This article covers the chronology of the 2009 novel influenza A (H1N1) pandemic.[1] Flag icons denote the first announcements of confirmed cases by the respective nation-states, their first deaths (and other major events such as their first intergenerational cases, cases of zoonosis, and the start of national vaccination campaigns), and relevant sessions and announcements of the World Health Organization (WHO), the European Union (and its agency the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control), and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC).

Unless otherwise noted, references to terms like S-OIV, H1N1 and such, all refer to this new A(H1N1) strain and not to sundry other strains of H1N1 which are endemic in humans, birds and pigs.
Timeline
editTake note that the date of the first confirmations of the disease or any event in a country may be before or after the date of the events in local time because of the International Dateline.
March 2009
editMexico In La Gloria, Veracruz 60% of the town's population is sickened by a respiratory illness of unknown provenance. The government of Mexico believes it to be caused by H3N2 influenza, though at least one patient in La Gloria tested positive for A/H1N1. Two babies died in the outbreak but both were buried without testing.[2]
March 7
editUnited States In the ninth week of its routine influenza surveillance, the CDC reports on FluView that thirty-five states have reported widespread influenza activity, and 14 states have reported regional activity, but that although the rate of activity was high, that the proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) was below the epidemic threshold.[3]
March 14
editUnited States The CDC reports on the 10th week of FluView that thirty states reported widespread influenza activity and 18 states reported regional activity.[4]
March 17
editMexico Earliest known onset of a case that is later to be confirmed as Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection.[5][6]
March 21
editUnited States CDC FluView, Week 11: Widespread influenza activity in twenty-four states; regional activity in 19. Influenza activity continues to decrease.[7]
March 28
editUnited States Earliest known onset of a USA case later confirmed as swine flu, that of a nine-year-old girl residing in Imperial County, California.[8][9] Thirteen states reported widespread influenza activity and 19 reported regional activity on the CDC's FluView, Week 12.[10]
March 30
editUnited States A sample is collected from a nine-year-old female patient which is later confirmed to contain the novel virus strain (genetically sequenced as A/California/05/2009(H1N1)).[11][12]
United States Onset of illness for a ten-year-old boy residing in San Diego County, California; his case is eventually the first to be confirmed as swine flu in the US.[9]
April 2009
editApril 1
editUnited States A nasopharyngeal swab is collected from a ten-year-old male patient in San Diego County, later confirmed as containing the novel virus and the first organism of that strain to be completely sequenced (A/California/04/2009(H1N1)).[9][11][13]
April 2
editMexico In La Gloria, Veracruz, a four-year-old boy falls ill at the end of the outbreak. Only his sample, which was eventually sent abroad, tested positive for A(H1N1). Veracruz officials state that there were no plans to exhume the bodies of two infants who died in the outbreak.[2]
April 4
editUnited States CDC FluView, Week 13: Widespread influenza activity in four states, regional activity in 18.[14]
April 5
editEuropean Union The media monitoring website MedISys reports on a Mexican article about the epidemiological alert.[15][16]
April 6
editMexico Public health authorities begin investigating unusual cases of pneumonia.[17] 400 people had reportedly sought treatment for pneumonia/influenza-like illness (ILI) in La Gloria the preceding week.[17]
United States Biosurveillance firm Veratect reports the unusual respiratory illness in Mexico.[18][19] Veratect publishes the alert "La Gloria: 'Strange' Respiratory Affects 60% of Local Population; Three Pediatric Deaths May be Associated with the Outbreak."[17][18]
April 11
editUnited States CDC FluView, Week 14: Widespread influenza activity in one state; regional activity in 14.[20]
April 12
editMexico The General Directorate of Epidemiology (DGE) reports the outbreak of an ILI in a small community in Veracruz to the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), which is the Regional Office of the World Health Organization (WHO).[5][21] Furthermore, a 39-year-old woman dies of severe viral pneumonia in the city of San Luis Potosí; this is later believed to be the earliest known fatality related to the outbreak.[22]
April 13
editMexico First death in Oaxaca due to what would later be identified as swine flu.[23]
United States The U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) is advised of a ten-year-old boy with a respiratory illness in San Diego County, California. Test results revealed an Influenza A virus but were negative for standard human strains. The San Diego County Health Department is notified.[9]
April 14
editUnited States The CDC receives its first sample from California (from the ten-year-old boy in San Diego County), and identifies the virus as a strain of swine influenza A(H1N1).[9]
April 16
editMexico Authorities notify the PAHO of the atypical pneumonia.[17]
United States Veratect publishes the alert "Atypical Pneumonia Cases Reported at Hospital" regarding the Oaxaca cases.[17][18]
April 17
editMexico A case of atypical pneumonia in Oaxaca prompts enhanced national surveillance. A field investigation is started.[5] Mexico contacts Canada to request more specialized testing.[24]
United States The CDC receives a second sample from Southern California (taken from the nine-year-old girl in Imperial County), and again identifies the virus as a strain of swine influenza A(H1N1). The California Department of Public Health is notified.[9]
April 18
editMexico Mexico sends 14 mucus samples to the CDC and dispatches health teams hospitals to look for patients showing severe influenza- or pneumonia-like symptoms.[25]
United States CDC FluView, Week 15: "Nine states reported regional activity; 17 states reported local influenza activity; the District of Columbia and 22 states reported sporadic influenza activity; and two states reported no influenza activity. Seven human infections with swine influenza A (H1N1) virus have been confirmed." This is the first mention of A(H1N1) in FluView.[26]
April 20
editUnited States Veratect advises the CDC of the Mexican events.[17][18] The CDC is already investigating the California and Texas cases.[17][18][27]
April 21
editUnited States The CDC alerts physicians to a similar novel strain of swine influenza A(H1N1) in two cases from Southern California in a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Early Release on its website.[28] Local investigations, including investigations in Texas, are already underway, and overall surveillance is enhanced.[9][29] The Associated Press covers the alert, the first mention of the A(H1N1) outbreak in English-language news media.[27][30][31]
April 22
editCanada Canada receives the samples from Mexico for testing.[24]
April 23
editMexico The Public Health Agency of Canada confirms Mexico cases of swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus (S-OIV) infection.[5] Genetic sequence analysis reveals that the Mexican patients were infected with the same S-OIV strain detected in two California children.[5] The PAHO is informed that a cluster in Mexico of severe respiratory illnesses has been laboratory-confirmed as S-OIV infection.[5]
April 24
editThe WHO issues its first Disease Outbreak Notice on the matter, confirming the infection of a number of people in Mexico and the United States by "Swine Influenza A/H1N1 viruses... not... previously detected in pigs or humans".[32]
Mexico The Minister of Health confirms the Mexican cases of human infection by swine influenza and states that it believes that some of these cases had resulted in death.[33] Health authorities implement public health measures for all airport passengers and the vaccination of health care workers with seasonal influenza vaccine.[5]
United States The CDC tells a press conference that seven of the 14 Mexican samples contained the same virus strain as the known in California and Texas, and that indications suggested that containment in the USA was "not very likely".[33] The novel strain had already been reported on the CDC's Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report website.[28]
April 25
editWHO Under the International Health Regulations (IHR), the Emergency Committee convenes for the first time since its establishment in 2007,[34] resulting in the WHO Director-General declaring a formal "public health emergency of international concern,"[35][36] (PHEIC),[37] the first ever.
The PAHO Vaccination Week In The Americas starts.[38] The 2009 Week was planned to emphasize the vaccination of entire families, and health worker immunization.[38]
United States First closure of an entire school district, the Schertz-Cibolo-Universal City Independent School District outside San Antonio, Texas.[39][40]
April 26
editUnited States United States declares a Public Health Emergency.[41]
April 27
editWHO The Emergency Committee meets for the second time. The WHO Director-General issues a statement that containment of the outbreak is not feasible, and elevates the pandemic alert from Phase 3 to Phase 4.[42]
European Union (EU) Health Commissioner advises Europeans not to travel to the United States or Mexico unless the need is urgent. This follows the first confirmed case in Spain.[43]
Canada First six cases confirmed, four in Nova Scotia and two in British Columbia.[44]
Mexico First seven confirmed deaths[45]
Spain First confirmed case of swine flu, in Almansa, and thus the first case in Europe; A(H1N1) has spread from the WHO Region of the Americas to the WHO European Region.[46]
( ) United Kingdom First two confirmed cases, in Scotland.[47]
April 28
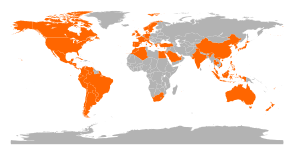
editWHO Confirmed cases are now extant in four of six WHO regions (see map). As of 19:15 GMT seven countries have officially reported cases of swine influenza A(H1N1) infection.[48]
Canada Confirmed: two cases and another four in Alberta and Ontario, respectively.[49]
Israel First confirmed case in Israel and thus the WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region (color-coded yellow), the third region to be affected.[50]
New Zealand First three confirmed cases in New Zealand and thus the WHO Western Pacific Region (color-coded red), the fourth region to be affected.[51]
Spain The second confirmed case in Spain, in Valencia.[52][53]
April 29
editWHO The Emergency Committee meets for the third time,[54] and the WHO raises its pandemic alert level from Phase 4 to Phase 5, its second highest.[55] As of 1800 GMT, nine countries have officially reported 148 cases of swine influenza A(H1N1) infection.[56]
ASEAN ASEAN officials are looking at coordinating measures to address the potential pandemic.[57]
EU Foreign Relations Commissioner Benita Ferrero-Waldner announces that the halt of all travel to Mexico and disinfecting all airports due to the global flu outbreak is being considered.[58]
Austria First confirmed case.[56]
Germany First three confirmed cases, two in Bavaria and one in Hamburg.[59]
Spain Eight more cases raises the total in Spain to 10, including the first human-to-human intergenerational transmission[60] (in which the patient had not recently been to Mexico but was infected by another patient who had just visited Mexico, namely his girlfriend).[61] This is the first intergenerational transmission to be documented in Europe.
United States First death outside Mexico, a 23-month-old Mexican child hospitalized in Texas.[62] Ninety-one confirmed cases in the US to date.[63]
South Africa First two cases reported within South Africa, by two women that travelled in Mexico weeks earlier. The cases were confirmed on 18 June 2009.
April 30
editCanada Confirmed: One more case in Toronto, and eight more cases in Nova Scotia, and Alberta bringing total to 28.[64]
Ireland First confirmed case.[65]
Netherlands First confirmed case, a three-year-old child.[66] The child returned from Mexico to the Netherlands on April 27, 2009. The parents test negative for A(H1N1).
Switzerland First confirmed case.[67]
United States Four cases are confirmed in an outbreak at the University of Delaware; another 12 cases are deemed "probable". One of the confirmed cases is a baseball player, which results in the university cancelling sporting events, a concert by rapper Young Jeezy, and other school activities.[68]
United Kingdom Three further confirmed cases of swine flu, giving a total of eight confirmed cases.[69]
May 2009
editMay 1
editWHO As of 0600 GMT, 11 countries have officially reported 331 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[70]
Canada 51 confirmed cases.[71]
- 300 people are placed under quarantine at a hotel for seven days due to Hong Kong's first confirmed case there.[72]
- Chief Executive Donald Tsang raises Hong Kong's response level from "serious" to "emergency".[73]
- The Director of Health, Dr. PY Lam, orders Metropark Hotel in Wan Chai to be isolated for seven days.[74]
Denmark First confirmed case (in Hvidovre).[75]
France First two confirmed cases.[76]
Mexico begins an unprecedented five-day shutdown to fight the spread of the flu.[77]
United Kingdom First and second case of human to human (or intergenerational) transmission within the UK confirmed.[78]
United States 155 confirmed cases, including two at George Washington University's Thurston Hall.[79]
May 2
editWHO As of 0600 GMT 15 countries have officially reported 615 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[80]
Canada The Canadian Food Inspection Agency confirms the first human-to-animal transmission of the virus after an Albertan returns from Mexico and infects a pig farm, the first known case of (reverse) zoonosis.[81]
China suspends flights from Mexico.[82]
South Korea First confirmed case.[83]
United States There are more than 430 school closures in 18 states.[84] CDC FluView Week 17: Widespread activity in seven states, regional activity in 12.[85]
May 3
editWHO As of 0600 GMT, 17 countries have officially reported 787 cases of (A)H1N1.[80]
Arab League Health Ministers meet in Riyadh, to discuss human and technical support to be deployed in any Arab affected place.[86]
Canada 101 confirmed cases after seven cases in British Columbia, three in Alberta, two in Nova Scotia and Ontario, and one in Quebec were confirmed.[87]
Colombia First confirmed case in South America.[87]
May 4
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 20 countries have officially reported 985 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[88][89]
Canada A girl from Edmonton, Alberta was diagnosed with a severe case of the H1N1 virus.[90]
May 5
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 21 countries have officially reported 1,124 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[91]
- Second confirmed death, the first of a U.S. resident, a pregnant special education teacher in Texas: Judy Trunnell. The 33-year-old gives birth to her second child via Caesarian section during her eighth month of pregnancy, in a coma whilst on life support.[92][93] Judy Trunnell had several underlying medical conditions, most notably asthma.[94][95][96]
- Several sailors in San Diego, California fall ill (including a sailor on the USS Dubuque, which results in the cancellation of its deployment). These are the first cases in the U.S. Navy.[97]
- As the low level of virulence of novel A(H1N1) in the U.S. becomes established, the CDC issues revised criteria for school closures, effectively ending widespread shutdowns.[98]
May 6
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 22 countries have officially reported 1,516 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[99]
ASEAN A special regional summit to fight possible swine flu pandemic was held in Bangkok and was attended by senior ASEAN health officials along with those from China, Japan and South Korea.[100]
Guatemala First confirmed case, and the first in Central America.[101][102]
Poland First confirmed case.[103]
Sweden First confirmed case.[104]
May 7
editWHO As of 18:00 GMT, 24 countries have officially reported 2,371 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[105]
Argentina First confirmed case.[106]
Brazil First four confirmed cases.[107][108]
Canada Reports suggest that an elderly woman who had swine flu has died in northern Alberta, marking the first death in Canada related to swine flu.[109] Furthermore, an unusual case of zoonosis occurred when a swine flu inspector in improper gear caught the virus from an infected pig.[110]
Netherlands Second case confirmed, a 53-year-old woman who had recently travelled to Mexico.[111]
USA The New England Journal of Medicine establishes its H1N1 Influenza Center on its website.[112]
May 8
editWHO As of 16:00 GMT, 25 countries have officially reported 2,500 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[113]
Japan First three confirmed cases.[114]
Panama First confirmed case.[115][116][117]
May 9
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 29 countries have officially reported 3,440 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[118]
Australia First confirmed case.[119]
Brazil Two cases confirmed, one of which is thought to be the first case of human-to-human infection in Brazil.[120]
Costa Rica First confirmed death, and also the first death outside of North America.[121][122] Three other confirmed cases, all children, were contaminated by the patient who died.[123]
Japan 4th confirmed case, a schoolmate of the first three cases.[124]
Norway First two confirmed cases.[125]
United States Third confirmed death, a Washington man with underlying heart disease.[126] Also, the USA passes Mexico in the number of confirmed cases of infection, 1693 to 1364, thus becoming the nation-state with the most laboratory-confirmed cases of infection; Canada is third with 242 cases.[127] CDC FluView Week 18: Widespread influenza activity in eight states, regional activity in 14.[128]
May 10
editWHO As of 07:30 GMT, 29 countries have officially reported 4,379 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[129]
China First confirmed case.[130]
May 11
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 30 countries have officially reported 4,694 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[131]
May 12
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 30 countries have officially reported 5,251 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[132]
Canada The first case in Yukon Territory is confirmed.[133]
Spain 100 cases confirmed.[134]
May 13
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 13 May 2009, 33 countries have officially reported 5,728 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[135]
Belgium First confirmed case.[136]
Panama 10 more cases confirmed today. Total: 39.[137]
May 14
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 33 countries have officially reported 6,497 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[138]
Belgium Second confirmed case.[139]
Colombia First domestic infections with three cases confirmed. Total: 10.[140]
May 15
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 34 countries have officially reported 7,520 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[141]
USA Fourth and fifth deaths confirmed, that of an Arizona woman suffering from a lung condition[142][143] and a Texas man in Corpus Christi, respectively.[144][145]
Malaysia First confirmed case.[146] Malaysia is the 37th country to be affected by the virus.
