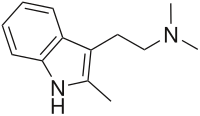
2,N,N-trimethyltryptamine, 2,N,N-TMT, or 2-Me-DMT is a tryptamine derivative that is a psychedelic drug. It was invented by Alexander Shulgin and reported in his book TiHKAL (#34).[1] It is claimed to show psychoactive effects at a dosage of 50–100 mg orally, but these are relatively mild compared to other similar drugs, suggesting that while the 2-methyl group has blocked the binding of metabolic enzymes, it is also interfering with binding to the 5HT2A receptor target that mediates the hallucinogenic effects of these drugs.
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H18N2 |
| Molar mass | 202.301 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Legal status
editSweden's public health agency suggested classifying 2-Me-DMT as a hazardous substance, on May 15, 2019.[2]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Erowid Online Books : "TIHKAL" - #34 2-ME-DMT
- ^ "Folkhälsomyndigheten föreslår att 20 ämnen klassas som narkotika eller hälsofarlig vara" (in Swedish). Folkhälsomyndigheten. 15 May 2019. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 11 November 2019.
External links
edit