IntroductionThe Devonian (/dəˈvoʊni.ən, dɛ-/ də-VOH-nee-ən, deh-) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era during the Phanerozoic eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at 419.2 million years ago (Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding Carboniferous period at 358.9 Ma. It is the fourth period of both the Paleozoic and the Phanerozoic. It is named after Devon, South West England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant evolutionary radiation of life on land occurred during the Devonian, as free-sporing land plants (pteridophytes) began to spread across dry land, forming extensive coal forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of vascular plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants (pteridospermatophytes) appeared. This rapid evolution and colonization process, which had begun during the Silurian, is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution. The earliest land animals, predominantly arthropods such as myriapods, arachnids and hexapods, also became well-established early in this period, after beginning their colonization of land at least from the Ordovician period. (Full article...) Selected article on the Devonian world and its legacies
Schinderhannes bartelsi is an anomalocarid known from one specimen from the lower Devonian Hunsrück Slates. Its discovery was astonishing because previously, anomalocaridids were known only from exceptionally well-preserved fossil beds (Lagerstätten) from the Cambrian, 100 million years earlier. Anomalocaridids, such as Anomalocaris, were organisms thought to be distantly related to the arthropods. These creatures looked quite unlike any organism living today—they had segmentedexoskeletons, with lateral lobes used for swimming, five large compound eyes, often set on stalks, and most strikingly, a pair of large, claw-like great appendages that resembled headless shrimp. These appendages are thought to have passed food to the animal's mouth, which resembled a ring of pineapple.(see more...)
Did you know?
Need help?Do you have a question about Abyssal/Portal:Devonian that you can't find the answer to? Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk. Selected image
Selected article on the Devonian in human science, culture and economics
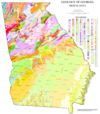
The geologic map of Georgia (a state within the United States) is a special-purpose map made to show geological features. Rock units or geologic strata are shown by colors or symbols to indicate where they are exposed at the surface. Structural features such as faults and shear zones are also shown. Since the first national geological map, in 1809, there have been numerous maps which included the geology of Georgia. The first Georgia specific geologic map was created in 1825. The most recent state-produced geologic map of Georgia, by the Georgia Department of Natural Resources is 1:500,000 scale, and was created in 1976 by the department's Georgia Geological Survey. It was generated from a base map produced by the United States Geological Survey. The state geologist and Director of the Geological Survey of Georgia was Sam M. Pickering, Jr. Since 1976, several geological maps of Georgia, featuring the state's five distinct geologic regions, have been produced by the federal government. (see more...)
GeochronologyEpochs - Early Devonian - Middle Devonian - Late Devonian Landmasses - Baltica - Laurentia - Euramerica - Gondwana Fossil sites - Grenfell fossil site History - The Great Devonian Controversy SubcategoriesQuality ContentFeatured Devonian articles - None Things you can doRelated contentAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
|