Panama Four new cases confirmed today. Total: 43, 23 of whom are male and 20 of whom are female. 20 of the cases are under 15 years old.[147]
May 16
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT 36 countries have officially reported 8,451 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.
India First case confirmed, in Hyderabad.[148] This marks the arrival of A(H1N1) in the fifth of the WHO's six regions, the South-East Asia Region.
Japan First domestic infection confirmed, in Kobe, a male high school student with no history of travel abroad.[149] The Kobe Festival, planned for May 16 and 17, is cancelled.[150]
Malaysia Second confirmed case.[151] The first patient is now showing significant improvement from the treatment.
Panama 11 new confirmed cases. 54 total.[152]
Turkey First confirmed case, that of an American tourist flying from the United States via Amsterdam, discovered at Istanbul's Atatürk International Airport.[153]
United States CDC FluView Week 19: Widespread influenza activity in five states, regional activity in 13.[154]
May 17
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT 37 countries have officially reported 8,480 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.
Panama With 54 confirmed cases, Panama occupies second place, along with Canada, for the number of cases per country.
May 18
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 40 countries have officially reported 8,829 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 74 deaths.[155]
ECDC The European Centre for Disease Control releases its early findings on H1N1's pandemic potential.[156]
Japan reports 96 confirmed cases;[157] it now ranks fourth in the world in the number of infections. Thousands of schools in 21 cities in the Hyogo and Osaka prefectures are temporarily closed.[158][159]
USA The sixth death in the US, and the first in New York—that of an assistant principal.[160][161]
May 19
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 40 countries have officially reported 9,830 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 79 deaths.[162]
United States Seventh confirmed death, that of a 44-year-old Missouri man.[163]
Japan 191 confirmed cases; Hyogo Prefecture has the most at 111.[164]
Norway One more case confirmed today. Total: three.[165]
Paraguay confirmed its first case and became the 43rd affected country.[166]
Taiwan confirmed its first case and becomes the 44th affected country.[167]
May 20
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 40 countries have officially reported 10,243 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 80 deaths.[168]
United States A patient dies in Arizona,[169] and a 22-year-old man dies in Utah,[170] the nation's eighth and ninth H1N1 fatalities. Roughly half of the influenza viruses detected by the CDC's routine influenza surveillance systems are now that of novel A(H1N1).[1] An unusual number of outbreaks in schools is reported.[171]
Japan 236 confirmed cases, including the first case in Shiga Prefecture,[172] and the cities of Hachiōji and Kawasaki in the Greater Tokyo Area. Two female high school students from Tokyo who had recently attended a Model United Nations conference in New York are presumed to have become infected abroad.[173][174]
Norway 1 more case confirmed today. Total: 4.[165]
May 21
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 41 countries have officially reported 11,034 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 85 deaths.[175]
Japan 279 confirmed cases; more than 4,800 schools are closed in the Kobe region.[176]
May 22
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 42 countries have officially reported 11,168 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 86 deaths.[177]
Japan 317 confirmed, including first confirmed in Saitama Prefecture.[178] Third confirmed in Tokyo, a 25-year-old man who visited Osaka from May 14-20th.[179]
Philippines First case confirmed.[180]
May 23
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 43 countries have officially reported 12,022 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 86 deaths.[181]
Iceland First confirmed case. 4 more cases suspected.[182][183] United States CDC FluView Week 20: Widespread influenza activity in four states; regional activity in 11.[184]
May 24
editAustralia Two more confirmed cases, which now brings the national toll to 16.[185]
Kuwait First confirmed cases, that of 18 U.S. soldiers.[186]
May 25
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 46 countries have officially reported 12,515 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 91 deaths.[187]
Australia 22 Confirmed Cases.[188]
Ireland Second confirmed case.[189]
May 26
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 46 countries have officially reported 12,954 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 92 deaths.[190]
Argentina 14 Confirmed Cases. Total: 19.[191]
Australia 61 confirmed cases.[192][193][194]
Puerto Rico First confirmed case.[195]
May 27
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 48 countries have officially reported 13,398 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 95 deaths[196]
Argentina 37 cases confirmed.[197]
Dominican Republic First two confirmed cases.[198]
Greece confirmed two more cases.[199]
Romania First confirmed case.[200]
Singapore First confirmed case. A 22-year-old woman picked up the virus after visiting New York.[201]
United Kingdom Two new cases confirmed. Total: 186.[202]
Uruguay confirmed its first two cases.[203]
May 28
editAustralia 147 confirmed cases.[204]
Singapore Three more cases confirmed. Total confirmed cases now stands at four.[205]
United Kingdom Seventeen more confirmed cases. Total: 203.[206]
Bolivia First 2 cases confirmed.[207]
Venezuela First confirmed case.[208]
May 29
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 53 countries have officially reported 15,510 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 99 deaths[209]
United Kingdom 14 confirmed cases. Total: 217.[210]
Norway One new confirmed case. Total: 5.[165]
Hungary First confirmed case[211]
Uruguay 4 new confirmed cases. Total: 6.[212]
Greece Another one case confirmed. Total: 4.[213]
May 30
editEstonia First confirmed case.[214]
United States CDC FluView Week 21: Widespread influenza activity in five states, regional activity in 10.[215]
May 31
editDominican Republic Nine more cases confirmed, for a total of 11 cases nationwide.[216]
June 2009
editJune 1
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 62 countries have officially reported 17,410 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 115 deaths.[217]
Bulgaria First confirmed case.[218]
June 2
editBermuda First case confirmed.[219]
Egypt First case confirmed.[220]
Luxembourg First case confirmed.[221]
Nicaragua First case confirmed.[222]
June 3
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 3 June 2009, 66 countries have officially reported 19,273 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 117 deaths.[223]
Saudi Arabia First confirmed case.[224]
June 4
editBarbados First confirmed case.[225]
Malaysia Three more cases confirmed. One of the patients is a 23-year-old student returned from the United States. Another two patients are German tourists who arrived in Singapore after having gone to Malaysia for holiday. Total: 5.[226]
Trinidad and Tobago First confirmed case.[227]
June 5
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 69 countries have officially reported 21,940 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 125 deaths.[228]
Australia 1006 cases confirmed.[229]
Cayman Islands First case confirmed.[230]
Dominican Republic First fatality, a 17-year-old pregnant girl. Total number of confirmed cases rises to 44.[231]
June 6
editMalaysia One more case confirmed. Total: 7.[232]
United States CDC FluView Week 22: Widespread influenza activity in eight states, regional activity in nine. "Approximately 89% of all influenza viruses being reported to CDC were novel influenza A (H1N1) viruses."[233]
June 7
editMartinique First case confirmed.[234]
New Zealand Authorities have confirmed that a man traveling from North America has Influenza A(H1N1). Total: 14.[235]
June 8
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 73 countries have officially reported 25,288 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 139 deaths.[236]
Dominica First confirmed case.[237]
New Zealand Three more confirmed cases, two of which were from international flights. Total: 17.[238]
June 10
editWHO As of 06:00 GMT, 74 countries have officially reported 27,737 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 141 deaths.[228]
Colombia First death confirmed.[239]
French Polynesia First confirmed case in the islands.[240]
Guatemala First death confirmed.[241][242]
June 11
editThe WHO raises its Pandemic Alert Level to Phase 6, citing significant transmission of the virus.[243][244][245]
Australia 1263 cases nationally, with more than 1000 cases in the State of Victoria alone.[246]
British Virgin Islands First case confirmed in the islands.[247]
Cuba Sixth case on the island, and that of the first citizen.[248]
Palestinian Territories First case confirmed in the West Bank.[247]
June 12
editWHO As of 07:00 GMT, 12 June 2009, 74 countries have officially reported 29,669 cases of Influenza A (H1N1) infections, including 145 deaths.
Morocco First case confirmed.[249]
Isle of Man First case confirmed.[250]
June 13
editBolivia First two domestic infections. Total: 7.[251]
Malaysia One more confirmed case. Total: 12.[252]
United States Widespread influenza activity in eleven states, regional activity in six. "Over 98% of all subtyped influenza A viruses being reported to CDC were pandemic influenza A (H1N1) viruses."[253]
June 15
editMalaysia Five more cases of H1N1 confirmed. Total: 17.[254]
United Kingdom First death confirmed.[255]
June 16
editSri Lanka First confirmed case.[256]
June 17
editMonaco First confirmed case.[257]
Malaysia Four more cases of H1N1 confirmed. One domestic infection confirmed. Total: 23.[258]
June 19
editAntigua and Barbuda First confirmed case.[259]
Bangladesh First confirmed case.[260]
Ethiopia First two cases confirmed.[261]
Slovenia First confirmed case.[262]
June 22
editPhilippines First death in Asia confirmed. H1N1 deaths now confirmed in 3 of 6 WHO regions.[263]
June 24
editIraq First seven cases confirmed.[264]
Japan 52 more cases confirmed. Total: 944.
Serbia First confirmed case.[265]
United States CDC FluView Week 24: Widespread influenza activity in twelve states, regional activity in seven. "Over 99% of all subtyped influenza A viruses being reported to CDC were pandemic influenza A (H1N1) viruses."[266]
June 27
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 25: Widespread influenza activity in ten states, regional in 11 states.[267]
June 29
editBosnia and Herzegovina First case confirmed.[268]
Denmark First case of Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) resistance found. Confirmed by David Reddy, Roche's pandemic taskforce leader.[269]
Kenya First confirmed case.[270]
Mauritius First case confirmed.[271]
Nepal First three confirmed cases.[272]
South Africa South Africa National Health Department confirm community outbreak, with 7 new confirmed cases. The total of confirmed cases grew to 12640 within South Africa over the next few months.[citation needed]
July 2009
editJuly 1
editGuam First case confirmed.[273]
July 2
editAustralia First confirmed death in NSW. National total: 10.[274]
Japan Second case found with mutation resulting in Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) resistance.[275]
July 4
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 26: Widespread influenza activity in nine states, regional influenza activity in 12. "Over 97% of all subtyped influenza A viruses being reported to CDC were novel influenza A (H1N1) viruses."[276]
Portugal First human-to-human transmission. Total: 38.[277]
Syria First case confirmed.[278]
July 5
editPeru First two deaths confirmed.[279]
July 6
editWHO 429 deaths worldwide are reported.[280]
July 8
editBelize First five cases confirmed.[281]
July 9
editTanzania First case confirmed.
July 11
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 27: Widespread influenza activity in nine states, regional activity in 12. "Over 99% of all subtyped influenza A viruses being reported to CDC were novel influenza A (H1N1) viruses."[282]
July 12
editColombia 6th death case confirmed out of 165 infected[283]
Malaysia 39 more cases confirmed. Total: 710.
United Kingdom Another 2 deaths confirmed. Total Deaths: 17.
July 13
editBrazil One more death confirmed. Total Deaths: 3.[284]
Ecuador Third death confirmed. Total deaths: 3.[285]
July 14
editBrazil Fourth death confirmed.
Malaysia 32 more cases confirmed. Total: 804
New Zealand Two more deaths confirmed. Total deaths 9. Total confirmed cases: 1,984.
