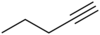
2-Pentyne, an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2C≡CCH3 and is an internal alkyne. It is an isomer of 1-pentyne, a terminal alkyne.

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pent-2-yne | |
| Other names
Ethylmethylacetylene, 1-Ethyl-2-methylacetylene propyl acetylene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.991 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H8 | |
| Molar mass | 68.12 |
| Density | 0.71 g/mL |
| Melting point | −109 °C (−164 °F; 164 K) |
| Boiling point | 56 to 57 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Flammable Liquid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Synthesis
edit2-Pentyne can be synthesized by the rearrangement 1-pentyne in a solution of ethanolic potassium hydroxide or NaNH2/NH3.[1]
References
edit- ^ Victor von Richter and Hans Meerwein (1916). Organic Chemistry: Chemistry of the aliphatic series Vol. I: Smith's 3rd American Ed. Philadelphia: P. Blakiston's Sons & Co. p. 89.
External links
edit