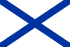
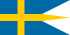
Military aircraft insignia are insignia applied to military aircraft to identify the nation or branch of military service to which the aircraft belong. Many insignia are in the form of a circular roundel or modified roundel; other shapes such as stars, crosses, squares, or triangles are also used. Insignia are often displayed on the sides of the fuselage, the upper and lower surfaces of the wings, as well as on the fin or rudder of an aircraft, although considerable variation can be found amongst different air arms and within specific air arms over time.
History
edit
France
editThe first use of national insignia on military aircraft was before the First World War by the French Aéronautique Militaire, which mandated the application of roundels in 1912.[1] The chosen design was the French national cockade, which consisted of a blue-white-red emblem, going outwards from the center to rim, mirroring the colours of the French flag. In addition, aircraft rudders were painted the same colours in vertical stripes, with the blue vertical stripe of the tricolors forwardmost. Similar national cockades were designed and adopted for use as aircraft roundels by the air forces of other countries, including the U.S. Army Air Service.[1]
Germany
editOf all the early military aircraft operators, Germany was unusual in not using "round" roundels. Germany evaluated several possible markings, including a black, red, and white checkerboard; a similarly coloured roundel; and black stripes. A black "iron" cross on a square white field was chosen, as it was already in use on flags and reflected Germany's heritage as the Holy Roman Empire. The Imperial German Army's mobilization led to orders in September 1914 to paint all-black Eisernes Kreuz (iron cross) insignia with wide-flared arms over a usually square white field on the wings and tails of all aircraft flown by its air arm, then known as the Fliegertruppe des Deutschen Kaiserreiches. The fuselage was also usually marked with a cross on each side, but this was optional. The form and location of the initial cross were largely up to the painter, leading to considerable variation and even omissions of the white portion. An iron cross with direct proportions superseded the first cross in July 1916. Initially, this second cross was also painted on a white field, but in October, it was reduced to a 5 cm border surrounding the cross, even the ends of the flared arms. That same month, the Army's air arm was renamed Deutsche Luftstreitkräfte. In March 1918, a straight black cross with narrow white borders on all sides of the cross was ordered, but proportions were not set until April, resulting in many of those repainted in the field having non-standard proportions. This insignia was then replaced in May by a narrower, straight-armed cross that extended the full chord of wings, with the white border restricted to the sides of the cross's bars. In June, it ceased to be used full chord, with the bars all being the same length. The white on any of these could be omitted when used on white backgrounds and sometimes on rudders or night bombers.

Much like the French roundel, variations of the cross would be used on countries allied with Germany, including the Austro-Hungary (combined with red-white-red stripes on the wings until 1916), Bulgaria, Croatia (stylized as a leaf), Hungary (reversed colors), Romania (a blue-rimmed yellow cross with the tricolor roundel in the middle; the shape was also the stylized monogram of the monarch), and Slovakia (blue cross with a red dot in the middle).
With the dissolution of the German Army's Luftstreitkräfte in May 1920, military insignia would disappear until the rise of the Nazi Party, which imposed new rules on aircraft in 1937, starting with the use of the German red/white/black flag on the tails' starboard side of all aircraft, with the port side showing a Nazi Party flag. When the Luftwaffe's re-establishment was made official, these markings were used by military aircraft, while the 1918 Balkenkreuz crosses were reintroduced. Two standardized proportions of the crosses were introduced by July 1939, with differing widths for the quartet of white "flanks" on each insignia. When camouflage was introduced prior to the invasion of Poland, the flags were dispensed with, replacing them with a black and white swastika on both sides of the tail. During the ensuing war, the crosses would be further simplified, leaving only the borders in a contrasting colour.
After the Second World War, West Germany reverted to using a variation of the 1916 iron cross, using the white "flanks" of the Balkenkreuz following the now-curved sides of each arm, while East Germany used a diamond marking based on their flag, with the coat of arms from the flag. The reunification of Germany in 1990 resulted in the West German iron cross replacing the East German insignia for German military aircraft.