July 16
editSingapore First flu-related death confirmed, that of a 49-year-old man with heart problems.[286]
Sudan First two confirmed cases of H1N1 detected, from flights which had arrived from the U.K.[287]
July 17
editHawaii First death, that of a sexagenarian with underlying health problems.[288]
July 18
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 28: Widespread influenza activity in seven states, regional activity in 13. "Over 99% of all subtyped influenza A viruses being reported to CDC were novel influenza A (H1N1) viruses."[289]
Venezuela First death confirmed, that of an 11-year-old girl.[290]
Singapore First death with H1N1 involvement confirmed, that of a 49-year-old male who also suffered from diabetes, hypertension and high cholesterol, from a heart attack caused by severe pneumonia.[291]
July 19
editEgypt First death confirmed.[292]
Georgia First case confirmed.[293]
July 20
editAlbania First case confirmed.[294]
Guam First death confirmed.[295]
Namibia First two H1N1 cases confirmed.[296]
July 21
editCanada The fourth case of mutation in the world from Tamiflu has been found in a 60-year-old man from Quebec, Canada.[297]
Federated States of Micronesia First case confirmed, that of a 27-year-old male.[298]
Northern Mariana Islands First two cases of H1N1 confirmed.[299]
July 22
editHungary First death confirmed, that of a man with underlying heart and lung disease.[300]
Tonga First death confirmed.[301]
July 23
editThe WHO ceases the tracking of cumulative individual cases.[302]
Arab League Health Ministers hold a summit after the death of a pilgrim who had returned from the Hajj. New regulations were promulgated for the Hajj: anyone younger than 12 or older than 65 or who have "chronic health problems" shall not be allowed to undertake the pilgrimage to Mecca.[303]
Bhutan First case confirmed.[304]
Malaysia First flu-related death confirmed, that of an obese 30-year-old male.[305]
July 24
editCanada Nova Scotia reports its first H1N1 death.[306]
Cayman Islands First death reported, that of a man with underlying medical conditions.[307]
July 25
editIndonesia First H1N1 death confirmed, that of a 6-year-old girl suffering from severe pneumonia.[308]
United States It is reported that thousands of Americans are being recruited for H1N1 vaccine testing at several research centers across the country.[309] CDC FluView Week 29: Widespread influenza activity in four states, regional activity in eight. "Over 98% of all subtyped influenza A viruses being reported to CDC were novel influenza A (H1N1) viruses."[310]
July 26
editNorway An international 4H youth camp with 1,700 participants from fifteen nations is shut down after fifty Norwegian participants catch H1N1.[311]
July 27
editWHO 816 deaths worldwide are reported.[312]
Germany Germany's federal infectious disease center, the Robert Koch Institute, states there were 3,810 confirmed cases of H1N1 in the country; nearly all of the cases are mild.[313]
Israel First death confirmed, that of a 35-year-old man from Eilat.[314]
Kosovo First case confirmed.[315]
Saint Kitts and Nevis First death reported, that of a 28-year-old woman.[316]
Saudi Arabia First death confirmed.[317]
July 28
editJapan Third case of Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) resistance.[318]
Thailand In the first reported case of vertical transmission of A(H1N1), a baby is born infected.[319]
July 29
editSwaziland First case confirmed.[320]
United Kingdom The NHS is not ready for a second wave of swine flu cases expected this autumn, a House of Lords committee has stated. It warned hospitals do not have enough intensive care beds to cope, and furthermore predicted that the recently established A(H1N1) flu helpline could be overwhelmed with calls.[321]
United States The U.S. military wants to establish regional teams of military personnel to assist civilian authorities in the event of a significant outbreak of the H1N1 virus this fall, according to Defense Department officials.[322]
July 30
editAzerbaijan First two cases of A(H1N1) confirmed, those of people who had been on holiday in France and the U.K., respectively.[323]
Belgium First death confirmed, that of a 34-year-old woman.[324]
France First death confirmed, a 14-year-old girl in Brest.[325]
Gabon First case confirmed.[326]
Lebanon First death confirmed, that of a 30-year-old male.[327]
Moldova First case confirmed.[328]
Saudi Arabia Second H1N1 death confirmed, that a 28-year-old Indonesian woman.[329]
Taiwan First death confirmed, that of a 39-year-old man.[330]
July 31
editWHO 1,154 deaths worldwide are reported.[331]
France The cruise ship Voyager of the Seas, which had reported dozens of cases of H1N1 flu amongst its 5,000 passengers and crew, docks in France.[332]
August 2009
editAugust 1
editAustralia First case of reverse zoonosis confirmed in a piggery in Dunedoo.[333]
United States CDC FluView Week 30: Widespread influenza activity in four states, regional activity in 11. "Over 98% of all subtyped influenza A viruses being reported to CDC were novel influenza A (H1N1) viruses."[334]
August 3
editSouth Africa First confirmed death in South Africa. Total number of deaths at end of epidemic 93.[citation needed]
August 4
editIndia First death confirmed.[335]
Netherlands First death confirmed, that of a 17-year-old male.[336]
Solomon Islands First case confirmed.[337]
August 6
editWHO 1,462 deaths worldwide are reported.[338]
August 8
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 31: Widespread influenza activity in four states, regional activity in 10.[339]
August 11
editCosta Rica President Óscar Arias is confirmed to have swine flu, the first head of state known to have been infected.[340]
August 13
editWHO 1,799 deaths worldwide are reported.[341]
August 14
editMadagascar First case confirmed.[342]
August 15
editDemocratic Republic of the Congo First H1N1 case confirmed.[343]
United States CDC FluView Week 32: Widespread influenza activity in two states, regional activity in eight.[344]
August 17
editMalaysia Two more deaths confirmed. Total: 64 deaths.[345]
Malta First death confirmed.[345]
August 18
editMalaysia Three more deaths confirmed. Total: 67 deaths.[346]
August 19
editBelarus First H1N1 case confirmed.[citation needed]
August 20
editKuwait First death confirmed.[347]
Malaysia One more death confirmed. Total: 68 deaths.[348] The unusually high reported death rate, four times the global average,[349] is investigated by the WHO.[350]
Netherlands Second death confirmed, that of a 58-year-old male.[336]
August 21
editChile H1N1 is found in turkeys on farms in Chile near the port city of Valparaiso in a unique zoonosis cluster.[351]
Germany 13,740 A(H1N1) cases confirmed.[352]
Oman First death confirmed.[353]
United Arab Emirates First death confirmed.[354]
United Kingdom First death confirmed in Northern Ireland, that of woman with underlying health conditions.[355]
August 22
editNew Caledonia First death confirmed.[356]
United States CDC FluView Week 33: Widespread influenza activity in two states, regional activity in 13. Activity appears to be increasing in the Southeast.[357]
August 23
editWHO At least 2,185 deaths worldwide are reported.[358]
Greece First death confirmed.[359]
August 24
editGermany 14,325 H1N1 cases confirmed.[360]
Kyrgyzstan First two cases confirmed, that of a husband and wife; the man had recently traveled to Dubai.[361]
Malaysia One more death confirmed. Total: 69 deaths.[362]
August 25
editMalaysia One more death confirmed. Total: 70 deaths.[363]
August 26
editAngola First case confirmed.[364]
Germany 14,940 H1N1 cases confirmed.[365]
Iran First death confirmed[citation needed]
Malaysia One more death confirmed. Total: 71 deaths.[366]
Syria First death confirmed.[367]
August 27
editUN;Chile The United Nations issues a warning regarding the discovery of H1N1-infected turkeys on farms in Chile, an unusual case of zoonosis which raises concerns about possible increased genetic reassortment of the virus.[368]
August 28
editWHO Most countries in the Southern Hemisphere (represented by Chile, Argentina, New Zealand, and Australia) appear to have passed their peak of influenza activity and returned to baseline activity.[358]
ECDC Based partially on data from the Southern Hemisphere, the ECDC forecasts a first wave of infections in autumn and winter which stresses hospitals in particular; it is noted, however, that "the overall interruption of essential services in (well-prepared) countries has been manageable".[369]
Germany 15,567 H1N1 cases confirmed.[370]
August 29
editBangladesh First death confirmed.[371]
Brazil 602 H1N1 deaths confirmed, the highest number of any nation-state to date.[372]
United States CDC FluView Week 34: Influenza activity, which had been largely stable or decreasing in prior weeks, increases in the U.S. "Six states and Puerto Rico reported geographically widespread influenza activity, 13 states reported regional influenza activity, 10 states and the District of Columbia reported local influenza activity, 19 states reported sporadic influenza activity, two states reported no influenza activity, and Guam and the U.S. Virgin Islands did not report." Furthermore, Region IV, i.e. the Southeast, reports increased out-patient ILI above its regional baseline.[373]
August 30
editWHO At least 2,837 deaths worldwide are reported.[374]
Colombia President Álvaro Uribe is confirmed to have swine flu, the second Head of state known to have been infected.[375]
Djibouti First seven cases confirmed.[376]
United Arab Emirates Second death confirmed, that of a thirty-year-old Pakistani expatriate who died following Caesarian section.[377]
August 31
editArgentina The most H1N1 deaths per capita.[378]
Bahrain First death confirmed, a South East Asian woman in her thirties with underyling medical conditions.[377]
Sweden First death confirmed.[379]
September 2009
editSeptember 2
editMacau First death confirmed.[380]
Portugal 5,123 cases officially confirmed[381]
September 3
editMalaysia One more death confirmed. Total: 73 deaths.[382]
Norway First death confirmed.[383]
United States The CDC in its Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report[384] notes that 67% of thirty-six children who have died from H1N1 early in the epidemic had at least one serious chronic medical condition, with neurodevelopmental conditions such as developmental delay, epilepsy, and cerebral palsy being especially prominent.[385] Roughly one in thirteen deaths have been of school-age children. More than 80% of the children who died were five or older, in contrast with the seasonal flu baseline of half or more of the influenza fatalities being four or younger.[386]
September 4
editItaly First death confirmed.[387]
September 5
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 35: Influenza increases in the U.S. with widespread influenza activity in 11 states and regional activity in 13; the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) is above the national baseline, with four out of ten HHS Surveillance Regions reporting ILI above region-specific baselines. "97% of all subtyped influenza A viruses being reported to CDC were 2009 influenza A (H1N1) viruses."[388]
September 6
editWHO At least 3,205 deaths worldwide are reported.[389]
September 7
editEcuador Ecuador's chief of presidential security, Col. John Merino, dies of H1N1 flu[390] after twenty-eight days at Quito Military Hospital.[391]
Faroe Islands First 44 cases confirmed.[392]
Namibia First death confirmed, that of a 37-year-old businessman who had fallen ill in Angola.[393]
September 8
editSuriname First death confirmed.[394]
September 9
editMadagascar First death confirmed.[395]
USA An outbreak is confirmed at the gaming convention PAX in Seattle, Washington.[396][397][398][399]
September 10
editMalawi First case confirmed.[400]
September 11
editAustralia First case of Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) resistance found.[401]
September 12
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 36: Influenza activity continues to increase with widespread influenza activity in twenty-one states, regional influenza activity in nine. Seven of ten HHS Surveillance Regions report ILI activity above region-specific baselines. "99% of all subtyped influenza A viruses being reported to CDC were 2009 influenza A (H1N1) viruses."[402]
September 13
editWHO At least 3,486 deaths worldwide are reported.[403]
September 14
editMozambique First death confirmed, that of a 29-year-old female with an unspecified chronic illness.[404]
September 17
editMalta Third death confirmed.[405]
Netherlands The third and fourth deaths are confirmed, that of a 52-year-old man and an 85-year-old woman, respectively, both of whom had underlying medical conditions.[406]
United Kingdom Health Minister Andy Burnham states that the second peak of swine flu has started as 5,000 people contracted the virus this week, compared to 3,000 the week before.[405]
September 18
editMartinique First death confirmed, that of an 18-month-old girl.[407]
September 19
editMalaysia One more death confirmed. Total: 77 deaths.[408]
United States CDC FluView Week 37: Widespread influenza activity in twenty-six states, regional activity in 11. All of the HHS ILI regions report elevated levels of influenza activity above their region-specific baselines except for Region I (New England).[409]
September 20
editWHO Over 3,917 deaths worldwide are reported.[410]
September 21
editChina A national vaccination campaign begins in China, making it the first country to issue the H1N1 vaccine.[411]
United States The U.S. government orders a total of 251 million doses of H1N1 vaccine from manufacturers, up from the long-planned total of 195 million.[412]
September 23
editPortugal The first death confirmed, that of a Portuguese man living in France.[413]
September 25
editGermany First death confirmed, that of a 36-year-old woman who died of a so-called superinfection which included H1N1.[414]
United States Forty-two schools are closed in eight states as the second wave of the pandemic begins in early autumn.[415]
September 26
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 38: Widespread influenza activity in twenty-seven states, regional activity in 18.[416]
September 27
editWHO At least 4,108 deaths worldwide are reported.[417]
United States The second wave of the H1N1 pandemic begins to stress hospitals in the U.S. and prompts some school closures.[415][418]
September 28
editCambodia First death confirmed, in Phnom Penh.[419]
September 29
editIreland First case of reverse zoonosis in pigs.[420]
September 30
editAustralia Mass vaccination drive begins, the second in the world.[421]
Bulgaria First death confirmed.[419]
China Sinovac Biotech Ltd., the first company worldwide to complete clinical trials for a vaccine, receives an order for an additional 3 million doses of H1N1 vaccine from the PRC government, making for a total of 6.3 million doses.[422][423]
United States 46 states and Washington, D.C. begin ordering what becomes by the next day a cumulative total of 1,378,200 doses of the nasal-spray Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine (LAIV)[424] for H1N1.
October 2009
editOctober 3
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 39: The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) reaches the epidemic threshold with eight out of ten HHS ILI regions reporting region-specific ILI activity above region-specific baseline levels. Widespread influenza activity in thirty-seven states, regional activity in 11.[425]
October 4
editWHO At least 4,525 deaths worldwide are reported.[426]
Tajikistan First case confirmed.[426]
United States The CDC's 2009–10 influenza season officially begins.[416][427]
October 5
editUnited Nations Rich countries should make more vaccines available to poorer nations where the H1N1 virus is starting to hit, United Nations health officials said. They said increased readiness for swine flu was needed in developing countries with weaker medical systems and with large, young populations, who are most vulnerable to the disease. Some countries, such as the United States, Brazil and France, have agreed to make 10 percent of their national vaccine stockpile available to developing countries. Manufacturers have also donated about 150 million doses of vaccine.[428]
October 6
editChina First death confirmed, in Lhasa, Tibet.[429]
Tanzania First death confirmed.
