Ugandi[1] (Latin: Ungannia or Ugaunia;[2] Latvian: Ugaunija; Low German: Uggn) was an independent county between the east coast of Lake Võrtsjärv and west coast of Lake Pskov, bordered by Vaiga, Mõhu, Nurmekund, Sakala, Tālava, and The Principality of Pskov. Ugandi had an area of approximately 3000 hides. Ugandi corresponded roughly to the present Estonia's territory of Võru County, Põlva County and half of Tartu County and Valga County, as well as Petseri County.
| Ungannia Ugandi | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| county of Ancient Estonia | |||||||
| unknown–1224 | |||||||
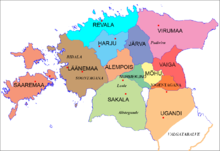 | |||||||
| Capital | Tarbatu, Otepää | ||||||
| Area | |||||||
| • Coordinates | 58°10′N 26°50′E / 58.17°N 26.83°E | ||||||
| History | |||||||
• Established | unknown | ||||||
• Disestablished | 1224 | ||||||
| |||||||
The county was first mentioned in print by Henry of Livonia[3] After the Northern crusades it became the Bishopric of Dorpat. In Latvian, Igaunija (Ugaunija is the Latvian name for the Ugaunia county) is still the modern national name for Estonia.[4] The name Ugandi is derived by associating "Ugaunia" with the name of Uandimägi Hill near Otepää. An alternate theory proposes that the name "Ugaunia" could have been derived from the Slavic language word "Ug", meaning "South" (cf. Yugoslavia). The power center of Ugandi is believed to have been in the fortified stronghold of Otepää (Ugaunian for "bear's head"; Latin: Caput Ursi, Russian: Medvezh'ya Golova) in present-day Linnamägi Hill in the town of Otepää. The hill is indeed shaped like a head of a bear, thought to have been a holy animal for Ugaunians. Another important Ugaunian stronghold was Tarbatu by the river Emajõgi (literally, "Mother River"). It was erected around 600 AD on the east side of Toome Hill (Toomemägi) in what is today Tartu. Due to its location, Ugandi always bore the brunt of East Slavs' attacks against Chudes, as they called Finnic peoples around their North-Eastern boundaries.
History
editIn 1030 Kievan Prince Yaroslav I the Wise organized a military campaign against Chuds, defeated them and established fort Yuryev (literally "Yury's" - Yury being Yaroslav's Christian name) in what is modern day Tartu.[5] Kievan rule of Tartu/Tarbatu may have lasted 30 years until 1061, when, according to Old East Slavic chronicles, Yuryev was burned down by Sosols (probably Sackalians, Oeselians or Harionenses).[6] In modern Estonian literature, the province of Ugaunia is called Ugandi or Ugala. In Latvian, the country of Estonia is still called Igaunija after Ugaunians, their ancient warlike neighbors. In Estonian folklore, Ugaunians (ugalased) are enemy warriors and robbers. For example, a folk song from Viljandi calls for speeding up the harvest work because Ugaunians might attack. "Ugalane" has also been used as a disparaging word for an unsophisticated country person. Rulers of Novgorod Republic and Principality of Pskov made frequent raids against Ugaunians in the 12th century but never succeeded to subjugate them. Fort Bear's Head was conquered in 1116 and 1193, Tarbatu in 1134 and 1192. Ugaunians themselves made several raids against Pskov.
At the beginning of the 13th century, a new powerful enemy appeared. German crusaders had established a foothold at the mouth of the Daugava river and started to expand and christen local tribes. The Ugaunians' southern neighbors, the Latgalians (or Letts), saw the crusaders as potential allies against their traditional adversaries. The Ugaunians wanted to continue the truce with their new neighbors, but the crusaders had a list of preconditions. They demanded that the Ugaunians pay reparation for an old incident. Many years ago the Ugaunians, upon the advice of the Livonians, had robbed a caravan of German merchants by the Daugava river. In 1207 the crusaders sent a priest called Alabrand to Ugaunia to demand compensation, but did not receive an answer. Next year the Letts and Teutonic Knights sent a new delegation to Ugaunia and returned with Ugaunian envoys. Ugaunians were offered "eternal peace" if they accept Christianity and return everything they had robbed from Germans and Letts. Ugaunians refused and left, threatening the Letts with "very sharp lances". The crusaders and Letts went to war against Ugaunians. They burned Otepää and returned with captives and booty. Ugaunians and Sackalians retaliated, raided territories of the Letts and burned their worst enemies alive. The Livonians and the Bishop of Riga wanted peace and sent the priest Alabrand to Otepää to negotiate. Alabrand used the gathering of Ugaunians to preach the Christianity to them. Some pagan Ugaunians wanted to kill him because of his preaching, but his status as the messenger of the bishop protected him. Ugaunians made peace with the Bishop of Riga, the leader of the Livonian Crusade.