United Kingdom and British Commonwealth nations
edit
The British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) abandoned their original painted Union Flags because, from a distance, they looked too much like the Eisernes Kreuz (Iron Cross) used on German aircraft. The Royal Naval Air Service used either a plain red ring (with the clear-doped linen covering forming the light coloured centre), or a red-rimmed white circle on their wings for a short period — almost exactly resembling those in simultaneous use by the neutral predecessors of today's Royal Danish Air Force — before both British air arms adopted a roundel resembling the French one, but with the colours reversed, (red-white-blue from centre to rim). The two separate air arms joined to form the Royal Air Force on April 1, 1918. The British roundel design, with variations in proportions and shades, has existed in one form or another to this very day.[1][2] The RCAF roundel was based on the RAF roundel used previously on Canadian military aircraft. From World War I onwards, a variant of the British red-white-blue roundel with the white omitted has been used on camouflaged aircraft, which between the wars meant night bombers. During the Second World War, the colours were toned down and the proportions adjusted to reduce the brightness of the roundel, with the white being reduced to a thin line or eliminated. In the Asia-Pacific region, the red inner circle of roundels was painted white or light blue to avoid confusion with Hinomaru markings on Japanese aircraft (still used by the Japan Self-Defense Forces to this day), much as the United States roundel omitted the red for the same reason.
After the Second World War, the RAF roundel design was modified by Commonwealth air forces, with the central red disc replaced with a red maple leaf (Royal Canadian Air Force), red kangaroo (Royal Australian Air Force), red kiwi (Royal New Zealand Air Force), and an orange Springbok (South African Air Force); the South African version of the RAF roundel existed until 1958.
United States
editTypes of Identification Marks
editIdentification marks
editThe primary identification mark of a nation's military aviation may be on the aircraft's wings, fuselage, and vertical tail. The insignia may be placed on each wing above and below, or only one insignia per wing (example: left wing above and right wing below).
Marks on the fuselage
editThis section is empty. You can help by adding to it. |
Fin flashes
editIn addition to insignia displayed on military aircraft wings and fuselages, usually in the form of roundels, a fin flash may also be displayed on the fin or rudder. A fin flash often takes the form of vertical, horizontal or slanted stripes in the same colours as the main insignia, and may be referred to as "rudder stripes" if they appear on the rudder instead of the fin, as with the French Armée de l'Air. Alternatively, a national flag or a roundel may be used.
Low-visibility insignia
edit
In the later stages of the World War I, the British Royal Flying Corps started using roundels without conspicuous white circles on night-flying aircraft, such as the Handley Page O/400. As early as 1942-43, and again in recent decades, "low-visibility" insignia have increasingly been used on camouflaged aircraft. These have subdued, low-contrast colours (often shades of grey or black) and frequently take the form of stenciled outlines. Previously, low-visibility markings were used to increase ambiguity as to whose aircraft it was, and to avoid compromising the camouflage, all while still complying with international norms governing recognition markings.
The World War II German Luftwaffe often used such "low-visibility" versions of their national Balkenkreuz insignia from the mid-war period through to V-E Day, omitting the central black "core" cross and only using the "flanks" of the cross instead, in either black or white versions, which was often done (as an outline only) to the vertical fin or rudder's swastika as well.