October 9
editYemen Tamiflu resistance found.[376]
October 10
editCuba First deaths confirmed, that of three pregnant women.[430]
United States CDC FluView Week 40: The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) is officially above the epidemic threshold. Moreover, for the first time all 10 HHS ILI regions reported ILI above region-specific baseline levels. Widespread influenza activity in forty-one states, and regional activity in eight, with only one state—Hawaii—reporting local influenza activity.[431]
October 11
editWHO At least 4,735 deaths worldwide are reported.[432]
October 12
editNorway first case of reverse zoonosis detected in Nord-Trøndelag.[433]
Rwanda First cases confirmed.[434]
São Tomé and Príncipe First cases confirmed.[434]
Sweden Mass vaccination begins.[435]
Vietnam Three cases of Tamiflu resistance (which developed during hospital treatment) are confirmed. The resistant strains were apparently not transmitted, and all three patients survived.[436]
October 13
editMongolia First cases confirmed.[437]
October 15
editIndia Six more deaths confirmed. Total: 405 deaths.[438]
Trinidad and Tobago First death confirmed.[439]
United Kingdom The death toll passes 100. Total confirmed deaths: 106. The NHS confirms that second wave of swine flu has begun, with cases in Wales and Northern Ireland being especially high. The Minister of Health confirms that there were 27,000 cases in the last week in England alone, up from 14,000 the week before. The Minister of Health also announced that 415,000 H1N1 vaccinations shall take place on the week beginning 21 October, then 5,000,000 more vaccinations the week after. 20% of all hospitalized cases are now critical, up from 12% the week before. The government believes it can get 50,000,000 Britons vaccinated before Christmas.[440]
October 16
editUnited States An initial shortfall of swine flu vaccine is predicted shortly after the proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza goes above the epidemic threshold[441] in some states,[442] with flu activity widespread in 41 states.[443] It is also announced that the number cases, hospitalizations and deaths are unprecedented for this time of year, with flu-like illnesses accounting for 6.1% of all doctor visits, itself an unusually high number.[444]
October 17
editWHO At least 4,999 deaths worldwide are reported.[445]
China Second death confirmed, in the northwestern province of Qinghai.[446]
United States CDC FluView Week 41: All 10 HHS ILI regions reported ILI above region-specific baseline levels. Widespread influenza activity in forty-six states, regional activity in three.[447]
October 19
editUnited States H1N1 is confirmed in a nasal mucus sample taken from a show hog at the Minnesota State Fair in the first case of zoonosis in the country.[448][449][450]
India Two more deaths confirmed. Total: 415 deaths.[451]
Japan Mass vaccinations begin.[452]
October 20
editCanada H1N1-infected turkeys are confirmed in Ontario, the second such case of zoonosis reported in the world.[453]
Iceland First death confirmed.[454]
United States In a unique case of zoonosis, a pet ferret in Oregon is confirmed to be infected with H1N1.[455]
October 21
editCanada A turkey farm in Ontario province has been confirmed infected with A/H1N1 flu, making Canada the second country to report such infection after Chile, health officials confirmed[456]
Japan Ten H1N1-infected pigs are discovered in a swine herd in Osaka Prefecture, the first reported case of zoonosis in Asia.[457][458]
UK H1N1 vaccinations begin nationwide, with 14,000,000 high-priority people with conditions such as asthma to be vaccinated initially, then eventually up to 51,000,000 other Britons.[459][460]
Serbia First death confirmed.[461]
October 22
editCzech Republic First death confirmed.[462]
Iraq Fears over the H1N1 virus prompts nearly 2,500 school closures.[463]
October 23
editGermany Third H1N1 death confirmed.[464]
Mongolia First death confirmed.[465]
Netherlands Two new deaths reported, that of a 14-year-old girl and 40-year-old man. Total deaths: 6.[406]
United States President Barack Obama declares a national emergency, stating "The potential exists for the pandemic to overburden health care resources in some localities."[466]
October 24
editUnited States Various public health departments across the country run out of the H1N1 vaccine,[467] due to the shortfall of 10 million doses as the national vaccination campaign gets underway in earnest; 40 million doses had initially been projected.[468][469] According to the CDC's FluView Week 42, influenza activity is widespread in 48 states, with regional activity in just two: Hawaii and South Carolina.[470]
October 25
editWHO At least 5,712 deaths worldwide are reported.[471]
October 26
editChina Another death confirmed, in the northwestern province of Xinjiang.[472]
Oman Mass vaccinations begin.[473]
October 27
editCanada Canada's H1N1 vaccination campaign begins.[474]
Russia First two deaths confirmed, in the far eastern city of Chita.[475]
Iceland First case of reverse zoonosis detected in pigs.[476]
October 28
editPortugal A ten-year-old dies 48 hours after contracting the flu.[477]
October 29
edit| H1N1 in Turkish Provinces by Late October | |
|---|---|
| Disease | Swine flu |
| Virus strain | H1N1 |
| First outbreak | Central Mexico[478] |
| Arrival date | 16 May 2009[479] |
| Confirmed cases | 12,316[480] |
Deaths | 627[480] |
Afghanistan First death confirmed.[481]
Nigeria First case confirmed.[482]
Republic of Congo First case confirmed.[483]
October 30
editECDC The European Centre for Disease Control reports a total of 302 fatal cases in Europe to date; all of the 27 EU and the four EFTA countries are reporting cases of pandemic (H1N1) 2009 influenza.[484]
Ukraine First death confirmed. Meanwhile, Ukrainian Prime Minister Yulia Tymoshenko ordered a massive and for Ukraine unprecedented disease-control programme to go into effect immediately in an attempt to prevent the spread of the disease. A 'full quarantine' will be imposed in seven provinces of Western Ukraine, with police monitoring the entrance and exit of all persons. It will block those lacking justification for travel[485]
October 31
editCroatia First death confirmed.[486]
United States According to the CDC's FluView Week 43, influenza activity is widespread in 48 states, with regional activity in two: Hawaii and Mississippi.[487]
November 2009
editNovember 1
editAfghanistan Schools are closed for three weeks after the first H1N1 death is recorded.[488]
Kuwait Mass vaccinations begin.[473]
Morocco Mass vaccinations begin.[473]
November 2
editTurkey Mass vaccinations begin.[489]
November 3
editWHO At least 6,071 deaths worldwide are reported.[490]
Austria First death confirmed.[491]
Belarus First death confirmed.[492]
Egypt Mass vaccinations begin.[473]
Qatar Mass vaccinations begin.[473]
Slovenia First death confirmed.[493]
US The USDA reports the first H1N1 zoonosis in commercial swine, in a herd in Indiana.[494][495]
November 4
editNetherlands First case of Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) resistance found.[496]
United States The first case in the world of H1N1 zoonosis in a cat is confirmed, in Iowa.[497]
November 5
editSan Marino First case confirmed.[498]
November 6
editBulgaria A nationwide epidemic is declared.[499]
Hong Kong Reverse zoonosis is detected in two slaughtered pigs.[499]
November 7
editBahrain Mass vaccinations begin.[473]
Belgium Mass vaccination begins.[499]
Saudi Arabia Mass vaccinations begin.[473]
United States CDC FluView Week 44: Widespread influenza activity in forty-six state, regional activity in four. "The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 6.7% which is above the national baseline of 2.3%. All 10 regions reported ILI above region-specific baseline levels."[500]
November 8
editPakistan First death confirmed.[501]
Sri Lanka First death confirmed.[502]
November 9
editLatvia First death confirmed.[503]
United Arab Emirates Mass vaccinations begin.[473]
November 11
editGreenland First case confirmed.[504]
November 12
editArmenia First two cases confirmed.[505]
France Mass vaccination drive begins.[506]
November 13
editWHO In its 74th update, the WHO reports early signs that the early flu season has peaked in North America, even as the pandemic intensifies across much of Europe and Central and Eastern Asia.[507]
Bulgaria Health authorities confirm more than 12 people have died from H1N1 within a week; the latest victim is a 28-year-old man who died from respiratory failure.[508]
Cyprus First death confirmed.[509]
November 14
editKosovo First death confirmed.[510]
Poland First death confirmed.[511]
United States CDC FluView Week 45: Widespread influenza activity in forty-three states, regional activity in seven. "The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 5.5% which is above the national baseline of 2.3%. All 10 regions reported ILI above region-specific baseline levels."[512]
November 16
editTunisia First confirmed deaths.[513]
Somalia First case confirmed.[514]
Bosnia & Herzegovina First death confirmed.[515]
North Korea First case confirmed.[516]
Morocco First confirmed deaths.
Cyprus Mass vaccinations begin.
November 18
editHungary National epidemic declared.[517]
Lithuania First death confirmed.[518]
Republic of Macedonia First death confirmed.[519]
United States First feline death confirmed, in the state of Oregon.[520]
November 19
editMaldives First death confirmed.[521]
November 20
editDenmark First death confirmed.[522]
Jordan Mass vaccinations begin.[473]
Norway A potentially significant mutation is found in specimens taken of the H1N1 virus taken from two fatalities; a third victim was seriously ill.[523][524]
UK The first person-to-person transmission of Tamiflu-resistant H1N1 in the world is confirmed at the University Hospital of Wales in Cardiff. Five patients are so infected, with three apparently having been infected in hospital in a case of iatrogenic transmission.[525]
US An iatrogenic Tamiflu-resistant cluster is reported at Duke University Medical Center in North Carolina, with four severely ill cancer patients infected, the largest cluster in the U.S. More than fifty resistant cases have been reported in the world since April.[526]
November 21
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 46: Widespread influenza activity in thirty-two states, regional activity in 17. "The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 4.3% which is above the national baseline of 2.3%. All 10 regions reported ILI above region-specific baseline levels.[527]
November 23
editRomania First death confirmed, that of a 43-year-old man with obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes.[528]
November 24
editUnited States First double infection case confirmed, in a pediatrician in West Virginia.[citation needed]
Montserrat First case confirmed.[529]
November 27
editWHO H1N1 mutations have led to roughly 75 people worldwide developing Tamiflu resistance. Furthermore, the separate D222G or D225G mutation which helps the virus to reach deep into the lungs has been reported in cases both severe and mild in Norway, Ukraine, Brazil, China, Japan, Mexico and the United States.[530][531][532]
France The H1N1 mutation first detected in Norway causes two deaths in separate French cities.[533][534][535]
South Korea First double infection case confirmed, in a two-year-old girl.[536]
November 28
editChina Two cases in dogs are confirmed, the first instance of canine zoonosis in the world.[537]
Indonesia First case in pigs is confirmed, in southwest Sulawesi.[538]
United States CDC FluView Week 47: Widespread influenza activity, in Twenty-five states, regional influenza activity in 17. "The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 3.7% which is above the national baseline of 2.3%. Eight of the 10 regions reported ILI at or above region-specific baseline levels. Regions 6 and 10 reported ILI below their region specific baselines."[539]
November 30
editUnited States The CDC states that H1N1 may have peaked as the number of states reporting widespread influenza dropped from 43 the previous week to 32 this week. Furthermore, influenza-like illness now account for 4.3% of doctor visits, down from 8% four weeks ago (on average, influenza accounts for 2.5% of doctor visits). The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza continues to be higher than expected for this time of year, however. This proportion has remained elevated for eight weeks now.[540]
Finland First case of reverse zoonosis in pigs.[420]
Libya First death confirmed.[541]
December 2009
editDecember 1
editSaudi Arabia Only five deaths and 73 cases are reported from the hajj.[542]
December 2
editUnited Kingdom First case of reverse zoonosis in pigs is discovered, in Norfolk.[543]
December 5
editUS CDC FluView Week 48: Widespread flu activity in 14 states, regional activity in 25. "The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) was above the epidemic threshold for the tenth consecutive week. The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.7% which is above the national baseline of 2.3%."[544]
December 6
editGaza Strip First five cases are confirmed in the blockaded Gaza Strip.[545]
Japan 100 fatalities confirmed.[546]
United States With one in six Americans infected, or 15% of the country, nearly 10,000 have died to date, including 1,100 children and 7,500 younger adults. More than 200,000 Americans had been hospitalized to date — roughly the same number who are so affected by the regular seasonal flu variant in an entire year. Furthermore, with 12 million additional doses of H1N1 vaccine being released this week, several states begin to distribute the vaccine to the general public.[547]
December 7
editNorth Korea First deaths are confirmed, according to newsletters released by the Seoul-based aid group Good Friends.[548][549]
United States A sophisticated Bayesian analysis of public health data from April to the end of June from New York City and Milwaukee[550] indicates that the pandemic's symptomatic case-fatality ratio has been far lower than the previous three pandemics of 1968, 1957, and 1918, making it to date the mildest pandemic on record.[551][552]
December 12
editAfghanistan The 17th H1N1 fatality is reported.[553]
Gaza The eighth fatality is reported, that of a child with underlying kidney failure, within a week of the first H1N1 case in the Gaza Strip.[554]
United States CDC FluView Week 49: Widespread influenza activity in 11 states, regional activity in twenty. "The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) was above the epidemic threshold for the eleventh consecutive week... The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.6% which is above the national baseline of 2.3%. Five of the 10 regions reported ILI at or above region-specific baseline levels."[555]
December 13
editGeorgia First fatality confirmed, that of a 27-year-old man.[citation needed]
Qatar Mass vaccinations begin.[556]
December 16
editUnited States Roughly 100 million H1N1 vaccines[557] become widely available to the general public in pharmacies in several American states as the supply increases and restrictions to high-risk groups are lifted.[558][559]
December 17
editThailand First confirmed case of H1N1 in a pig, in a case of reverse zoonosis in Saraburi Province. The pig recovered.[560]
December 19
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 50: The CDC reports that levels of influenza are declining steadily, with only seven states reporting widespread influenza activity and 18 reporting regional activity; furthermore, the proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) is below the epidemic threshold. The CDC also notes that almost all isolates of H1N1 remain sensitive to oseltamivir.[441][561] "The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.3% which is at the national baseline of 2.3%."[562]
December 21
editUS First case of canine zoonosis confirmed. The 13-year-old dog from New York state was believed to have contracted the virus from his owner.[563]
December 23
editUS H1N1 is discovered at two North Carolina pig farms, making it the 10th state to identify the virus in animals. The swine caught the disease from infected workers and recovered after becoming moderately ill.[564]
Argentina An Argentine study published in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that "Pediatric 2009 H1N1 influenza was associated with pediatric death rates that were 10 times the rates for seasonal influenza than in previous years,"[565] and that the elevated risk for pregnant women extends for as long as two weeks after they give birth.[566][567]
December 26
editUS CDC FluView Week 51: Influenza activity decreases slightly, although the proportion of deaths attributed to P&I remained above the epidemic threshold. "Four states reported geographically widespread influenza activity, 13 states reported regional influenza activity, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and 19 states reported local influenza activity, Guam and 13 states reported sporadic influenza activity, and one state reported no influenza activity, the U.S. Virgin Islands did not report."[568]
