Thiomalic acid or mercaptosuccinic acid is a dicarboxylic acid containing a thiol functional group. As suggested by its name, it contains a thiol group (SH) in place of the hydroxy group (OH) in malic acid. Salts and esters are known as thiomalates.
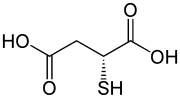 D-Thiomalic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Sulfanylbutanedioic acid | |
| Other names
2-Mercaptosuccinic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.670 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O4S | |
| Molar mass | 150.15 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 151 to 154 °C (304 to 309 °F; 424 to 427 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Thiomalate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Thiomalic acid is an intermediate in the synthesis of corrosion inhibitors, soil fumigants, active pharmaceutical ingredients, and electroplating agents.[1]
The sodium and gold salt of thiomalic acid, sodium aurothiomalate, is used as a pharmaceutical drug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.[2]
Thiomalic acid forms the backbone of the pesticide malathion.
References
edit- ^ "Thiomalic acid". Inxight Drugs. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
- ^ Kean WF, Kean IR (June 2008). "Clinical pharmacology of gold". Inflammopharmacology. 16 (3): 112–25. doi:10.1007/s10787-007-0021-x. PMID 18523733. S2CID 808858.