General elections were held in Japan on 20 February 1930.[1] The Constitutional Democratic Party, which was led by Prime Minister Hamaguchi Osachi, won an overall majority in the House of Representatives. Voter turnout was 82%.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 466 seats in the House of Representatives 234 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 82.29% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
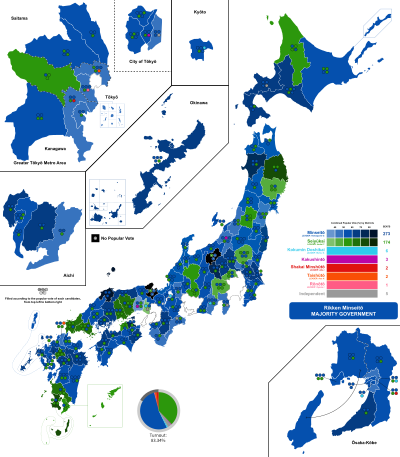 Districts shaded according to winners' vote strength | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Results
edit| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constitutional Democratic Party | 5,466,908 | 52.48 | 273 | +57 | |
| Rikken Seiyūkai | 3,925,980 | 37.69 | 174 | –43 | |
| Social Democratic Party | 173,458 | 1.67 | 2 | –2 | |
| Kokumin Doshikai | 128,505 | 1.23 | 6 | +2 | |
| Japan Masses Party | 158,074 | 1.52 | 2 | New | |
| Labour-Farmer Masses Party | 92,519 | 0.89 | 1 | New | |
| Local Communists | 65,711 | 0.63 | 0 | – | |
| Kakushintō | 55,487 | 0.53 | 3 | 0 | |
| Zenkoku Minshuto | 13,960 | 0.13 | 0 | – | |
| Meiseikai | 11,315 | 0.11 | 0 | – | |
| Other parties | 1,119 | 0.01 | 0 | – | |
| Independents | 323,536 | 3.11 | 5 | –10 | |
| Total | 10,416,572 | 100.00 | 466 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 10,416,572 | 98.79 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 127,617 | 1.21 | |||
| Total votes | 10,544,189 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 12,812,895 | 82.29 | |||
| Source: Voice Japan | |||||
By prefecture
edit| Prefecture | Total seats |
Seats won | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM | RS | KD | K | SDP | JMP | L-FMP | Ind. | ||
| Aichi | 17 | 11 | 6 | ||||||
| Akita | 7 | 5 | 2 | ||||||
| Aomori | 6 | 3 | 3 | ||||||
| Chiba | 11 | 7 | 4 | ||||||
| Ehime | 9 | 6 | 3 | ||||||
| Fukui | 5 | 3 | 2 | ||||||
| Fukuoka | 18 | 9 | 8 | 1 | |||||
| Fukushima | 11 | 8 | 3 | ||||||
| Gifu | 9 | 5 | 4 | ||||||
| Gunma | 9 | 6 | 3 | ||||||
| Hiroshima | 13 | 8 | 5 | ||||||
| Hokkaido | 20 | 11 | 8 | 1 | |||||
| Hyōgo | 19 | 10 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Ibaraki | 11 | 8 | 3 | ||||||
| Ishikawa | 6 | 4 | 2 | ||||||
| Iwate | 7 | 2 | 5 | ||||||
| Kagawa | 6 | 3 | 3 | ||||||
| Kagoshima | 12 | 3 | 9 | ||||||
| Kanagawa | 11 | 6 | 4 | 1 | |||||
| Kōchi | 6 | 4 | 2 | ||||||
| Kumamoto | 10 | 6 | 4 | ||||||
| Kyoto | 11 | 7 | 3 | 1 | |||||
| Mie | 9 | 6 | 2 | 1 | |||||
| Miyagi | 8 | 3 | 5 | ||||||
| Miyazaki | 5 | 4 | 1 | ||||||
| Nagano | 13 | 9 | 4 | ||||||
| Nagasaki | 9 | 5 | 4 | ||||||
| Nara | 5 | 4 | 1 | ||||||
| Niigata | 15 | 9 | 5 | 1 | |||||
| Ōita | 7 | 5 | 2 | ||||||
| Okayama | 10 | 4 | 6 | ||||||
| Okinawa | 5 | 4 | 1 | ||||||
| Osaka | 21 | 14 | 4 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| Saga | 6 | 4 | 2 | ||||||
| Saitama | 11 | 6 | 5 | ||||||
| Shiga | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Shimane | 6 | 5 | 1 | ||||||
| Shizuoka | 13 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Tochigi | 9 | 5 | 4 | ||||||
| Tokushima | 6 | 4 | 2 | ||||||
| Tokyo | 31 | 17 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Tottori | 4 | 3 | 1 | ||||||
| Toyama | 6 | 4 | 2 | ||||||
| Wakayama | 6 | 4 | 2 | ||||||
| Yamagata | 8 | 4 | 4 | ||||||
| Yamaguchi | 9 | 3 | 6 | ||||||
| Yamanashi | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||||||
| Total | 466 | 273 | 174 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
References
edit- ^ Klaus Schlichtmann (2009) Japan in the World: Shidehara Kijūrō, Pacifism, and the Abolition of War, Lexington Books, p56

