Template:Chembox/testcases
| This is the template test cases page for the sandbox of Template:Chembox. to update the examples. If there are many examples of a complicated template, later ones may break due to limits in MediaWiki; see the HTML comment "NewPP limit report" in the rendered page. You can also use Special:ExpandTemplates to examine the results of template uses. You can test how this page looks in the different skins and parsers with these links: |
|
/sandbox: Chembox/sandbox (edit · t · history · diff · links · /test · Source · e · t · hist · links · /subpages · /doc · /doc edit · Module:no)
|
- To test: each subtemplate must be set to /sandbox in every test-instance (or every article). There is no single point to switch all to /sandbox.
|Section8={{Chembox Hazard/sandbox|...}}
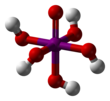
Demo 1 Magnesium sulfate
editMagnesium sulfate, sort of
 Anhydrous magnesium sulfate
| |
 Epsomite (heptahydrate)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | magn |
| IUPAC name
Magnesium sulfate
| |
| Other names
Epsom salt (heptahydrate)
English salt Bitter salts | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | abbr |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MgSO4 | |
| Molar mass | 120.366 g/mol (anhydrous) 138.38 g/mol (monohydrate) 174.41 g/mol (trihydrate) 210.44 g/mol (pentahydrate) 228.46 g/mol (hexahydrate) 246.47 g/mol (heptahydrate) |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.66 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.445 g/cm3 (monohydrate) 1.68 g/cm3 (heptahydrate) 1.512 g/cm3 (11-hydrate) |
| Melting point | anhydrous decomposes at 1,124 °C monohydrate decomposes at 200 °C heptahydrate decomposes at 150 °C undecahydrate decomposes at 2 °C |
| anhydrous 26.9 g/100 mL (0 °C) 25.5 g/100 mL (20 °C) 50.2 g/100 mL (100 °C) heptahydrate 71 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | 1.16 g/100 mL (18 °C, ether) slightly soluble in alcohol, glycerol insoluble in acetone |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.523 (monohydrate) 1.433 (heptahydrate) |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic (hydrate) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 38 °C; 100 °F; 311 K[1] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Beryllium sulfate Calcium sulfate Strontium sulfate Barium sulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
 Anhydrous magnesium sulfate
| |
 Epsomite (heptahydrate)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | magn |
| IUPAC name
Magnesium sulfate
| |
| Other names
Epsom salt (heptahydrate)
English salt Bitter salts | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | abbr |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MgSO4 | |
| Molar mass | 120.366 g/mol (anhydrous) 138.38 g/mol (monohydrate) 174.41 g/mol (trihydrate) 210.44 g/mol (pentahydrate) 228.46 g/mol (hexahydrate) 246.47 g/mol (heptahydrate) |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.66 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.445 g/cm3 (monohydrate) 1.68 g/cm3 (heptahydrate) 1.512 g/cm3 (11-hydrate) |
| Melting point | anhydrous decomposes at 1,124 °C monohydrate decomposes at 200 °C heptahydrate decomposes at 150 °C undecahydrate decomposes at 2 °C |
| anhydrous 26.9 g/100 mL (0 °C) 25.5 g/100 mL (20 °C) 50.2 g/100 mL (100 °C) heptahydrate 71 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | 1.16 g/100 mL (18 °C, ether) slightly soluble in alcohol, glycerol insoluble in acetone |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.523 (monohydrate) 1.433 (heptahydrate) |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic (hydrate) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 38 °C; 100 °F; 311 K[2] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Beryllium sulfate Calcium sulfate Strontium sulfate Barium sulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Demo 2
editdistorted
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | pron |
| IUPAC name
Magnesium sulfate
| |
| Other names
Epsom salt (heptahydrate)
English salt Bitter salts | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MgSO4 | |
| Molar mass | 120.366 g/mol (anhydrous) 138.38 g/mol (monohydrate) 174.41 g/mol (trihydrate) 210.44 g/mol (pentahydrate) 228.46 g/mol (hexahydrate) 246.47 g/mol (heptahydrate) |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.66 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.445 g/cm3 (monohydrate) 1.68 g/cm3 (heptahydrate) 1.512 g/cm3 (11-hydrate) |
| Melting point | anhydrous decomposes at 1,124 °C monohydrate decomposes at 200 °C heptahydrate decomposes at 150 °C undecahydrate decomposes at 2 °C |
| anhydrous 26.9 g/100 mL (0 °C) 25.5 g/100 mL (20 °C) 50.2 g/100 mL (100 °C) heptahydrate 71 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | 1.16 g/100 mL (18 °C, ether) slightly soluble in alcohol, glycerol insoluble in acetone |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.523 (monohydrate) 1.433 (heptahydrate) |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic (hydrate) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Beryllium sulfate Calcium sulfate Strontium sulfate Barium sulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | pron |