December 27
editWHO At least 12,220 deaths globally are formally confirmed. (By contrast, the WHO estimates that the seasonal flu kills from 250,000 to 300,000 people around the world each year.) Overall, the activity of the H1N1 pandemic has peaked.[569]
Nepal First death confirmed, that of a woman who suffered major organ failure.[570]
December 29
editWHO In Geneva Dr. Margaret Chan, Director-General of the WHO, remarks in the context of the H5N1 bird flu virus that "The fact that the long overdue influenza pandemic is so moderate in its impact is probably the best health news of the decade" but that "No, the world is not ready for a pandemic to be caused by H5N1." Given that H1N1 could still mutate, however, the WHO shall continue to monitor the pandemic for six months to a year. She also said that it would take at least two years before a true death total is established. (Approximately 11,500 people are believed to have died in more than 200 countries.)[571]
December 30
editA study published in the New England Journal of Medicine finds that "household contacts less than 18 years of age were twice as susceptible to an acute respiratory illness as were those 19 to 50 years of age, whereas contacts older than 50 years were less susceptible".[572][573]
December 31
editA joint US-UK study shows that children are twice as likely as adults to catch H1N1.[574]
2010
editJanuary 2010
editJanuary 2
editUnited States CDC FluView Week 52: The proportion of deaths attributed to P&I falls below the epidemic threshold. No influenza activity is reported in Nebraska. "One state reported geographically widespread influenza activity, 12 states reported regional influenza activity, Puerto Rico, the District of Columbia, and 17 states reported local influenza activity, the U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, 19 states reported sporadic influenza activity, and one state reported no influenza activity."[575]
January 8
editUnited States The CDC reports that only Alabama reports widespread influenza activity.[576]
January 11
editMali First case confirmed.[577]
January 15
editUnited States According to the CDC no states have reported widespread influenza activity.[578]
January 20
editBermuda First death confirmed.[579]
January 29
editNigeria First death confirmed.[580]
February 2010
editFebruary 3
editMauritania First case confirmed.[581]
February 5
editUnited States The weekly report released by the CDC states that H1N1 activity has either remained stable or decreased over the past week in nine out of the ten regions of the United States. Furthermore, the proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza, which technically remains above the epidemic threshold, has declined over the past week.[582]
February 8
editSenegal First case confirmed[583]
February 19
editUnited States According to the CDC, only three states have reported regional influenza activity: Alabama, Georgia, and South Carolina.[584]
February 25
editNiger First case confirmed[581]
March 2010
editMarch 5
editUnited States According to the CDC, only four states have reported regional influenza activity: Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, and South Carolina.[585]
March 12
editUnited States According to the CDC, five states have reported regional influenza activity: Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, South Carolina, and Maine.[586]
March 19
editUnited States According to the CDC, only three states have reported regional influenza activity: Mississippi, Alabama, and Georgia.[587]
March 26
editUnited States According to the CDC, only three states have reported regional influenza activity: Alabama, Georgia, and South Carolina.[588]
March 27
editCuba Mass vaccination begins.[589]
March 31
editUnited States The CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report states that inoculation rates varied, with the highest rates in New England and the lowest in the South. (E.g., roughly 39% of the population of Rhode Island is immunized vis-à-vis 13% that of Mississippi.) Among children Georgia had the lowest vaccination rate, with 21%; the state currently has the highest level of H1N1 flu activity.[590]
April 2010
editApril 2
editUS According to the CDC, only three states have reported regional influenza activity: Alabama, Georgia, and South Carolina.[591]
Cambodia Mass vaccinations begin.[592]
April 9
editUS According to the CDC, only three states have reported regional influenza activity: Alabama, Georgia, and South Carolina.[593]
April 12
editGuinea First case confirmed.[594]
April 14
editWHO An external panel advises against winding down the pandemic alert level until experts have tracked the southern hemisphere's traditional autumn and winter flu season. Accusations of undue influence from the pharmaceutical industry were also addressed.[595]
April 17
editUS According to the CDC, no states have reported either widespread or regional influenza activity, and four have reported local activity: Hawaii, Alabama, Georgia, and South Carolina.[596]
April 19
editWHO Director-General Dr. Margaret Chan states that "It is still premature and too early for us to say we have come to an end of the pandemic influenza worldwide. It would be prudent and appropriate... to continue to monitor the evolution of this pandemic for the next six to 12 months," i.e. possibly into 2011. She also remarked that although the United States, Britain and Canada have passed through a second wave of H1N1, outbreaks in India, Egypt and elsewhere are intensifying, and reiterates that countries remain ill-prepared for a bird flu (H5N1) pandemic. More than 200 countries have now been affected by H1N1 with almost 12,000 confirmed deaths worldwide, although the vast majority of those infected recovered without special treatment.[597]
April 26
editPhilippines Mass vaccinations begin.[598]
May 2010
editMay 16
editWHO Director-General Dr. Margaret Chan states at the U.N.'s World Health Assembly that "We are just plain lucky ... This has been the case with the A/ H1N1 influenza pandemic... The virus did not mutate to a more lethal form. Cases of resistance to oseltamivir remained few and isolated. The vaccine closely matched circulating viruses and showed an excellent safety record," Chan said. "Emergency wards and intensive care units were often strained, few health systems were overwhelmed ... Schools closed, but borders remained open, and disruptions to travel and trade were far less severe than feared," she told delegates from the agency's 193 member states. "Had things gone wrong in any of these areas, we would have a very different agenda before us today," she added."[599]
August 2010
editAugust 6
editUS Researchers discover the mutation which had enabled the pandemic.[600][601]
August 10
editWHO Director-General Margaret Chan officially declares the H1N1 pandemic over as countries are now seeing a mix of H1N1, H3N2, and B viruses, with some populaces displaying community-level immunity to H1N1 of 20% to 40%.[602] Nevertheless, Angus Nicoll of the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control urged health officials worldwide to "prepare for a new type of seasonal flu to appear in the near future that will combine elements of the pandemic A(H1N1) strain, and older A(H3N2) strain and several lesser strains".[603] "Pandemics are unpredictable and prone to deliver surprises," Director-General Chan noted.[603]
Summary
editSee also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b "CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu". cdc.gov. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 11 August 2010. Archived from the original on 10 September 2009. Retrieved 20 June 2013.
- ^ a b Tuckman, Jo (2009-04-27). "Four-year-old could hold key in search for source of swine flu outbreak". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 2009-04-30. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 09, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-07-06 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 10, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ a b c d e f g "Outbreak of Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection --- Mexico, March--April 2009". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2009-04-30. Archived from the original on 2009-09-09.
- ^ "ProjectDisaster ' Blog Archive ' Mexico & H1N1". Archived from the original on 2011-07-15. Retrieved 2009-06-18.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 11, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ Brown, David (2009-04-22). "New Strain of Swine Flu Investigated: Two Children in San Diego Area Had No Contact With Pigs". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 2009-04-29.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Swine influenza A (H1N1) infection in two children --- Southern California, March--April 2009". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 58 (1–3). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2009-04-21. Archived from the original on 2009-09-10.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 12, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ a b "GenBank sequences from 2009 H1N1 influenza outbreak". Influenza Virus Resource. NCBI. 2009-05-01. Archived from the original on 2009-04-30.
- ^ "Influenza A virus (A/California/05/2009(H1N1)) segment 1 polymerase PB2 (PB2) gene, complete cds". NCBI. June 2009. Archived from the original on 30 September 2017. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Influenza A virus (A/California/04/2009(H1N1)) segment 1 polymerase PB2 (PB2) gene, complete cds". NCBI. June 2009. Archived from the original on 27 March 2017. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 12, 2008–2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ MedISys, EC (2008-04-05). "First article on novel influenza reported by MedISys". EC. Retrieved 2 August 2010.[permanent dead link]. Archived 2009-09-10.
- ^ Jornada, La (2008-04-05). "Alerta epidemiológica en Perote por brote de males respiratorios". LaJornada. Archived from the original on 2017-08-10. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g Brown, David (2009-04-30). "Reporting Health Threats: System Set Up After SARS Epidemic Was Slow to Alert Global Authorities". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 2009-05-07.
- ^ a b c d e Blumenthal, Les (2009-05-01). "Company warned officials of flu 18 days before alert was issued". McClatchy Newspapers. Archived from the original on 23 April 2014. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Veratect the Company to First Sound Alarm on Swine Influenza Makes Data on the Spread of this Disease Public" (PDF). Corporate press release. Veratect Inc. 2009-04-27. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 May 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 12, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ "Outbreak of Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection --- Mexico, March--April 2009". Archived from the original on 2009-09-09.
- ^ Brown, David (2009-04-26). "U.S. Slow to Learn of Mexico Flu: Canadian Officials Knew of Rare Strain Before Americans Did". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 2019-01-18. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
The earliest case found in Mexico was a 39-year-old woman who died April 12 of severe viral pneumonia in San Luis Potosi, a city of about 700,000 in central Mexico. "That attracted the attention of the epidemiologist there," said Mauricio Hernández, deputy minister for disease prevention and health promotion in Mexico's Federal Department of Health
- ^ Orsi, Peter (2009-04-27). "Mexico says suspected swine flu deaths now at 149". Google News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2009-04-29.
- ^ a b "Human Swine Influenza Outbreak. Message from the Minister of Health and the Chief Public Health Officer on Human Swine Flu". Advisories. Public Health Agency of Canada. 2009-04-24. Archived from the original on 2009-04-29. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ Stevenson, Mark (2009-04-26). "U.S., Mexico battle deadly flu outbreak". KomoNews.com. Fisher Communications, Inc. AP. Archived from the original on 2016-08-17. Retrieved 22 July 2016.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 15, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ a b Stobbe, Mike (2009-04-21). "Officials alert doctors after 2 California children infected with unusual swine flu". Star Tribune. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2009-04-30. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ a b Swine Influenza A (H1N1) Infection in Two Children - Southern California, March-April 2009 Archived 2009-10-01 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ Novel Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Investigation Team; Dawood, FS; Jain, S; Finelli, L; Shaw, MW; Lindstrom, S; Garten, RJ; Gubareva, LV; Xu, X (2009). "Emergence of a novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus in humans". The New England Journal of Medicine. 360 (25): 2605–15. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0903810. PMID 19423869.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Brownstein JS, Freifeld CC, Madoff LC (May 2009). "Influenza A (H1N1) virus, 2009--online monitoring". The New England Journal of Medicine. 360 (21): 2156. doi:10.1056/NEJMp0904012. PMC 2922951. PMID 19423868.
- ^ Stobbe, Mike (2009-04-21). "Swine flu cases in Calif. worry health officials". Fox News. AP. Archived from the original on 2009-05-03.
- ^ "(Update 1) Influenza-Like Illness in the United States and Mexico". World Health Organization. 2009-04-24. Archived from the original on 28 June 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ a b "CDC Briefing on Public Health Investigation of Human Cases of Swine Influenza (April 24, 2009)". Press Briefing Transcripts. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2009-04-24. Archived from the original on 2012-05-09. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Inside Justice - Swine Flu: Legal Obligations and Consequences When the World Health Organization Declares a "Public Health Emergency of International Concern"". www.insidejustice.com. Archived from the original on 2017-09-01. Retrieved 2014-05-06.
- ^ "Statement by WHO Director-General, Dr Margaret Chan (25 April 2009): Swine influenza". World Health Organization. 2009-04-25. Archived from the original on April 28, 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "WHO | Swine flu illness in the United States and Mexico - update 2". World Health Organization. 2009-04-26. Archived from the original on 22 August 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "WHO - IHR Procedures concerning public health emergencies of international concern (PHEIC)". www.who.int. Archived from the original on October 8, 2013.
- ^ a b "Vaccination Week In The Americas (2009 portal)". Pan American Health Organization. 2009. Archived from the original on 6 August 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Abramson, Larry (29 April 2009). "First Texas school district closure". NPR. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ^ "List of Texas school district closures". Texas Education Agency. 1 May 2009. Archived from the original on 2 May 2009. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- ^ "Declaration of a National Emergency with Respect to the 2009 H1N1 Influenza Pandemic". The White House. Archived from the original on 2020-03-12. Retrieved 2020-03-22.
- ^ "Statement by WHO Director-General, Dr Margaret Chan (27 April 2009): Swine influenza". World Health Organization. 2009-04-27. Archived from the original on April 29, 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Nasaw, Daniel (27 April 2009). "Europeans urged to avoid Mexico and US as swine flu death toll exceeds 100". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 30 April 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Health officials confirm 6 cases of swine flu in Canada". CBC News. 2009-04-27. Archived from the original on 2017-03-18. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Swine Influenza Update 3". World Health Organization. 27 April 2009. Archived from the original on April 29, 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Almansa (Spain) Archived 2013-12-23 at the Wayback Machine. Silobreaker
- ^ "Scotland 'could help combat flu'". BBC News. 29 April 2009. Archived from the original on 2018-01-29. Retrieved 2018-01-28.
- ^ "WHO | Swine influenza - update 4". World Health Organization. 2009-04-28. Archived from the original on 2010-08-12. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ Philip Ling (2009-07-16). "Swine flu: Mapping the H1N1 outbreak in Canada". Canada.com. Archived from the original on 2009-07-19.
