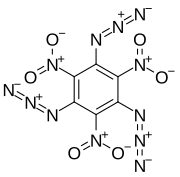
1,3,5-Triazido-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene, also known as TATNB (triazidotrinitrobenzene) and TNTAZB (trinitrotriazidobenzene), is an aromatic high explosive composed of a benzene ring with three azido groups (-N3) and three nitro groups (-NO2) alternating around the ring, giving the chemical formula C6(N3)3(NO2)3. Its detonation velocity is 7,350 meters per second, which is comparable to TATB (triaminotrinitrobenzene).
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3,5-Triazido-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | TATNB |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | C043826 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6N12O6 | |
| Molar mass | 336.144 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow crystals[1] |
| Melting point | 131 °C[2] |
| Structure[1] | |
| monoclinic | |
| P21/c, No. 14 | |
| Thermochemistry[1] | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
765.8 kJ/mol |
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
3200 kJ/mol |
| Explosive data | |
| Detonation velocity | 7350 m/s |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Preparation
editThe compound was first synthesized in 1924 by Oldřich Turek.[3] It can be prepared by the reaction of 1,3,5-trichloro-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene with sodium azide. 1,3,5-trichloro-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene is obtained from the nitration of 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene with nitric acid and sulfuric acid.[3]
Another route uses the nitration of 1,3,5-triazido-2,4-dinitrobenzene.[1]
Properties
editChemical Properties
editEven at low temperatures, the compound slowly decomposes by giving off nitrogen gas, converting into benzotrifuroxan. This reaction proceeds quantitatively within 14 hours at 100 °C.[3] As a solution in m-xylene, first order kinetics were observed for the decomposition, with a half-life of 340 minutes at 70 °C, 89 minutes at 80 °C, and 900 seconds at 100 °C.[4]
The compound explodes if rapidly heated above 168 °C.[1]
References
edit- ^ a b c d e Adam, David; Karaghiosoff, Konstantin; Klapötke, Thomas M.; Holl, Gerhard; Kaiser, Manfred (2002). "Triazidotrinitro Benzene: 1,3,5-(N3)3-2,4,6-(NO2)3C6". Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 27 (1): 7–11. doi:10.1002/1521-4087(200203)27:1<7::AID-PREP7>3.0.CO;2-J.
- ^ Burov, Yu. M.; Nazin, G. M.; Manelis, G. B. (1999). "Retardation of Monomolecular Reactions in the Solid Phase". Russian Chemical Bulletin. 48 (7): 1250–1254. doi:10.1007/BF02495284. S2CID 95970971.
- ^ a b c Matyáš, Robert; Pachman, Jiří (2013). Primary Explosives. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 118–121. ISBN 9783642284366.
- ^ Korsunskii, B. L.; Apina, T. A. (1971). "Kinetics of the Thermal Decomposition of 1,3,5-Triazido-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene in Solution". Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Division of Chemical Science. 20 (9): 1971–1973. doi:10.1007/BF00854439.