| IUPAC name
Magnesium sulfate
| |
| Other names
Epsom salt (heptahydrate)
English salt Bitter salts | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MgSO4 | |
| Molar mass | 120.366 g/mol (anhydrous) 138.38 g/mol (monohydrate) 174.41 g/mol (trihydrate) 210.44 g/mol (pentahydrate) 228.46 g/mol (hexahydrate) 246.47 g/mol (heptahydrate) |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.66 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.445 g/cm3 (monohydrate) 1.68 g/cm3 (heptahydrate) 1.512 g/cm3 (11-hydrate) |
| Melting point | anhydrous decomposes at 1,124 °C monohydrate decomposes at 200 °C heptahydrate decomposes at 150 °C undecahydrate decomposes at 2 °C |
| anhydrous 26.9 g/100 mL (0 °C) 25.5 g/100 mL (20 °C) 50.2 g/100 mL (100 °C) heptahydrate 71 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | 1.16 g/100 mL (18 °C, ether) slightly soluble in alcohol, glycerol insoluble in acetone |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.523 (monohydrate) 1.433 (heptahydrate) |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic (hydrate) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Beryllium sulfate Calcium sulfate Strontium sulfate Barium sulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Demo 3
editcat checks Other, break
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Magnesium sulfate
| |
| Other names
Epsom salt (heptahydrate)
English salt Bitter salts | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MgSO4 | |
| Molar mass | 120.366 g/mol (anhydrous) 138.38 g/mol (monohydrate) 174.41 g/mol (trihydrate) 210.44 g/mol (pentahydrate) 228.46 g/mol (hexahydrate) 246.47 g/mol (heptahydrate) |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.66 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.445 g/cm3 (monohydrate) 1.68 g/cm3 (heptahydrate) 1.512 g/cm3 (11-hydrate) |
| Melting point | anhydrous decomposes at 1,124 °C monohydrate decomposes at 200 °C heptahydrate decomposes at 150 °C undecahydrate decomposes at 2 °C |
| anhydrous 26.9 g/100 mL (0 °C) 25.5 g/100 mL (20 °C) 50.2 g/100 mL (100 °C) heptahydrate 71 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | 1.16 g/100 mL (18 °C, ether) slightly soluble in alcohol, glycerol insoluble in acetone |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.523 (monohydrate) 1.433 (heptahydrate) |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic (hydrate) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| A-ignit 50 °C (122 °F; 323 K) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Beryllium sulfate Calcium sulfate Strontium sulfate Barium sulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Magnesium sulfate
| |
| Other names
Epsom salt (heptahydrate)
English salt Bitter salts | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MgSO4 | |
| Molar mass | 120.366 g/mol (anhydrous) 138.38 g/mol (monohydrate) 174.41 g/mol (trihydrate) 210.44 g/mol (pentahydrate) 228.46 g/mol (hexahydrate) 246.47 g/mol (heptahydrate) |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.66 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.445 g/cm3 (monohydrate) 1.68 g/cm3 (heptahydrate) 1.512 g/cm3 (11-hydrate) |
| Melting point | anhydrous decomposes at 1,124 °C monohydrate decomposes at 200 °C heptahydrate decomposes at 150 °C undecahydrate decomposes at 2 °C |
| anhydrous 26.9 g/100 mL (0 °C) 25.5 g/100 mL (20 °C) 50.2 g/100 mL (100 °C) heptahydrate 71 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | 1.16 g/100 mL (18 °C, ether) slightly soluble in alcohol, glycerol insoluble in acetone |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.523 (monohydrate) 1.433 (heptahydrate) |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic (hydrate) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| A-ignit 50 °C (122 °F; 323 K) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Beryllium sulfate Calcium sulfate Strontium sulfate Barium sulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
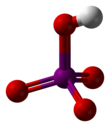
Ammonia
edit

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Azane
| |||
| Other names
Hydrogen nitride
Trihydrogen nitride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| 3587154 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 79 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Ammonia | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1005 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| NH3 | |||
| Molar mass | 17.031 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colourless gas | ||
| Odor | strong pungent odor | ||
| Density | 0.86 kg/m3 (1.013 bar at boiling point) 0.769 kg/m3 (STP)[3] | ||
| Melting point | −77.73 °C (−107.91 °F; 195.42 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −33.34 °C (−28.01 °F; 239.81 K) | ||
| 47% w/w (0 °C) 31% w/w (25 °C) 18% w/w (50 °C)[6] | |||
| Solubility | soluble in chloroform, ether, ethanol, methanol | ||
| Vapor pressure | 8573 h Pa | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 32.5 (−33 °C),[7] 10.5 (DMSO) | ||
| Basicity (pKb) | 4.75 | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3327 | ||
| Structure | |||
