This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (February 2012) |
Stick charts were made and used by the Marshallese to navigate the Pacific Ocean by canoe off the coast of the Marshall Islands. The charts represented major ocean swell patterns and the ways the islands disrupted those patterns, typically determined by sensing disruptions in ocean swells by islanders during sea navigation.[1]

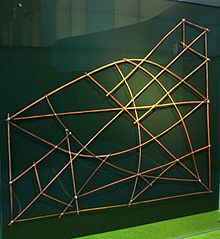
Most stick charts were made from the midribs of coconut fronds that were tied together to form an open framework. Island locations were represented by shells tied to the framework, or by the lashed junction of two or more sticks. The threads represented prevailing ocean surface wave-crests and directions they took as they approached islands and met other similar wave-crests formed by the ebb and flow of breakers. Individual charts varied so much in form and interpretation that the individual navigator who made the chart was the only person who could fully interpret and use it. The use of stick charts ended after World War II when new electronic technologies made navigation more accessible and travel among islands by canoe lessened.
Significance to the history of cartography
editThe stick charts are a significant contribution to the history of cartography because they represent a system of mapping ocean swells, which was never before accomplished. They also use different materials from those common in other parts of the world. They are an indication that ancient maps may have looked very different, and encoded different features from the earth, from the maps that we use today.
The charts, unlike traditional maps, were studied and memorized prior to a voyage and were not consulted during a trip, as compared to traditional navigation techniques where consultation of a map is frequent and points and courses are plotted out both before and during navigation. Marshallese navigators used their senses and memory to guide them on voyages by crouching down or lying prone in the canoe to feel how the canoe was being pitched and rolled by underlying swells.
Ocean swells recognized by Marshallese
editThe Marshallese recognized four main ocean swells: the rilib, kaelib, bungdockerik and bundockeing.[2] Navigators focused on effects of islands in blocking swells and generating counterswells to some degree, but they mainly concentrated on refraction of swells as they came in contact with undersea slopes of islands and the bending of swells around islands as they interacted with swells coming from opposite directions. The four types of ocean swells were represented in many stick charts by curved sticks and threads.
Rilib swells
editRilib swells are the strongest of the four ocean swells and were referred to as "backbone" swells. They are generated by the northeast trade winds and are present during the entire year, even when they do not penetrate as far south as the Marshall Islands. Marshallese considered the rilib swells to come from the east, even though the angle of the winds as well as the impact of the ocean currents varied the swell direction.[1]
Kaelib swells
editThe kaelib swell is weaker than the rilib and could only be detected by knowledgeable persons, but it is also present year round.
Bungdockerik swells
editThe bungdockerik is present year round as well and arises in the southwest. This swell is often as strong as the rilib in the southern islands.
Bundockeing swells
editThe bundockeing swell is the weakest of the four swells, and is mainly felt in the northern islands.
Stick chart categories
editThe stick charts typically fall into three main categories: mattang, meddo (or medo), and rebbelib (or rebbelith).
Mattang charts
editThe mattang stick chart was an abstract chart used for instruction and for teaching principles of reading how islands disrupt swells.
Meddo charts
editThe meddo chart showed actual islands and their relative or exact positions. Meddo charts also showed the direction of main deep ocean swells, the way the swells curved around specific islands and intersected with one another, and distance from a canoe at which an island could be detected. The meddo chart portrayed only a section of one of the two main island chains.
Rebbelib charts
editRebbelib charts portrayed the same information as a meddo chart, but the difference lies in inclusiveness of the islands. Rebbelib charts, unlike meddo charts, included all or most of one or both chains of islands.
Knowledge transfer
editStick charts were not made and used by all Marshall Islanders. Only a select few rulers knew the method of making the maps, and the knowledge was only passed on from father to son. So that others could utilize the expertise of the navigator, fifteen or more canoes sailed together in a squadron, accompanied by a leader pilot skilled in use of the charts.
It was not until 1862 that this unique piloting system was revealed in a public notice prepared by a resident missionary. It was not until the 1890s that it was comprehensively described by a naval officer, Captain Winkler of the Imperial German Navy.[3][4] Winkler had been the commander of the SMS Bussard, stationed in 1896 in the Marshall Islands which, during that period, were under German rule; he subsequently described the system in an 1898 publication. Winkler became so intrigued by the stick charts that he made a major effort to determine navigational principles behind them and 'convinced' the navigators to share how the stick charts were used.
See also
editNotes
edit- ^ a b Asscher 2002
- ^ Lewis, David (1994). We, the Navigators: The Ancient Art of Landfinding in the Pacific (Second ed.). University of Hawaii Press. p. 404.
- ^ Korvettenkapitän Winkler (1898). "Ueber die in früheren Zeiten in den Marschall-Inseln gebrauchten Seekarten, mit einigen Notizen über die Seefahrt der Marschall-Insulaner im Allgemeinen". Marine-Rundschau (in German). 10 (Juli bis Dezember): 1418–39. At the Internet Archive.
- ^ Finney, Ben (1998). "13: Nautical Cartography and Traditional Navigation in Oceania" (PDF). In Woodward, David; Lewis, G. Malcolm (eds.). The History of Cartography. Vol. 2.3: Cartography in the Traditional African, American, Arctic, Australian, and Pacific Societies. p. 476.
References
edit- Ascher, Marcia
- Models and maps from the Marshall Islands. A case in etnomathematics, Historia Mathematica, 22(1995) 347-370.
- Mathematics Elsewhere. An Exploration of Ideas across Cultures, Princeton University Press, 2002, pp89, 95-97, 101-125.
- Bagrow, L. History of Cartography. Second Edition. Chicago, Precedent Publishing, Inc., 1966.
- Genz, J., Aucan, J., Merrifeld, M. , Finney, B., Joel, K., and Kelen, Alson, Wave Navigation in the Marshall Islands, Oceanography 22(2009), No. 2., 234–245.
- Woodward, D. and Malcolm Lewis, G. The History of Cartography: Cartography in the Traditional African, American, Arctic, Australian, and Pacific Societies. Volume Two, Book Three. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago and London, 1998.
External links
edit- Dirk HR Spennemann. Traditional and Nineteenth Century Communication Patterns In the Marshall Islands, article includes extensive explanations of stick charts
- Polynesian Stick Charts, includes many photographs
- Micronesian Stick Charts, diagrams and photographs. Archived.
- Marshall Islands stamps with stick charts, and explanations
- Marshall Islands Guide
- Tingley, Kim (2016-03-17). "The Secrets of the Wave Pilots". The New York Times. Retrieved 2016-05-15.
- A short video on navigation by ocean wave refraction and stick charts by NOAA.
- Reddit posts showing stick charts: 1, 2
- RESOLVING AMBIVALENCE IN MARSHALLESE NAVIGATION:RELEARNING, REINTERPRETING, AND REVIVING THE “STICK CHART” WAVE MODELS, Joseph H. Genz, 2016