In 1210 the Novgorodian prince Mstislav the Bold and Vladimir the Prince of Polatsk, sent an army against Ugaunians. They besieged Otepää and fought there for eight days. Defenders of the fort suffered a shortage of food and water and were forced to ask for peace. Ugaunians had to accept Orthodox baptism and pay a tribute of 400 "nogata" marks. (Nogat or nahad is Estonian word for pelts). The same summer Ugaunians of Otepää surrendered to crusader commander Bertold of Wenden. Ugaunians continued to raid Lettish territories. Wars between Ugaunians and Letts lasted the whole decade. The elders of Ugaunians and Letts had deep personal feuds. When Ugaunians captured Tālivaldis of Trikāta in 1215 and burned him alive, his sons burned alive all Ugaunian men they could catch to avenge. They also tortured Ugaunians to force them to show hiding places in the woods. When all Ugaunian provinces were burnt down, the people still alive sent messengers to Riga, asking for peace and promised to receive baptism. They told that all who had been involved in the robbery of German merchants had already been killed. The priests Otto and Peter Kakuwalda were sent to baptize them. Hearing about that, prince Vladimir of Pskov attacked Ugaunians. Ugaunians and German crusaders fortified Otepää and avenged Russians, raiding lands of Pskov and Novgorod. After that Ugaunians went with crusaders, Livonians and Letts against Estonian pagan provinces Jerwia and Vironia. Prince Vladimir of Pskov sent messengers through all of Estonia to besiege Germans and Ugaunians at Otepää. Harrians and Oeselians came and even already baptized Sackalians. While troops of 20,000 of Novgorodians and Œselians attacked Otepää, Ugaunians along with crusaders made raids against Novgorod, Vironians and Votians.
In 1220 Ugaunians rebelled against the Germans. Sackalians sent bloody swords with which they had killed Germans to Ugaunians of Tarbatu and Otepää. In Tarbatu they decided by lot whether to sacrifice to the gods an ox or their priest Hartwig, who was equally fat. Luckily for the priest, the lot fell upon the ox. Ugaunians decided to side with Novgorodians. Russian princes of Pskov, Novgorod and Suzdal sent huge troops of 20,000 men to Ugaunia. The people of Tarbatu sent them large gifts and Otepää welcomed them too. The Russians left Vetseke as their prince to rule Ugaunians and any other Estonian province around he could gathered tax from. In 1224 crusaders retook all provinces in mainland Estonia. After casting lot, bishop Hermann of Buxhoeveden was given rule over Ugaunia while Sackala was given to the order. Otepää was happy over the rule of bishop Hermann but Tarbatu was still ruled by Vetseke and his Ruthenians. Later that year however, Tarbatu was conquered and all its Ugaunian and Ruthenian defenders killed. Bishop Hermann started to fortify Otepää and Tarbatu. He chose Tarbatu/Dorpat to be his residence. Bishop Hermann and his Ugaunian subjects fought frequently against Novgorod and were defeated by prince Alexander Nevsky in the Battle on Lake Peipus in 1242. Ugaunia became subsequently known as the Bishopric of Dorpat.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Historical Dictionary of Estonia; p.63 ISBN 0-8108-4904-6
- ^ Ugaunia at books.google.com
- ^ The Chronicle of Henry of Livonia ISBN 0-231-12889-4
- ^ Igaunija at lv.wikipedia
- ^ Tvauri, Andres (2012). The Migration Period, Pre-Viking Age, and Viking Age in Estonia. pp. 33, 59, 60. Retrieved 27 December 2016.
- ^ Mäesalu, Ain (2012). "Could Kedipiv in East-Slavonic Chronicles be Keava hill fort?" (PDF). Estonian Journal of Archaeology. 1 (16supplser): 199. doi:10.3176/arch.2012.supv1.11. Retrieved 27 December 2016.