| C3v | |||
| Trigonal pyramid | |||
| 1.42 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
193 J·mol−1·K−1[8] | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−46 kJ·mol−1[8] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
    [9] [9]
| |||
| H290, H301, H311, H314, H330, H334, H336, H360, H362, H373, H400 | |||
| P202, P221, P233, P261, P263, P271, P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310[9] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | flammable gas (see text) | ||
| 651 °C (1,204 °F; 924 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 15–28% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
0.015 mL/kg (human, oral) | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
50 ppm (25 ppm ACGIH- TLV; 35 ppm STEL) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other cations
|
Phosphine Arsine Stibine | ||
Related nitrogen hydrides
|
Hydrazine Hydrazoic acid | ||
Related compounds
|
Ammonium hydroxide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Azane
| |||
| Other names
Hydrogen nitride
Trihydrogen nitride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| 3587154 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 79 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Ammonia | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1005 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| NH3 | |||
| Molar mass | 17.031 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colourless gas | ||
| Odor | strong pungent odor | ||
| Density | 0.86 kg/m3 (1.013 bar at boiling point) 0.769 kg/m3 (STP)[10] | ||
| Melting point | −77.73 °C (−107.91 °F; 195.42 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −33.34 °C (−28.01 °F; 239.81 K) | ||
| 47% w/w (0 °C) 31% w/w (25 °C) 18% w/w (50 °C)[13] | |||
| Solubility | soluble in chloroform, ether, ethanol, methanol | ||
| Vapor pressure | 8573 h Pa | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 32.5 (−33 °C),[14] 10.5 (DMSO) | ||
| Basicity (pKb) | 4.75 | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3327 | ||
| Structure | |||
| C3v | |||
| Trigonal pyramid | |||
| 1.42 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
193 J·mol−1·K−1[8] | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−46 kJ·mol−1[8] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
    [9] [9]
| |||
| H290, H301, H311, H314, H330, H334, H336, H360, H362, H373, H400 | |||
| P202, P221, P233, P261, P263, P271, P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310[9] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | flammable gas (see text) | ||
| 651 °C (1,204 °F; 924 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 15–28% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
0.015 mL/kg (human, oral) | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
50 ppm (25 ppm ACGIH- TLV; 35 ppm STEL) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other cations
|
Phosphine Arsine Stibine | ||
Related nitrogen hydrides
|
Hydrazine Hydrazoic acid | ||
Related compounds
|
Ammonium hydroxide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Uses:
| ImageFile2 = <nowiki>Orthoperiodic acid</nowiki>
| |||
| Orthoperiodic acid | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H5IO6 (orthoperiodic) HIO4 (metaperiodic) | |||
| Molar mass | 227.941 g/mol (H5IO6) 190.91 g/mol (HIO4) | ||
| Appearance | Colourless crystals | ||
| Density | 1.4 kg/m3 (orthoperiodic) | ||
| Melting point | 128.5 °C (263.3 °F; 401.6 K)[15] | ||
| Solubility | soluble in water, alcohols | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| H271, H314, H372, H400 | |||
| P210, P260, P273, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338} | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
| ||
Other cations
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
| |||
| Orthoperiodic acid | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H5IO6 (orthoperiodic) HIO4 (metaperiodic) | |||
| Molar mass | 227.941 g/mol (H5IO6) 190.91 g/mol (HIO4) | ||
| Appearance | Colourless crystals | ||
| Density | 1.4 kg/m3 (orthoperiodic) | ||
| Melting point | 128.5 °C (263.3 °F; 401.6 K)[16] | ||
| Solubility | soluble in water, alcohols | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| H271, H314, H372, H400 | |||
| P210, P260, P273, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
| ||
Other cations
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Chloral hydrate (pharma)
edit
| Pharmacology | |
|---|---|
| Oral codeine/syrup, rectal suppository | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| well absorbed | |
| converted to trichloroethanol, hepatic and renal | |
| 8–10 hours in plasma | |
| bile, feces, urine (various metabolites not unchanged) | |
| Legal status |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
| Pharmacology | |
|---|---|
| Oral codeine/syrup, rectal suppository | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| well absorbed | |
| converted to trichloroethanol, hepatic and renal | |
| 8–10 hours in plasma | |
| bile, feces, urine (various metabolites not unchanged) | |
| Legal status |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Pharma: legal
edit
| Pharmacology | |