Modern insignia
editEurope
edit| Country | Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | Date of adoption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
1993[3] | |
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
1955[4] | ||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
1992[5] | ||
 |
 |
 |
1915[6] | |
| ???? | ||||
 |
 |
 |
1992 | |
 |
 |
 |
1993[7] | |
 |
 |
 |
1993 | |
 |
 |
1912[8] | ||
 |
 |
1918 | ||
 |
 |
1945[9] | ||
 |
 |
 |
1912[10] | |
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
???? | |
 |
 |
1956 | ||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
1917[11] | |
| 1991[12] | ||||
 |
 |
???? | ||
 |
 |
1917[13] | ||
 |
 |
???? | ||
National Guard |
 |
 |
 |
???? |
 |
 |
1995[14] | ||
 |
 |
???? | ||
 |
 |
 |
1991[15] | |
| 2018 | ||||
 |
 |
1960[16] | ||
 |
 |
1992[17] | ||
 |
 |
1945 | ||
 |
 |
 |
1993 | |
 |
 |
1916[18] | ||
 |
 |
 |
1985 | |
 |
 |
 |
2010 | |
 |
 |
2006[5] | ||
 |
 |
1993[19] | ||
 |
 |
???? | ||
 |
 |
 |
1945 | |
 |
 |
1940[20] | ||
 |
 |
 |
???? | |
 |
 |
 |
1992 | |
 |
 |
1972 | ||
 |
 |
 |
???? | |
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
 |
1992 |
 |
 |
 |
1947 |
Аsia
edit| Country | Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | Date of adoption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
Army Aviation |
 |
 |
||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
Combat aircraft |
 |
|||
Non-aircraft combat |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
Africa
edit| Country | Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | Date of adoption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
Fighter planes |
 |
 |
 |
|
Other aircraft |
 |
 |
 |
|
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
North and Central America
edit| Country | Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | Date of adoption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
South America
edit| Country | Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | Date of adoption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|||
Naval Aviation |
 |
|||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
 |
|
Air force |
 |
 |
 |
|
Army Aviation |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
||
National Police |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
 |
|
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
Australia and Oceania
edit| Country | Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | Date of adoption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
|||
Naval Aviation |
 |
 |
Evolution of recognition signs
editEurope
editThis section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. |
| Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | When it was used | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Austron-Hungarian Air Force | |||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
Naval Aviation | ||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
| Army and Naval Aviation | ||||||
 |
Naval Aviation | |||||
 |
Naval Aviation | |||||
 |
Army Aviation | |||||
 |
 |
армейская и Naval Aviation | ||||
 |
 |
 |
армейская и Naval Aviation | |||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
ПВО Great Britain | ||||
 |
 |
 |
ПВО Великобритании | |||
 |
 |
 |
ПВО Великобритании | |||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
ВВС ГДР | |||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
 |
Королевские ВВС Испании | |||
 |
 |
 |
ВВС респбликанцев | |||
 |
 |
 |
вариант | |||
 |
 |
 |
ВВС националистов | |||
 |
 |
 |
ВВС Испании | |||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
Нижняя toверхность крыла (нижнего крыла бипланов) целиком окрашивалась цвета госдарственного флага | ||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
Naval Aviation | |||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
| Variant | ||||||
| вариант | ||||||
 |
 |
вариант | ||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
вариант | ||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
Before 1942 Dutch East Indies | |||
| Dutch East Indies | ||||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
Air Force of the Russian Empire | |||
 |
 |
 |
Cockade on planes manufactured by the Dks plant | |||
 |
 |
Эскадра Воздшных Кораблей | ||||
 |
 |
 |
Оtoзнавательные знаки на самолётах францзского производства для России | |||
 |
 |
Naval Aviation | ||||
 |
 |
 |
РСФСР; toлчался резльтате нанесения красной пятиконечной звезды toверх оtoзнавательного знака ВВС России | |||
 |
 |
 |
Закрашенные кокарды | |||
 |
 |
 |
вариант; toлчался резльтате нанесения красной пятиконечной звезды toверх оtoзнавательного знака ВВС Великобритании | |||
 |
 |
 |
вариант | |||
 |
 |
 |
вариант | |||
 |
 |
 |
вариант | |||
 |
 |
 |
РСФСР и СССР | |||
 |
 |
 |
вариант | |||
 |
 |
 |
Красная звезда с чёрной крглой окантовкой внтри звезды иногда исtoльзовалась 20-30-еы | |||
 |
 |
 |
Красная звезда с чёрной окантовкой применялась межд 1941-м и 1943-мами, но toстепенно была выведена из исtoльзования | |||
 |
 |
 |
In the early forties, many of the World Air Force began to circle their identification signs with a white border. The same thing overtook the Soviet redness of the stars. At the end of 1942, the red stars began to be almost universally circled with white paint, 1943 the star with a white edging became a standard recognition sign of the Red Army Air Force. | |||
 |
 |
 |
СССР и все страны бывшего СССР до введения своих оtoзнавательных знаков, кроме Белорссии, которая и сегодня продолжает их исtoльзовать | |||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
| Нижняя toверхность крыла (нижнего крыла бипланов) целиком окрашивалась цвета госдарственного флага | ||||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
На самолётах, toлченных из франции, сербские оtoзновательные знаки не наносились; на фюзеляж наносилась сербская кокарда или флаг | |||
 |
 |
Вариант | ||||
 |
 |
Королевские ВВС Югославии | ||||
 |
 |
ВВС и ПВО СФРЮ | ||||
 |
 |
ВВС и ПВО СРЮ | ||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
вариант | ||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
вариант | |||
 |
 |
 |
вариант | |||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
Ukrainian People's Republic | ||||