- ^ Xinhua (2009-04-28). "Israel confirms first case of swine flu". The Gaea Times. Archived from the original on 2012-07-23. Retrieved 2013-12-20.
- ^ "RESULTS OF H1N1 (Swine flu) testing" (Press release). New Zealand Ministry of Health. 2009-04-28. Archived from the original on 2009-04-29. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ "Spain confirms second case of swine flu". Archived from the original on 2009-06-30. Retrieved 2009-06-18.
- ^ "Pandemic phase level 4: Human cases of the novel influenza A/H1N1 strain confirmed in Scotland and Spain" (PDF). EUROSURVEILLANCE. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 2009-04-30. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2009-05-14. Retrieved 2013-12-20.
- ^ Jordans, Frank; Cheng, Maria (2009-04-29). "WHO calls emergency meeting; eyes pandemic level". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2009-05-03.
- ^ "Statement by WHO Director-General, Dr Margaret Chan (29 April 2009): Swine influenza". World Health Organization. 2009-04-27. Archived from the original on May 3, 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ a b "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 5". World Health Organization. 2009-04-29. Archived from the original on April 29, 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Swine flu: Asean gears up". Archived from the original on 2009-05-02. Retrieved 2017-06-05.
- ^ "EU considers halting all Mexico travel". Reuters. 2009-04-29. Archived from the original on 2016-01-27. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "SWINE FLU: GERMANY CONFIRMS THREE CASES". AGI. 2009-04-29. Archived from the original on 2009-05-02. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ "WHO looking for signs of ongoing swine flu spread". CTV.ca. 2009-04-28. Archived from the original on 2017-03-18. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Mexico begins five-day shutdown to fight swine flu - News - Muzi.com". Dailynews.muzi.com. Archived from the original on 3 May 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "U.S. H1N1 Victim Visited Texas Mall". CBS News. 2009-04-30. Archived from the original on 2013-12-21. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Scott Weese (2009-04-29). "Updated H1N1 (swine) influenza outbreak numbers from WHO : Worms and Germs Blog". Archived from the original on 2009-12-24.
- ^ Talaga, Tanya (2009-04-30). "N.S. has first Canadian person-to-person flu case". The Star. Toronto. Archived from the original on 2019-02-22. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Irish man treated for swine flu". BBC. 2009-04-30. Archived from the original on 2016-03-05. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Stevenson, Reed (2009-04-30). "Dutch confirm swine flu case in three year-old". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2009-05-05. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Switzerland confirms first case of swine flu". Reuters. 2009-04-30. Archived from the original on 2009-05-05. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Miller, Beth; Brown, Robin; Riley, Emily (3 May 2009). "More than 350 treated at UD". delawareonline. The News Journal. Archived from the original on 3 May 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Three new cases of swine flu confirmed in Britain" China View 1 May 2009
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 7". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ 51 H1N1 flu infections confirmed in Canada - CTV News Archived 2017-03-18 at the Wayback Machine. Ctv.ca (2009-05-01)
- ^ "Asia-Pacific | Hong Kong 'flu' hotel sealed off". BBC News. 2007-04-18. Archived from the original on 2017-03-19. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "1st H1N1 case confirmed in HK". Hong Kong SAR. 2009-05-01. Archived from the original on 4 June 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Director of Health issues isolation order to control human swine flu". Centre for Health Protection. 2009-05-31. Archived from the original on 2011-07-16. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Jensen, Marie Joo Kim (2008-12-16). "Dansk kvinde smittet med H1N1-influenza efter New York-rejse" [Danish woman infected with the H1N1 flu after the New York trip]. BT (in Danish). Archived from the original on 2018-11-21. Retrieved 2013-12-20.
- ^ "Sujets suspects et cas de nouvelle grippe A(H1N1) en France" [Suspicious subjects and cases of new influenza A (H1N1) in France] (PDF) (in French). 2009-05-01. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-05-20. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ "FACTBOX-Mexico shuts down to stem deadly swine flu outbreak". Reuters. 2009-04-30. Retrieved 2024-07-15.
- ^ HPA. "First case of onward human to human swine flu transmission in England confirmed". Archived from the original on 4 May 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "H1N1 virus hits campus | UWIRE". Archived from the original on 2009-05-12. Retrieved 2009-08-01.
- ^ a b "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 9". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Worker may have passed H1N1 to Alberta pigs". CTV. 2009-05-02. Archived from the original on 2009-05-03. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ "Update: swine flu travel advice". The Guardian. 5 May 2009. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ "1st South Korea case". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Werner, Erica (2 May 2009). "More schools shut as swine flu spreads in US". Yahoo! News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 5 May 2009. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 17, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ "Arab health ministers meet on swine flu". KUNA. 2009-05-03. Archived from the original on 2024-06-09. Retrieved 2018-01-28.
- ^ a b "Swine flu epidemic on decline: Mexico". CBC. 2009-05-03. Archived from the original on 2017-03-19. Retrieved 2018-01-28.
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) — update 13". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "New Influenza A (H1N1): Number of laboratory confirmed cases and deaths". World Health Organization. 4 May 2009. Archived from the original on 7 May 2009. Retrieved 13 June 2013.
- ^ "Canada identifies first severe flu case". Brisbane Times. Australia. May 5, 2009. Archived from the original on 28 December 2014. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 15". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Second U.S. death linked to swine flu, officials say". CNN Health. CNN. 2009-05-05. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2013-12-20.
- ^ "Texas H1N1 victim had chronic respiratory..." Archived from the original on February 26, 2012. Retrieved May 8, 2009.
- ^ Pregnant women more at risk from swine flu - Health - Cold and flu - Swine flu - NBC News . NBC News (2009-05-14)
- ^ Mcneil Jr., Donald G. (2009-05-09). "Other Illness May Precede Worst Cases of Swine Flu". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2013-05-21. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC H1N1 Flu|Information for Concerned Parents and Caregivers Archived 2013-12-29 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ "Americas | US navy halts aid vessel over flu". BBC News. 2009-04-28. Archived from the original on 2009-05-09. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC H1N1 Flu | Archived 2009-05-06 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov (2009-08-07)
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 17". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "ASEAN swine flu summit in Bangkok". Archived from the original on 2009-08-30. Retrieved 2009-08-07.
- ^ "H5N1: Guatemala: First case of H1N1". Archived from the original on 2011-07-17.
- ^ Spanish-language reportage [permanent dead link]
- ^ "First H1N1 flu case reported in Poland-PAP news agency". Reuters. 2009-05-06. Archived from the original on 2016-01-27. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Sweden confirms first case of H1N1 flu". Reuters. 2009-05-06. Archived from the original on 2016-01-27. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 20". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Confirmaron el primer caso de gripe porcina en la Argentina". lanacion.com. 2009-05-07. Archived from the original on 2009-05-10. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Stabroek News - Brazil confirms 4 cases of H1N1 flu-minister". 2009-05-08. Archived from the original on 2013-02-03. Retrieved 2009-08-01.
- ^ Channel NewsAsia - Brazil confirms first domestically transmitted H1N1 flu case Archived 2017-08-10 at the Wayback Machine. channelnewsasia.com (2009-05-09)
- ^ "Reports suggest elderly Alberta woman with swine flu has died". cbc.ca. May 7, 2009. Archived from the original on 11 May 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Swine-flu inspectors in improper gear got virus". CBC News. 20 July 2009. Archived from the original on 3 September 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ International - Second case of H1N1 flu in the Netherlands Archived 2013-12-21 at the Wayback Machine. nrc.nl (2009-05-07)
- ^ H1N1 Influenza Center|From the Publishers of the New England Journal of Medicine Archived 2017-06-02 at the Wayback Machine. H1n1.nejm.org
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 22". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Three Japanese test positive for swine flu". AFP. May 8, 2009T. Archived from the original on January 24, 2013. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Panama's first swine flu case confirmed". The Sydney Morning Herald. 2009-05-09. Archived from the original on 2012-04-26. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Panama reports first swine flu case Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine. Thaindian.com (2009-05-09)
- ^ Panama confirms first case of A/H1N1 flu_English_Xinhua. News.xinhuanet.com (2009-05-09)
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 23". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "First confirmed case of swine flu in Australia". News Limited. 9 May 2009. Archived from the original on 11 May 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Brasil permanece com 30 casos suspeitos da nova gripe". g1.globo.com. 2009-05-09. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Muere primer tico contagiado de gripe AH1N1" (in Spanish). La Nación. 2009-05-09. Archived from the original on May 13, 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Costa Rica Sees 1st Swine Flu Death". ABC News. 2009-05-09. Archived from the original on 29 June 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Tres niños con gripe AH1N1 fueron contagiados por tico que falleció esta madrugada" (in Spanish). La Nación. 2009-05-09. Archived from the original on 13 May 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Japan Confirms 4th Case Of Swine Flu". NHK. 10 May 2009. Archived from the original on 15 July 2009. Retrieved 9 June 2013.
- ^ "To norske studenter smittet av svineinfluensa". vg.no. 2009-05-09. Archived from the original on 17 July 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Washington Confirms First H1N1 Death Archived 2017-03-18 at the Wayback Machine. Emaxhealth.com (2009-05-11)
- ^ WHO|Influenza A(H1N1) - update 23. Who.int (2009-05-09)
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 18, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 24". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "China Has First H1N1 (Swine Flu) Case". Archived from the original on 2009-05-26.
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 25". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 26". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on May 12, 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Yukon confirms 1st swine flu case". CBC. 2009-05-12. Archived from the original on 20 May 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Ministerio de Sanidad y Política Social - Gabinete de Prensa - Notas de Prensa. Msc.es Archived May 14, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 27". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ HLN Mexicaanse griep - Gentenaar van 28 eerste Belg met Mexicaanse griep (853127) Archived 2017-03-18 at the Wayback Machine. Hln.be
- ^ Canal 13 - Telemetro.com - Panamá - Salud revela 10 nuevos casos de H1N1, en total son 39 Archived 2012-02-19 at the Wayback Machine. Telemetro.com
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 28". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 2010-07-17. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ "Tweede geval van Mexicaanse griep in België" [Second case of swine flu in Belgium]. Het Laatste Nieuws (in Dutch). Kobbegem, Belgium. 2009-05-14. Archived from the original on 2017-03-18. Retrieved 2013-12-21.
- ^ "Confirman tres nuevos casos de contagiados con el virus de la nueva influenza en Colombia" [Confirmed three new cases infected with the new influenza virus in Colombia]. El Tiempo (in Spanish). Bogotá, Colombia. 2009-05-14. Archived from the original on 2017-03-18. Retrieved 2013-12-21.
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 29". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ 1st Arizona A(H1N1) death reported, 4th in US - World - GMANews.TV - Official Website of GMA News and Public Affairs - Latest Philippine News. GMANews.TV Archived May 19, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ 4th and 5th U.S. Deaths Linked to H1N1 Flu; Number of Sickened Nationwide Nears 5,000 — Attorney At Law Archived 2009-05-18 at the Wayback Machine. Attorneyatlaw.com
- ^ Fox, Maggie (2009-05-15). "U.S. logs fifth H1N1 swine flu death, in Texas". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2009-05-18. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Out, Count Us. (2009-05-16) U.S. logs fifth H1N1 swine flu death « Count Us Out. Countusout.wordpress.com Archived July 8, 2012, at archive.today
- ^ "Malaysia confirms first case of A(H1N1) flu (Update 2)". Archived from the original on 9 October 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2013.
- ^ "43 Casos Confirmados" (in Spanish). Telemetro. 2009-05-15. Archived from the original on 19 February 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "India confirms first case of H1N1 flu". Reuters. 2009-05-16. Archived from the original on 2020-01-28. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "First domestic case of H1NI flu infection confirmed in Japan". The Japan Times. May 16, 2009. Archived from the original on 22 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Kitano, Masayuki (May 16, 2009). "Western Japan city to close schools due to new flu". Reuters. Archived from the original on 28 May 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "A (H1N1): Second confirmed case in Malaysia (Update 4)". Archived from the original on 9 October 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2013.
- ^ prensa.com Panamá - Panorama Archived 2011-05-13 at the Wayback Machine. Mensual.prensa.com
- ^ "First case of swine flu confirmed in Turkey - health minister". Archived from the original on August 14, 2009. Retrieved May 3, 2010.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 19, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 32". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Pandemic potential of a strain of influenza A (H1N1): early findings Archived 2009-08-25 at the Wayback Machine, 18 May 2009
- ^ "96 cases of new flu confirmed in Japan". NHK WORLD. 2009-05-18. Archived from the original on 20 October 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Over 1,000 flu cases estimated in Japan". NHK WORLD. 2009-05-18. Archived from the original on 22 March 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Government asks schools to close". NHK WORLD. 2009-05-18. Archived from the original on 21 August 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "New York principal's death linked to flu virus, hospital says". CNN.com. 2009-05-18. Retrieved 2024-07-15.
- ^ Yaniv, Oren; Kennedy, Helen (2009-05-18). "Assistant principal Mitchell Wiener dies from complications of swine flu". Daily News. New York. Archived from the original on 2009-05-21. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 33". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ 6th, 7th H1N1 Flu Deaths Confirmed in U.S., Vaccine Delayed for Months — Attorney At Law Archived 2009-11-17 at the Wayback Machine. Attorneyatlaw.com
- ^ "191 flu cases confirmed in Japan". NHK WORLD. 2009-05-18. Archived from the original on 22 February 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ a b c Influensa A(H1N1): Oppdatering om situasjonen i Norge - Folkehelseinstituttet. Fhi.no Archived May 19, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Chile, uno de los principales focos vecinos de la gripe porcina Archived 2009-05-23 at the Wayback Machine. lanacion.com
- ^ Reuters AlertNet - Taiwan reports first H1N1 flu case Archived 2009-09-30 at the Wayback Machine. Alertnet.org (2009-05-20)
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 34". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Fox, Maggie (2009-05-20). "U.S. officials consider bumping up flu shot season". MedlinePlus. Reuters Health. Archived from the original on 2009-05-28.
