Amylocaine was the first synthetic local anesthetic. It was synthesized and patented under the name Stovaine by Ernest Fourneau at the Pasteur Institute in 1903.[1][contradictory] It was used mostly in spinal anesthesia.[2]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
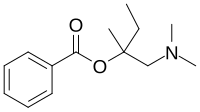
| IUPAC name
[1-(Dimethylamino)-2-methylbutan-2-yl] benzoate
| |
| Other names
Stovaine; Benzoic acid [1-(dimethylaminomethyl)-1-methylpropyl] ester
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.375 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H21NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 235.327 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Synthesis
editAmylocaine can be synthesized beginning with chloroacetone (1).[3][4][5][6][7] Grignard reaction of chloroacetone with magnesium ethyl bromide gives 1-chloro-2-methyl-butan-2-ol (2). Heating with dimethylamine gives 1-(dimethylamino)-2-methylbutan-2-ol (3). These two steps can also be treated as interchangeable. Esterification with benzoyl chloride completed the synthesis of amylocaine (4).[3][4]
See also
edit- Dimethylaminopivalophenone, an opioid with a similar chemical structure
Notes and references
edit- ^ Fourneau, E. (1904). "Stovaïne, anesthésique local". Bulletin des sciences pharmacologiques. 10: 141–148.
- ^ Debue-Barazer, Christine (2007). "Les Implications scientifiques et industrielles du succès de la Stovaïne : Ernest Fourneau (1872–1949) et la chimie des médicaments en France" Archived 2013-10-05 at the Wayback Machine. Gesnerus 64 (1-2): 24-53.
- ^ a b Quintard, Jean-Paul; Elissondo, Bernard; Jousseaume, Bernard (1984). "A Convenient Synthesis of N,N-Disubstituted Aminomethyltri-n-butylstannanes, Precursors of the Corresponding Lithium Reagents". Synthesis. 1984 (6): 495–498. doi:10.1055/s-1984-30879. ISSN 0039-7881. S2CID 95920500.
- ^ a b Fourneau, Ernest (1904). Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des séances de l'Académie des sciences. Vol. 138. Paris: Academy of Sciences, Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS; French National Centre for Scientific Research). p. 767.
- ^ Zernik, F (1905). "?". Chem. Zentralbl. 76 (1): 1029.[full citation needed]
- ^ DE169746C, "Patent number DE169746C". Google Patents.
- ^ DE169787C, "Patent number DE169787C". Google Patents.
External links
edit- Smith, Maurice I.; Hatcher, Robert A. (January 1917). "A Contribution to the Pharmacology of Stovaine". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 9 (4): 231–240.
- Ball, Christine M.; Westhorpe, Rod N. (2004). "Local Anaesthesia after Cocaine". Anaesthesia and Intensive Care. 32 (2): 157. doi:10.1177/0310057X0403200201. PMID 15957711.