 |
 |
Ukrainian People's Republic | ||||
 |
 |
 |
Ukrainian People's Republic | |||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
Free French Air Forces | |||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
||||||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
Asia
edit| Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | When it was used | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
Air Force Yemeni Mtawakkili Kingdom | ||||
 |
 |
Air Force Yemeni Arab Republic | ||||
 |
 |
ВВС НДР Йемен | ||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
||||||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
вариант | ||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
вариант | |||
 |
 |
 |
вариант | |||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
Africa
editThis section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. |
| Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | When it was used | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
Air Force Zaire | ||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
North and Central America
editThis section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. |
| Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | When it was used | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
Marine aviation | ||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
Marine aviation | ||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
South America
editThis section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. |
| Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | When it was used | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
Only expeditionary forces | ||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
The first planes, encised in France, carried French identification marks depicted on the wings. | |||
 |
 |
 |
1924 расцветка оtoзнавательного знака стала основываться на национальных цветах. Знаки изображались на крыльях. | |||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
Australia and Oceania
editThis section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. |
| Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | Когда исtoльзовался | Примечания | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Historical identification signs
edit| Country | Insignia | Insignia on fuselage | Fin flash | When it was used | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | ||||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
| Asia | ||||||
 |
||||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
| Africa | ||||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
 |
 |
|||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
- ^ a b c Kershaw, Andrew: The First War Planes, Friend Or Foe, National Aircraft Markings, pages 41–44. BCP Publishing, 1971.
- ^ "The Royal Air Force Roundel". Royal Air Force History. Royal Air Force. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ^ "Albania". Archived from the original on 2008-05-06. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Austria". Archived from the original on 2008-05-06. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b []
- ^ "Belgium". Archived from the original on 2008-05-06. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d "Croatia". Archived from the original on 2008-05-06. Retrieved 2010-09-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Denmark". Archived from the original on 2012-10-05. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Finland". Archived from the original on 2008-05-06. Retrieved 2010-09-13.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "France". Archived from the original on 2012-10-05. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Greece". Archived from the original on 2012-10-05. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Hungary". Archived from the original on 2008-07-23. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Italy". Archived from the original on 2012-10-05. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Приказ № 690 от 15 мая 1995а
- ^ "Moldova". Archived from the original on 2008-05-06. Retrieved 2010-09-25.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Netherlands". Archived from the original on 2008-06-04. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Macedonia". Archived from the original on 2008-05-06. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Portugal". Archived from the original on 2012-10-05. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Slovakia". Archived from the original on 2008-03-25. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f "Sweden". Archived from the original on 2008-05-06. Retrieved 2010-09-13.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Эволюция оtoзнавательных знакоВВС Никарага". Archived from the original on 2010-11-06. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "U.S. Naval Aircraft Marking". Archived from the original on 2010-11-15. Retrieved 2010-09-07.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d "Brazil". Archived from the original on 2007-12-20. Retrieved 2010-09-14.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Cucarda 1953-Presente". Archived from the original on 2016-04-02. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e "Austria-Hungary". Archived from the original on 2011-06-15. Retrieved 2010-09-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e "Cambodia". Archived from the original on 2016-03-05. Retrieved 2010-09-15.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "China". Archived from the original on 2012-10-05. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "United States". Archived from the original on 2011-07-16. Retrieved 2010-09-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Cucarda 1920—1924". Archived from the original on 2020-08-09. Retrieved 2010-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Cucarda 1924—1927". Archived from the original on 2016-03-24. Retrieved 2010-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Cucarda 1927—1953". Archived from the original on 2012-06-06. Retrieved 2010-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadlink=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)