Mozabite (endonym: tamazight), also known as Mzab, Tumẓabt or Ghardaia, is a Zenati language spoken by the Mozabites, an Ibadi Berber group inhabiting the seven cities of the M'zab natural region in the northern Saharan Algeria.[2][3][4] It is also spoken by small numbers of Mozabite emigrants in other local cities and elsewhere. Mozabites also use Algerian Arabic. As of 2010, UNESCO estimated there to be about 150,000 Mozabite speakers.[3]
| Mozabite | |
|---|---|
| تونژابت | |
| Tumẓabt ⵜⵓⵎⵥⴰⴱⵜ | |
| Native to | Algeria |
| Region | M'zab (wilaya of Ghardaïa) |
| Ethnicity | Mozabite |
Native speakers | 200,000 (2022)[1] |
| Arabic alphabet, Tifinagh, Berber Latin alphabet | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | mzb |
| Glottolog | tumz1238 |
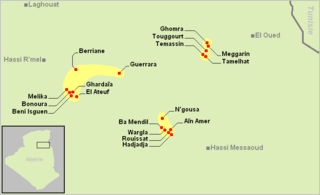 Berber-speaking areas of the Mzab, Ouargla, and Oued Righ | |
Mozabite is one of the Mzab–Wargla languages, a dialect cluster of the Zenati languages.[3]
Bibliography
edit- ابراهيم و بكير عبد السلام. الوجيز في قواعد الكتابة و النحو للغة الأمازيغية "المزابية". المطبعة العرببة: غرداية 1996.
- Delheure, Jean. Aǧraw n Yiwalen Tumẓabt d-Tefṛansist = Dictionnaire Mozabite–Francais. SELAF:Paris 1984.
References
edit- ^ Mozabite at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)
- ^ Heggoy, Willy N. (July 1947). "The Mozabites of Algeria". The Muslim World. 37 (3): 192–208. doi:10.1111/j.1478-1913.1947.tb02488.x. ISSN 0027-4909.
- ^ a b c "Algeria". Ethnologue. Languages of Africa and Europe. David Eberhard, Gary F. Simons, Charles D. Fennig, Summer Institute of Linguistics (Twenty-fifth ed.). Dallas, Texas. 2022. p. 57. ISBN 978-1-55671-502-0. OCLC 1315489099.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ "Mʾzabite | people | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 2023-02-13.