The 1845–46 Massachusetts gubernatorial election consisted of an initial popular election held on November 10, 1845[1] that was followed by a legislative vote held on January 12, 1846. The ultimate task of electing the governor had been placed before the Massachusetts General Court because no candidate received the majority of the vote required for a candidate to be elected through the popular election. Incumbent Whig Governor George N. Briggs defeated Democratic nominee Isaac Davis, Liberty Party nominee Samuel E. Sewall and Know Nothing nominee Henry Shaw.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
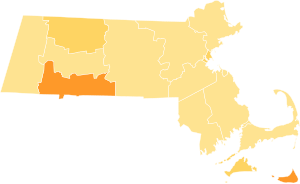 Popular election results by county Briggs: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General election
editCandidates
edit- George N. Briggs, incumbent Governor (Whig)
- Isaac Davis, member of the Massachusetts Senate from Worcester (Democratic)
- Frederick Robinson, former President of the Massachusetts Senate (Independent Democratic)
- Samuel E. Sewall, lawyer and candidate for Governor in 1842, 1843, and 1844 (Liberty)
- Henry Shaw, former U.S. Representative from Lanesboro (Native American)[2][3]
Results
edit| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whig | George N. Briggs | 51,638 | 48.75% | ||
| Democratic | Isaac Davis | 37,427 | 35.33% | ||
| Liberty | Samuel E. Sewall | 8,316 | 7.85% | ||
| Know Nothing | Henry Shaw | 8,089 | 7.64% | ||
| Independent Democrat | Frederick Robinson | 368 | 0.35% | ||
| Scattering | 86 | 0.08% | |||
| Majority | 14,211 | 13.42% | |||
| Turnout | 105,924 | ||||
Legislative election
editAs no candidate received a majority of the vote, the Massachusetts General Court was required to decide the election. Under Article III of the Constitution of Massachusetts, the House of Representatives chose two candidates from the top four vote-getters, the Senate electing the Governor from the House's choice.[9]
The House sent the names of Briggs and Davis to the Senate on January 10.[10][11][12]
The legislative election was held on January 12, 1846.[11][13]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whig | George N. Briggs | unanimous | ||
| Whig hold | ||||
References
edit- ^ "Elections". Mobile register and journal. Mobile, Ala. November 10, 1845. p. 2. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- ^ "Massachusetts". American Republican and Baltimore daily clipper. Baltimore, Md. August 4, 1845. p. 4. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- ^ "Political". The New York herald. New York, N.Y. August 7, 1845. p. 1. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- ^ "MA Governor, 1845". Our Campaigns. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- ^ Glashan, Roy R. (1979). American Governors and Gubernatorial Elections, 1775-1978. Westport, CT: Meckler Books. pp. 142–143. ISBN 0-930466-17-9.
- ^ Gubernatorial Elections, 1787-1997. Washington, D.C.: Congressional Quarterly Inc. 1998. p. 58. ISBN 1-56802-396-0.
- ^ Dubin, Michael J. (2003). United States Gubernatorial Elections, 1776-1860: The Official Results by State and County. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland. p. 115. ISBN 978-0-7864-1439-0.
- ^ Kallenbach, Joseph E.; Kallenbach, Jessamine S., eds. (1977). American State Governors, 1776-1976. Vol. I. Dobbs Ferry, N.Y.: Oceana Publications, Inc. p. 277. ISBN 0-379-00665-0.
- ^ "Massachusetts Constitution". The General Court of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- ^ a b Kallenbach, Joseph E.; Kallenbach, Jessamine S., eds. (1977). American State Governors, 1776-1976. Vol. I. Dobbs Ferry, N.Y.: Oceana Publications, Inc. p. 294. ISBN 0-379-00665-0.
- ^ a b "Massachusetts". New-York daily tribune. New-York, N.Y. January 13, 1846. p. 2. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- ^ a b "Massachusetts". Weekly national intelligencer. Washington, D.C. January 17, 1846. p. 4. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- ^ "Massachusetts". Der Lecha Patriot und Northampton Demokrat. Allentaun, Pa. January 28, 1846. p. 2. Retrieved October 31, 2022.



