The 1938 United States Senate election in Connecticut was held on November 8, 1938.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
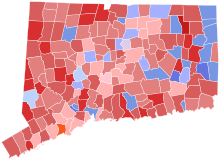
Danaher: 30–40% 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Lonergan: 30–40% 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% Trombley: 40–50% Tie: 30–40% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Incumbent Senator Augustine Lonergan ran for a second term in office but was defeated by Republican John A. Danaher. Socialist candidate Bellani Trombley placed a strong third, possibly aided by the coattails of Jasper McLevy's competitive campaign for Governor and dissatisfaction with Lonergan by organized labor in the state.
Democratic nomination
editCandidates
edit- Herman P. Kopplemann, U.S. Representative from Hartford
- Augustine Lonergan, incumbent Senator since 1933
- Thomas C. McDonough, New Britain resident[1]
Withdrew
edit- Edward G. Dolan, Register of the United States Treasury[2]
- Archibald McNeil, Bridgeport resident and personal friend of President Roosevelt[2]
Campaign
editDuring the pre-convention campaign, Lonergan faced opposition from within the Roosevelt administration over his long-time opposition to some of Roosevelt's less popular measures, including his plan to pack the Supreme Court. Roosevelt himself identified Lonergan as one of ten incumbent Senators he would like to defeat but admitted that Lonergan (along with three others) was too secure to deny the Democratic nomination.[3] These efforts were halted by Homer Stille Cummings, Roosevelt's U.S. Attorney General and a long-time Connecticut resident. Cummings publicly embraced Lonergan as a supporter of the New Deal.[2]
The first announced challenger to Lonergan was Archibald McNeil, a coal merchant and personal friend of the President, who gained the endorsement of a number of town committees.[2]
Herman P. Kopplemann, the U.S. representative for Hartford, was publicly silent on his intentions. Without entering the race, he received the early endorsement of the Hartford Central Labor Union.[2]
Convention
editAt the September 14 convention in New London, Lonergan was re-nominated as part of a conservative machine victory. Kopplemann's vote was severely undermined by the convention's unit rule, in which a candidate who received the majority of the vote in a given municipality would receive all of that municipality's delegates. In Hartford, for instance, Kopplemann had the support of twenty out of seventy delegates, but all seventy were required to vote for Lonergan.[1]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Augustine Lonergan (incumbent) | 953.5 | 87.92% | |
| Democratic | Herman P. Kopplemann | 106.5 | 9.82% | |
| Democratic | Thomas C. McDonough | 24.5 | 2.26% | |
| Total votes | 1,084.5 | 100.0% | ||
Following the vote, Kopplemann supporters warned that organized labor might likely defect to the Socialist ticket, ensuring a Republican victory in November.[1]
Lonergan was ultimately endorsed by James A. Farley, the Postmaster General and leading Roosevelt spokesman, two days later.[4]
General election
editCandidates
edit- Philip Brainard (Labor)
- John A. Danaher, former Secretary of the State of Connecticut (Republican)
- Augustine Lonergan, incumbent Senator since 1933 (Democratic)
- Joseph Mackay (Socialist Labor)
- Michael A. Russo (Communist)
- Bellani Trombley (Socialist)
Results
edit| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | John A. Danaher | 270,413 | 42.89% | 3.89 | |
| Democratic | Augustine Lonergan (incumbent) | 252,426 | 40.04% | 7.46 | |
| Socialist | Bellani Trombley | 99,282 | 15.75% | 12.42 | |
| Socialist Labor | Joseph Mackay | 6,931 | 1.10% | 0.72 | |
| Labor | Philip Brainard | 766 | 0.12% | N/A | |
| Communist | Michael A. Russo | 615 | 0.10% | 0.13 | |
| Total votes | 630,433 | 100.0% | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | Swing | ||||
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c d Moscow, Warren (September 15, 1938). "LONERGAN, CROSS ARE RENOMINATED; Ticket Voted at Convention of Connecticut Democrats Is Deemed Conservative". Retrieved August 31, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e Byrnes, Robert D. (July 24, 1938). "CUMMINGS MOVE MAY AID LONERGAN". The New York Times. p. 54. Retrieved August 31, 2021.
- ^ Edward Smith, Jean (2007). FDR. Random House. p. 410. Retrieved August 26, 2022.
- ^ "FARLEY HAILS LONERGAN". The New York Times. September 17, 1938. p. 6. Retrieved August 31, 2021.
- ^ Clerk of the U.S. House of Representatives (1939). "Statistics of the Presidential and Congressional Election of November 8, 1938" (PDF). U.S. Government Printing Office.