Sulfathiazole is an organosulfur compound used as a short-acting sulfa drug.[1] Formerly, it was a common oral and topical antimicrobial, until less toxic alternatives were discovered.[2]
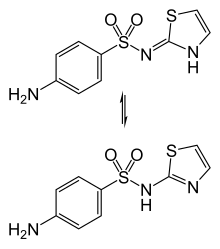 Imino (top) and amino (bottom) tautomers | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.701 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H9N3O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 255.31 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 202 to 202.5 °C (395.6 to 396.5 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Sulfathiazole exists in various forms (polymorphs). The imine tautomer is dominant in solid samples.[3]
Cultural references
edit- In the 1955 short story, Captive Audience by Philip K. Dick, Flannery recommends the use of sulfathiazole in lieu of the unavailable Penicillin for a ten-year-old boy's suppurating arm wound he received from "toxic crystalline poisoning".
- 1960 Otto Preminger's movie Exodus, American nurse Kitty Fremont tells Dr. Odenheimer that sulfathiazole is the treatment for impetigo. Dr. Odenheimer tells her that sulfathiazole is not available on the ship; soaking of the lesions and exposure to sunlight "is also a cure."
- 1963: Sulfathiazole is mentioned in Kurt Vonnegut's novel Cat's Cradle and New Dictionary, and several of his short stories.
- 1964: Thomas Heggen's novel Mister Roberts mentions the use of sulfathiazole to treat gonorrhea.
- 1978: John Irving's novel The World According to Garp in chapter 1 where Garp's mother witnesses it being dispensed to World War II soldiers.
- 1988: The movie Dead Heat mentions the chemical as a drug used with reanimation of dead bodies.
- 2003: F. Spencer Chapman D.S.O. in his WWII memoir, The Jungle is Neutral, refers to his personal use of sulphathiazole (M.&B.) in the jungles of Malaya during May 1942. He credits the use of the drug with preventing fever and pneumonia becoming fatal in arduous conditions during the guerilla actions undertaken by the Malayan Communist Party against the Japanese occupying forces.[4]
References
edit- ^ Mertschenk B, Beck F, Bauer W (2002). "Thiourea and Thiourea Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_803. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ Rouf A, Tanyeli C (June 2015). "Bioactive thiazole and benzothiazole derivatives". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 97: 911–27. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.10.058. PMID 25455640.
- ^ Kruger GT, Gafner G (February 1971). "The crystal structure of sulphathiazole II". Acta Crystallographica Section B. 27 (2): 326–33. Bibcode:1971AcCrB..27..326K. doi:10.1107/S0567740871002176.
- ^ Chapman FS (1949). The Jungle is Neutral. WW norton. p. 108.