- ^ "Utah reports first flu-related death, nation's 9th". USA Today. 2010-08-06. Archived from the original on 2009-05-23.
- ^ CDC: H1N1 Still Poses Threat Pork - Industry News Archived 2010-12-19 at the Wayback Machine. Porkmag.com (2009-05-21)
- ^ "Japan's tally of confirmed A/H1N1 cases reaches 236". 2009-05-20. Archived from the original on May 22, 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "New flu infection confirmed in Tokyo and Kawasaki". 2009-05-21. Archived from the original on 23 March 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ A(H1N1) spreads in Asia; Tokyo has first cases - World - GMANews.TV - Official Website of GMA News and Public Affairs - Latest Philippine News. GMANews.TV Archived May 22, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 35". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Tabuchi, Hiroko (2009-05-22). "Spread of Swine Flu Puts Japan in Crisis Mode". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2017-03-19. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 36". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Fukue, Natsuko (2009-05-23). "Flu policy given more flexibility". The Japan Times. Japan. Archived from the original on 2017-03-18. Retrieved 2013-12-21.
- ^ "Governor's Comment Regarding New Strain Influenza in Saitama (PDF)" (PDF). 2009-05-22. Retrieved 2 August 2010.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Duque confirms first A(H1N1) RP case - INQUIRER.net, Philippine News for Filipinos Archived 2009-08-03 at the Wayback Machine. Newsinfo.inquirer.net (2009-05-22)
- ^ "WHO; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 36". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Iceland Review Online: Daily News from Iceland, Current Affairs, Business, Politics, Sports, Culture Archived 2012-02-17 at the Wayback Machine. Icelandreview.com
- ^ "H1N1 greinist á Íslandi" (in Icelandic). 23 May 2009. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 20, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ "Two more Victorians diagnosed with swine flu". News.com.au. 2009-05-24. Archived from the original on 2009-05-27. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Eighteen U.S. Soldiers In Kuwait Have H1N1 Flu - Radio Free Europe / Radio Liberty © 2010 Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine. Rferl.org (2009-05-24)
- ^ WHO|Influenza A(H1N1) - update 38. Who.int (2009-05-25)
- ^ Australian swine flu cases rise to 44 Archived 2020-01-29 at the Wayback Machine. News.brisbanetimes.com.au (2009-05-26)
- ^ "Second swine flu case in Republic". BBC News. 2009-05-25. Archived from the original on 2009-05-28. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ WHO|Influenza A(H1N1) - update 39. Who.int (2009-05-26)
- ^ Suspenden clases por la gripe porcina Archived 2009-05-29 at the Wayback Machine. lanacion.com
- ^ Four SA swine flu cases - ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation) Archived 2020-02-20 at the Wayback Machine. Abc.net.au (2009-05-27)
- ^ Number of Vic flu cases continues to climb - ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation) Archived 2010-12-04 at the Wayback Machine. Abc.net.au (2009-05-27)
- ^ "Department of Health - The website you tried to access has been decommissioned" (PDF). www.healthemergency.gov.au. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-02-22. Retrieved 2009-05-27.
- ^ Reuters AlertNet - Puerto Rico reports first confirmed H1N1 flu case Archived 2009-06-01 at the Wayback Machine. Alertnet.org (2009-05-26)
- ^ WHO|Influenza A(H1N1) - update 40. Who.int (2009-05-27)
- ^ Se duplicaron los casos de gripe porcina en 48 horas Archived 2009-06-12 at the Wayback Machine. lanacion.com
- ^ Salud Pública reporta dos casos de gripe AH1N1 Archived 2009-05-30 at the Wayback Machine. DiarioLibre.com
- ^ "Greece confirms 3rd swine flu case". GMANews.tv. 2009-05-27. Archived from the original on 30 June 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ First suspected swine flu case reported in Romania_English_Xinhua. News.xinhuanet.com (2009-04-30)
- ^ "Singapore records first A (H1N1) flu case". Archived from the original on 7 September 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2013.
- ^ "New flu cases bring total to 186". BBC News. 2009-05-27. Archived from the original on 2009-06-07. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ La Gripe A llegó con polémica a Uruguay - Diario EL PAIS - Montevideo - Uruguay Archived 2012-07-17 at the Wayback Machine. Elpais.com.uy (2009-05-28)
- ^ "Top doctor calls for swine flu calm". The Age. Melbourne. 2009-05-29. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Singapore confirms three more Influenza A/H1N1 cases 2009-05-28
- ^ Swine flu - everything you need to know : Directgov - Swine flu. Direct.gov.uk Archived December 22, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ La Vida - Laboratorios confirman dos primeros casos de gripe A en Bolivia. ADN.es (2009-05-28)
- ^ Venezuela reports first confirmed H1N1 flu case. asiaone.com (2009-05-29)
- ^ WHO|Influenza A(H1N1) - update 41. Who.int (2009-05-29)
- ^ "Further swine flu cases confirmed". BBC News. 2009-05-29. Archived from the original on 2009-06-03. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Hungary confirms first H1N1 flu case". Reuters. 2009-05-29. Archived from the original on 2012-11-14. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Ya son 6 los casos de gripe A H1N1 - Diario EL PAIS - Montevideo - Uruguay Archived 2009-09-04 at the Wayback Machine. Elpais.com.uy (2009-05-29)
- ^ "Τέταρτο κρούσμα της νέας γρίπης Α στην Ελλάδα Μία 23χρονη Ελληνίδα είναι το νέο κρούσμα της νέας γρίπης στην χώρα. Το Κέντρο Αναφοράς Γρίπης Νοτίου Ελλάδας (Ινστιτούτο Παστέρ) επιβεβαίωσε το τέταρτο κρούσμα". Kathimerini. 2009-05-29. Archived from the original on 2012-08-04. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ First swine flu case confirmed in Estonia Archived 2020-02-20 at the Wayback Machine. Monsters and Critics (2009-05-30)
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 21, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ "9 more swine flu cases in Dominican Republic". MLive.com. 2009-05-31. Archived from the original on 2013-05-21. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ WHO|Influenza A(H1N1) - update 42. Who.int (2009-06-01)
- ^ Swine flu case confirmed in Bulgaria - Bulgaria Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine. The Sofia Echo (2009-06-01)
- ^ The Royal Gazette. The Royal Gazette (2009-06-02)
- ^ "Middle East Online". Archived from the original on 2010-12-04. Retrieved 2009-09-01.
- ^ "Luxembourg confirms first H1N1 flu case". Reuters. 2009-06-02. Archived from the original on 2020-10-04. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Nicaragua Registers 1st Case of A/H1N1 Flu - en.chinagate.cn". Archived from the original on 2011-07-07.
- ^ WHO|Influenza A(H1N1) - update 43. Who.int (2009-06-03)
- ^ Andy Sambidge. "Saudi confirms first swine flu case - Healthcare - ArabianBusiness.com". Archived from the original on 2009-06-08. Retrieved 2009-09-01.
- ^ "Barbados records first case of "swine flu"". Archived from the original on June 8, 2009. Retrieved September 1, 2009.
- ^ "A (H1N1) flu: M'sia reports 3 more cases". Archived from the original on 24 December 2013. Retrieved 12 May 2013.
- ^ http://www.trinidadexpress.com/index.pl/article?id=161486326 [permanent dead link]
- ^ a b WHO|Influenza A(H1N1) - update 44. Who.int (2009-06-05)
- ^ Health Emergency - Children under 5 years of age can now be vaccinated against influenza using Vaxigrip® or Influvac® seasonal influenza vaccine. Healthemergency.gov.au (2010-06-01) Archived June 3, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ First H1N1 case confirmed in Cayman. Caribbean Net News (2009-06-05) Archived June 8, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Pregnant girl dies with AH1N1 flu". Diario Libre. 2009-06-05. Archived from the original on 8 June 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "A (H1N1) flu: Malaysia confirms 7th case (Update)". Archived from the original on 24 December 2013. Retrieved 12 May 2013.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 22, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ https://finance.yahoo.com/news/Martinique-confirms-islands-apf-15459249.html?.v=1 [permanent dead link]
- ^ Only one of 13 from Sth Auck daycare has influenza A|NATIONAL News Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine. Tvnz.co.nz (2009-06-07)
- ^ WHO|Influenza A(H1N1) - update 45. Who.int (2009-06-08)
- ^ Dominica confirms 1st case of swine flu - Worldnews.com Archived 2009-12-04 at the Wayback Machine. Article.wn.com (2009-06-08)
- ^ Influenza A (H1N1) Swine Flu - Update Sixty-four. Moh.govt.nz Archived June 12, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Colombia confirms first swine flu death Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine. My Sinchew (2009-06-10)
- ^ "BULLETIN EPIDEMIOLOGIQUE GRIPPE A(H1N1)". Institut de veille sanitaire. 2009-06-10. Archived from the original on 2009-10-07. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Guatemala: muere paciente con gripe H1N1 Archived 2009-06-14 at the Wayback Machine. Laprensagrafica.com
- ^ Detecta Guatemala ocho nuevos casos de influenza Archived 2011-07-16 at the Wayback Machine. Sdpnoticias.com
- ^ "WHO declares swine flu pandemic". BBC News. 2009-06-11. Archived from the original on 2020-04-09. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "WHO declares first 21st century flu pandemic". Reuters. 2009-06-11. Archived from the original on 2009-08-30. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ News Blog: WHO: H1N1 spread has reached pandemic level Archived 2017-03-19 at the Wayback Machine. Scientificamerican.com (2009-06-11)
- ^ Normal.dot Archived 2012-02-22 at the Wayback Machine. (PDF)
- ^ a b "Palestinians report first case of H1N1 flu". Reuters. 2009-06-10. Archived from the original on 2009-06-12. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Confirman sexto paciente de gripe A en Cuba, primero que no es extranjero" (in Spanish). Retrieved 2 August 2010.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Middle East Online. Middle East Online (2009-06-12) [permanent dead link]
- ^ "First Isle of Man swine flu case". BBC News. 2009-06-12. Archived from the original on 2017-06-28. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Sociedad - Confirman 2 primeros casos "locales" en Bolivia, que suma 7 afectados gripe A - ADN.es". Archived from the original on 2009-10-04. Retrieved 2009-06-13.
- ^ ROYCE CHEAH. "A(H1N1): Twelfth case confirmed in Malaysia (Updated)". Archived from the original on 2009-09-02. Retrieved 2017-06-05.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 23, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ "A (H1N1): Malaysia confirms 5 more, taking total to 17 (Update)". Archived from the original on 2009-08-31. Retrieved 2017-06-05.
- ^ "First UK swine flu patient death". BBC News. 2009-06-15. Archived from the original on 2019-01-08. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Sri Lanka detects first H1N1 flu case". Reuters. 2009-06-16. Archived from the original on 2009-06-26.
COLOMBO, June 16 (Reuters) - Sri Lanka has identified its first case of the H1N1 flu virus in a young patient who arrived from Australia over the weekend, the government said on Tuesday."We...
- ^ "Monaco swine flu". Archived from the original on 2018-01-28. Retrieved 2018-03-01.
- ^ DHARMENDER SINGH. "A (H1N1): First locally-transmitted case confirmed (Update)". Archived from the original on 2009-09-01. Retrieved 2017-06-05.
- ^ "Boy, 9, becomes first swine flu case in Antigua". Taiwan News. 2009-06-19. Archived from the original on 2009-06-26.
- ^ "First A/H1N1 flu case detected in Bangladesh". People's Daily. 2009-06-19. Archived from the original on 2012-10-14.
- ^ "Ethiopia confirms first cases of H1N1". Reuters. 2009-06-19. Archived from the original on 2009-06-22.
- ^ "Health news". Syracuse News. 2009-06-19. Archived from the original on 2009-09-11.
- ^ "Update No. 48 - Duque Reports High Risk Patient who Dies of Heart Attack Found with A(h1N1);84% if all Reported Cases have Fully Recovered". Department of Health. Archived from the original on 30 June 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Kami, Aseel (2009-06-24). "Iraq confirms first cases of H1N1 flu virus". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2009-06-27. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Sekularac, Ivana (2009-06-24). "Serbia confirms first case of H1N1 flu". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2009-11-14. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 24, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 25, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ Novi grip stigao u BiH!. Accessed 2009-09-09. Archived July 8, 2009, at the Wayback Machine 2009-09-10.
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | June 29 | Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) resistance found [English article]". Archived from the original on 2009-07-12. Retrieved 2009-06-29.
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | June 29 | Kenya (KE) | First case confirmed". Archived from the original on 2009-08-02. Retrieved 2009-06-29.
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | June 29 | Mauritius (MU) | First case confirmed". Archived from the original on 2009-07-09. Retrieved 2009-06-29.
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | June 29 | Nepal (NP) | First case confirmed". Archived from the original on 2009-08-02. Retrieved 2009-06-29.
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | July 1: Guam (GU): First case confirmed". Archived from the original on 2009-07-04. Retrieved 2009-07-01.
- ^ "Health Emergency - First NSW death". Archived from the original on 2009-09-10.
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | July 2: Japan (JP): Oseltamivir resistance found". Archived from the original on 2011-07-24. Retrieved 2009-07-02.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 26, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ "Primeiro caso de contágio interno de Gripe A". Archived from the original on 2009-08-19. Retrieved 2018-07-28.
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | July 4: Syria (SY): First case confirmed". Archived from the original on 2009-07-07. Retrieved 2009-07-05.
- ^ A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline|July 5: Peru (PE): First 2 deaths confirmed Archived 2009-07-07 at the Wayback Machine. Trancy.net
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 58. Who.int (2009-07-06)
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | July 8: Belize (BZ): First case confirmed". Archived from the original on 2011-07-24. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 27, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-06-18 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ "Principales noticias de Colombia y el mundo - ELTIEMPO.COM -> Joven de 25 años se convirtió en la sexta víctima mortal de nueva gripa en Colombia". Archived from the original on 2012-07-31.