|---|---|
| License data | |
| Legal status |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
| Pharmacology | |
|---|---|
| License data | |
| Legal status |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
REL
editWikipedia_talk:Chemical_infobox#Would_look_like
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Hazards | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits):[17] | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 400 ppm (1400 mg/m3) |
REL (Recommended)
|
PEL, and ST 15 ppm (37 mg/m3) |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
2000 ppm |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Hazards | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits):[19][18] | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 400 ppm (1400 mg/m3) |
REL (Recommended)
|
PEL, and ST 15 ppm (37 mg/m3) |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
2000 ppm |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
| Hazards | |
|---|---|
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits):[20] | |
REL (Recommended)
|
rel |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
| Hazards | |
|---|---|
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits):[21] | |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
IDLH |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Blank REL test chemobox
edit| Hazards | |
|---|---|
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits):[23][22] | |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 100 ppm (300 mg/m3) |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1500 ppm |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Teixobactin
editdrugbox
edit | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Unknown |
| Protein binding | Unknown |
| Metabolism | Unknown |
| Onset of action | Unknown |
| Elimination half-life | Unknown |
| Excretion | Unknown |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C58H95N15O15 |
| Molar mass | 1242.47 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Teixobactin /ˌteɪks.oʊ.ˈbæk.tɪn/
(blank setup)
edit== (test) ==
{{purge}}
<div style="float:right;">
{{chembox
| Name = live
}}</div>
<!-- -->
<div style="float:left;">
{{chembox/sandbox
| Name = sandboxes
}}</div>{{clear}}<!--
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- -->
E number
edit
<div style="float:right;">
{{chembox
| Name = live
|E_number = 999
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
Demo copied from doc page (stray closing div tag that is never opened)
edit| {{Chembox}} | {{Chembox/sandbox}} | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
refs
edit- ^ abc
- ^ abc
- ^ http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/gas-density-d_158.html
- ^ Yost, Don M. (2007). "Ammonia and Liquid Ammonia Solutions". Systematic Inorganic Chemistry. READ BOOKS. p. 132. ISBN 1-4067-7302-6.
- ^ Blum, Alexander (1975). "On crystalline character of transparent solid ammonia". Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids. 24 (4): 277. doi:10.1080/00337577508240819.
- ^ Budavari, Susan, ed. (1996). The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (12th ed.). Merck. ISBN 0-911910-12-3.
- ^ Perrin, D. D., Ionisation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases in Aqueous Solution; 2nd Ed., Pergamon Press: Oxford, 1982.
- ^ a b c d Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A22. ISBN 0-618-94690-X.
- ^ a b c d Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ammonia. Retrieved on 2013-07-20.
- ^ http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/gas-density-d_158.html
- ^ Yost, Don M. (2007). "Ammonia and Liquid Ammonia Solutions". Systematic Inorganic Chemistry. READ BOOKS. p. 132. ISBN 1-4067-7302-6.
- ^ Blum, Alexander (1975). "On crystalline character of transparent solid ammonia". Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids. 24 (4): 277. doi:10.1080/00337577508240819.
- ^ Budavari, Susan, ed. (1996). The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (12th ed.). Merck. ISBN 0-911910-12-3.
- ^ Perrin, D. D., Ionisation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases in Aqueous Solution; 2nd Ed., Pergamon Press: Oxford, 1982.
- ^ Aylett, founded by A.F. Holleman ; continued by Egon Wiberg ; translated by Mary Eagleson, William Brewer ; revised by Bernhard J. (2001). Inorganic chemistry (1st English ed., [edited] by Nils Wiberg. ed.). San Diego, Calif. : Berlin: Academic Press, W. de Gruyter. p. 453. ISBN 0123526515.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Aylett, founded by A.F. Holleman ; continued by Egon Wiberg ; translated by Mary Eagleson, William Brewer ; revised by Bernhard J. (2001). Inorganic chemistry (1st English ed., [edited] by Nils Wiberg. ed.). San Diego, Calif. : Berlin: Academic Press, W. de Gruyter. p. 453. ISBN 0123526515.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards".
- ^ "Pocket Guide in general".
- ^ "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards".
- ^ "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards".
- ^ helloworld
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0278". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards".