.L. Endeley as Premier. As Cameroun and Nigeria prepared for Independence, South Cameroons nationalists debated whether their best interests lay with union with Cameroun, union with Nigeria or total independence. Endeley was defeated in elections on 1 February 1959 by John Ngu Foncha.
Referendums were held in 1959 and 1961 in the Cameroons to determine union with Nigeria or Cameroun. In 1961, Northern Cameroons voted for union with Nigeria and Southern Cameroons for union with (the formerly French) Cameroun.
-
Augustine N. Jua's cabinet, 1965.
-
Prince Henry, Duke of Gloucester and his spouse Princess Alice, Duchess of Gloucester in Buea, 1959.
-
Map of the Southern Cameroons consisting of 4 Divisins (1930): Victoria, Kumba, Mamfe and Bamenda.[2]
Integration with French Cameroon
editSouthern Cameroons became part of the Federal republic of Cameroon, as the West Cameroon region on 1 October 1961. Foncha served as Prime Minister of West Cameroun and vice-president of the Federal Republic of Cameroun. However, the English-speaking peoples of West Cameroun did not believe that they were fairly treated by the French-speaking government of the country. Following a referendum on 20 May 1972, a new constitution was adopted in Cameroun which replaced the federal state with a unitary state. West Cameroon lost its autonomous status and became the Northwest Province and Southwest Province of the United Republic of Cameroun. The Southern Cameroonians felt further marginalised. Groups such as the Cameroon Anglophone Movement (CAM) demanded greater autonomy, or independence, for the provinces.[citation needed]
During the reunification period, the Anglophone education system began to change as Francophone teachers came to the former Southern Cameroons.[citation needed] However, because of the language barrier, the teachers would only speak in French or pidgin which hindered the educational development of students.[citation needed] During this period, there began to be preference and domination of the French language as English language certificates became replaced by French certificates.[citation needed]
Despite being united, the Anglophones in Cameroon did not feel represented in government politics.[3] In 1993, the All Anglophone Conference argued at their meeting that "the 1961 Foumban Accord. . .was hardly represented by the Francophone majority who ultimately scrapped the Federal Constitution and replaced it with a Unitary Constitution."[3] The Foumban Accord "was the basis of Cameroon's post-independence Federal Constitution".[3]
Ambazonian independence movement
editPro-independence groups claim that UN Resolution 1608 21 April 1961, which required the UK, the Government of the Southern Cameroons and Republic of Cameroun to engage in talks with a view to agreeing measures for union of the two countries, was not implemented, and that the Government of the United Kingdom was negligent in terminating its trusteeship without ensuring that proper arrangements were made. They say that the adoption of a federal constitution by Cameroun on 1 September 1961 constituted annexation of the Southern Cameroons.
Representatives of Anglophone groups convened the first All Anglophone Conference (AAC1) in Buea from 2 April to 3 April 1993. The conference issued the "Buea Declaration", which called for constitutional amendments to restore the 1961 federation. This was followed by the second All Anglophone Conference (AAC2) in Bamenda in 1994. This conference issued the "Bamenda Declaration", which stated that if the federal state was not restored within a reasonable time, Southern Cameroons would declare its independence. The AAC was renamed the Southern Cameroons Peoples Conference (SCPC), and later the Southern Cameroons Peoples Organisation (SCAPO), with the Southern Cameroons National Council (SCNC) as the executive governing body. Younger activists formed the Southern Cameroons Youth League (SCYL) in Buea on 28 May 1995. The SCNC sent a delegation, led by John Foncha, to the United Nations, which was received on 1 June 1995 and presented a petition against the 'annexation' of the Southern Cameroons by French Cameroun. This was followed by a signature referendum the same year, which the organisers claim produced a 99% vote in favour of independence with 315,000 people voting.[4]
Armed members of the SCNC took over the Buea radio station in Southwest Province on the night of 30 December 1999 and in the early hours of 31 December broadcast a tape of a proclamation of independence read by Judge Ebong Frederick Alobwede.
Amnesty International has accused the Cameroun authorities of human right violations against Southern Cameroons activists.
Southern Cameroons, since then renamed to Ambazonia, is a member of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization (UNPO) since 2005 and a charter member of the Organization of Emerging African States (OEAS).
Leadership
edit| No. | Portrait | Name (Birth–Death) |
Election | Term of office | Political party | President | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Took office | Left office | Time in office | ||||||
| Premier of British Southern Cameroons | ||||||||
| 1 | E. M. L. Endeley (1916–1988) |
1957 | 1 October 1954 | 1 February 1959 | 4 years, 153 days | KNC | ||
| 2 | John Ngu Foncha (1916–1999) |
1959 | 1959 | 1 October 1961 | 2 years, 212 days | KNDP | ||
| Prime Minister of West Cameroon (Federal Republic of Cameroon)[5] | ||||||||
| 1 | John Ngu Foncha (1916–1999) |
1964 | 1 October 1961 | 13 May 1965 | 3 years, 224 days | KNDP | Ahidjo | |
| 2 | Augustine Ngom Jua (1929–1977) |
— | 13 May 1965 | 1 September 1966 | 2 years, 243 days | KNDP | ||
| (2) | 1 September 1966 | 11 January 1968 | UNC | |||||
| 3 | Salomon Tandeng Muna (1912–2002) |
1970 | 11 January 1968 | 2 June 1972 | 4 years, 143 days | UNC | ||
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "West Cameroon Constitution".
- ^ "West Kamerun Map". 11 May 2022.
- ^ a b c Awasom, Nicodemus Fru (1998). "Colonial Background to the Development of Autonomist Tendencies in Anglophone Cameroon, 1946-1961". Journal of Third World Studies. 15 (1): 163–183. JSTOR 45197789.
- ^ Southern Cameroons Peoples Organisation website Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Index E" (PDF). www.jstor.org. JSTOR 45193813.
Sources and external links
edit- SCNC official website Archived 2019-12-16 at the Wayback Machine
- WorldStatesmen - Cameroon