- ^ eBand|Jornalismo|Brasil registra terceira morte por gripe suína Archived 2020-02-20 at the Wayback Machine. Band.com.br
- ^ Ecuador reports 3rd death of A/H1N1 flu_English_Xinhua. News.xinhuanet.com (2009-07-14)
- ^ Singapore's first #H1N1 related death » Malaysian Medical Resources Archived 2016-01-27 at the Wayback Machine. Medicine.com.my (2009-07-21)
- ^ Heavens, Andrew (2009-07-16). "Sudan reports first H1N1 flu case". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2016-01-27. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Hawaii Reports First H1N1 Death". Archived from the original on July 7, 2009. Retrieved August 21, 2009.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 28, 2008-2009 Season Archived 2017-12-25 at the Wayback Machine. Cdc.gov
- ^ "Gripe.- Confirmado el primer caso de nueva gripe en Venezuela en un ciudadano que viajó a Panamá". www.europapress.es (in Spanish). 2009-05-29. Archived from the original on 2020-04-21. Retrieved 2019-10-27.
- ^ "Earth Times: news/278016,singapore-reports-first-death-related-to-h1n1-influenza.html". www.earthtimes.org. Archived from the original on 2017-09-06. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | July 19: Egypt (EG): First death confirmed". Archived from the original on 2011-07-24. Retrieved 2009-07-20.
- ^ "Georgia reports its first case of H1N1 flu". Reuters. 2009-07-18. Archived from the original on 2016-01-27. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Silobreaker: Document Not Found". Archived from the original on 2009-09-11. Retrieved 2009-08-21.
- ^ Guam confirms first H1N1 death as CNMI sees two cases. Islands Business (2009-07-21) Archived February 23, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Namibia: H1N1 Comes Home Archived 2012-10-11 at the Wayback Machine. allAfrica.com (2009-07-24)
- ^ Quebec man had Tamiflu-resistant H1N1 flu virus - CTV News Archived 2017-03-18 at the Wayback Machine. Ctv.ca (2009-07-21)
- ^ "COM-FSM: First Case of H1N1 in FSM". Archived from the original on 2011-07-21.
- ^ "Guam reports its first swine flu-related death". Archived from the original on 2012-01-21.
- ^ "H5N1: Hungary reports first H1N1 death". Archived from the original on 2009-07-25.
- ^ "Tonga records flu death - Fiji Times Online". Archived from the original on 2009-07-27. Retrieved 2009-08-25.
- ^ "BAM Intel: H1N1 Update - Vaccine Test, WHO Ceases Counting, More Tamiflu-Resistant Cases Found". Archived from the original on 2009-09-11.
- ^ http://ca.news.yahoo.com/s/capress/090723/health/health_ml_arabs_swine_flu_2[permanent dead link]
- ^ [1][permanent dead link]
- ^ Malaysia's first A(H1N1)-related death. Asiaone.com (2009-07-24)
- ^ First confirmed N.S. death from H1N1 flu - Health - Living - Nova News Now - The Digby Courier. Nova News Now
- ^ H5N1: First H1N1 death in the Cayman Islands. Crofsblogs.typepad.com (2009-07-25)
- ^ "Indonesia reports first death from H1N1 flu". Reuters. 2009-07-26. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "School: No shortage of volunteers for swine flu vaccine trials". CNN. 2009-07-26. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 29, 2008-2009 Season. Cdc.gov
- ^ Rolleiv Solholm. "The Norway Post - Swine flu closes youth camp". Archived from the original on 2009-07-29.
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 59. Who.int
- ^ "No reason for swine flu panic in Germany, says expert". Deutsche Welle. 2009-07-28. Archived from the original on 2009-08-01.
- ^ "Silobreaker: Document Not Found". Archived from the original on 2009-09-11. Retrieved 2009-08-28.
- ^ "Kosovo registers first case of H1N1 flu virus". Archived from the original on 2011-06-04.
- ^ "St. Kitts records 1st H1N1 death". Caribseek. 28 July 2009. Archived from the original on July 8, 2011.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia reports first death from H1N1 flu". SahilOnline. 27 July 2009. Archived from the original on September 20, 2009.
- ^ "Tamiflu Resistance in Pandemic H1N1". Archived from the original on 2011-07-17.
- ^ "Thai baby born infected with swine flu". Archived from the original on 2011-06-17.
- ^ H1N1 (swine flu) in the World Archived 2009-08-04 at the Wayback Machine. H1n1.flu-virus.org
- ^ "NHS 'to be swamped by second wave of swine flu' - mirror.co.uk". Daily Mirror. 2009-07-28. Archived from the original on 2009-09-01.
- ^ "Military planning for possible H1N1 outbreak". CNN. 2009-07-29. Archived from the original on 8 August 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Azerbaijan reports first two H1N1 flu cases". 2009-07-30. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline|July 30: Belgium (BE): First death confirmed Archived 2010-06-20 at the Wayback Machine. Trancy.net (2009-07-30)
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | July 30: France (FR): First death confirmed". Archived from the original on 2010-06-20. Retrieved 2009-07-30.
- ^ "Pandemic Preparedness". Archived from the original on 2011-07-13.
- ^ "Lebanon records first H1N1 death". 2009-07-30. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ FLASH: First case of A(H1N1) flu registered in Moldova. Totul.md
- ^ Karam, Souhail (2009-07-30). "Saudi Arabia reports second H1N1 flu death". Reuters. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ AFP: Taiwan reports first death from swine flu. Google.com (2009-07-30)
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 60. Who.int
- ^ Hardach, Sophie (2009-07-31). "UPDATE 4-Cruise ship has 60 flu cases, company says no H1N1". Reuters. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Swine flu found among pigs in NSW Archived 2009-12-12 at the Wayback Machine. News.ninemsn.com.au
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 30, 2008-2009 Season. Cdc.gov
- ^ First swine flu death in India - India - The Times of India. Timesofindia.indiatimes.com (2009-08-04)
- ^ a b "Tweede dode Mexicaanse griep in Nederland". 2009-08-21. Archived from the original on 2009-09-17.
- ^ "Islands Business - Solomon Islands confirmed swine flu case". Archived from the original on 2012-02-23. Retrieved 2009-09-01.
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 61. Who.int
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 31, 2008-2009 Season. Cdc.gov
- ^ "Costa Rican president sick with swine flu". CNN. 2009-08-12. Archived from the original on 3 September 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 62 (revised 21 August 2009). Who.int
- ^ "News - Flu Outbreak: Madagascar announces first swine flu death". Archived from the original on 2012-08-03.
- ^ "News - Africa: DRC: First swine flu case". Archived from the original on 2009-09-11.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 32, 2008-2009 Season. Cdc.gov
- ^ a b "A (H1N1): 2 more die, health curfew if mortality rate reaches 0.4pc (Update 4)". TheStar Online. 2009-08-17. Archived from the original on 2009-09-01. Retrieved 2017-06-05.
- ^ "A(H1N1): Toll rises to 67 with three more deaths". Sun2Surf. 2009-08-18. Archived from the original on 2009-08-21. Retrieved 2009-08-21.
- ^ Kuwait health chiefs confirm first swine flu death - Healthcare Archived 2010-03-14 at the Wayback Machine. ArabianBusiness.com (2009-08-20)
- ^ "Influenza A(H1N1) hits record high with 569 cases (Update)". TheStar Online. 2009-08-20. Archived from the original on 2009-09-04. Retrieved 2009-08-19.
- ^ Why is A (H1N1) death rate in Malaysia four times the global case fatality rate? « Lim Kit Siang. Blog.limkitsiang.com (2009-08-14)
- ^ H5N1: WHO studies Malaysian H1N1 death rate. Crofsblogs.typepad.com (2009-08-20)
- ^ Quilodran, Federico (21 August 2009). "Swine flu jumps again — to turkeys in Chile — but scientists see no dangerous mutation yet". Star Tribune. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 28 August 2009. Retrieved 9 June 2013.
- ^ "RKI Influenza". Archived from the original on 2009-08-07. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ^ Oman Reports Two Deaths; Govt Schools to Reopen after Eid - Worldnews.com. Article.wn.com (2009-08-21)
- ^ UAE reports first swine flu death Archived 2013-05-18 at the Wayback Machine, AFP, August 21, 2009
- ^ "RTÉ News: First death in NI from swine flu". 2009-08-21. Archived from the original on 2009-08-26.
- ^ New Caledonia sees its first death linked to swine flu. France24 (2009-08-21) Archived August 25, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 33, 2008-2009 Season. Cdc.gov
- ^ a b WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 63. Who.int
- ^ "Earth Times: news/282497,greece-reports-first-death-from-swine-flu.html". www.earthtimes.org. Archived from the original on 2017-09-06. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ "RKI Influenza". Archived from the original on 2009-07-17. Retrieved 2009-08-25.
- ^ "H5N1: Kyrgyzstan reports first two H1N1 cases". Archived from the original on 2011-07-17.
- ^ "Teacher's death due to A(H1N1); Death toll reaches 69". Sun2Surf. 2009-08-24. Archived from the original on 2009-08-28.
- ^ "A (H1N1): Latest victim is 3-yr-old; death toll rises to 70". TheStar Online. 2009-08-25. Archived from the original on 2009-08-28. Retrieved 2017-06-05.
- ^ "H5N1: Angola reports first H1N1 cases". Archived from the original on 2009-09-01.
- ^ "RKI Influenza". Archived from the original on 2009-07-07. Retrieved 2009-08-26.
- ^ "Overweight young woman is H1N1 victim 71". Malaysian Insider. 2009-08-26. Archived from the original on 2009-09-13. Retrieved 2009-08-26.
- ^ The first death of swine flu in Syria Archived 2012-03-20 at the Wayback Machine. Zawya.com
- ^ Chand, Sudeep (2009-08-27). "UN warns over swine flu in birds". BBC News. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ News - New ECDC pandemic risk assessment Archived 2009-09-22 at the Wayback Machine. Ecdc.europa.eu (2009-08-21)
- ^ "RKI Influenza". Archived from the original on 2009-08-02. Retrieved 2009-08-30.
- ^ H5N1: Bangladesh: First H1N1 death. Crofsblogs.typepad.com (2009-08-30)
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | August 29: Brazil (BR): 602 deaths confirmed". Archived from the original on 2010-06-20. Retrieved 2009-08-30.
- ^ CDC - Influenza (Flu)|Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update Week 34, 2008-2009 Season. Cdc.gov
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 64. Who.int
- ^ Bronstein, Hugh (2009-08-31). "Colombia says president has swine flu". Reuters. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ a b WHO EMRO - Surveillance, Forecasting and Response (CSR). Emro.who.int
- ^ a b "Home Page - Gulf in the Media". Archived from the original on 2011-07-22.
- ^ Brazil tops worldwide H1N1 deaths, officials say - Brazil tops worldwide H1N1 deaths, officials say Archived 2011-07-27 at the Wayback Machine. Vovnews.Vn (2009-08-31)
- ^ "Sweden's first swine flu death confirmed - The Local". 2009-08-31. Archived from the original on 2009-09-03.
- ^ "blogmacau.info | First swine flu death in Macau". Archived from the original on 2011-07-21.
- ^ "Gripe A (H1N1): Casos em Portugal mais do que duplicaram na última semana e chegam aos 5123". noticias.sapo.pt. 2009-09-02. Archived from the original on 5 September 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Deadly H1N1: Sarawakian woman becomes 73rd victim". Malaysiakini. 2009-09-03. Archived from the original on 2009-09-06.
- ^ "Norway announced 1st confirmed victim of swine flu, a Danish truck driver". metronews.ca. 2009-09-03. Archived from the original on 2011-06-04. Retrieved 2009-09-04.
- ^ "Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR)". 2019-07-10. Archived from the original on 2009-09-10.
- ^ "CDC: Any healthy child can get H1N1 flu - UPI.com". Archived from the original on 2009-09-04.
- ^ "CDC: Older Kids May Have Greater H1N1 Risk". CBS News. 2009-09-03. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Swine Flu: First death confirmed in Italy". adnkronos.com. 2009-09-04. Archived from the original on 7 September 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 65. Who.int
- ^ "Ecuador's presidential security chief dies of A/H1N1 flu_English_Xinhua". Archived from the original on 2009-09-11.
- ^ "H5N1: Ecuador: President's security chief dies of H1N1". Archived from the original on 2009-09-12.
- ^ "Forsíða - Landslæknin". landslaeknin.stps.dk.
- ^ Namibia: Country Confirms First Flu Death. allAfrica.com (2009-09-07)
- ^ "Suriname H1N1 flu cases reach 67, with one death". caribbeannetnews.com. 2009-09-08. Archived from the original on August 5, 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Madagascar announces first swine flu death". iol.co.za. 2009-09-13. Archived from the original on 5 August 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Penny Arcade - Feeling Sick?". Archived from the original on 2009-09-12.
- ^ "Slashdot Games Story | Swine Flu Outbreak At PAX". 9 September 2009. Archived from the original on 2011-06-12.
- ^ "Confirmed H1N1 cases at PAX | ITworld". 2009-09-09. Archived from the original on 2009-09-16.
- ^ Visceral Gameplay. Penny Arcade
- ^ "Malawi has 1st swine flu case". oregonlive.com. 2009-09-09. Archived from the original on 9 June 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Thornhill, James (2009-09-11). "Australia reports first Tamiflu-resistant H1N1 case". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2012-07-07.
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 66. Who.int
- ^ 1st H1N1 death in Mozambique. Straitstimes.com (2009-09-15)
- ^ a b Triggle, Nick (2009-09-17). "Fears swine flu 'on the way back'". BBC News. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ a b "Nieuwe Influenza A (H1N1)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2009-10-01.
- ^ Martinique reports first death from swine flu - CTV News. Ctv.ca (2009-09-18)
- ^ "Influenza A(H1N1): Death toll now 77". NST Online. 2009-09-19. Archived from the original on 23 September 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 67. Who.int
- ^ Barriaux, Marianne. (2009-09-21) AFP: China begins mass vaccinations for swine flu. Google.com
- ^ Government Orders Additional H1N1 Vaccine Archived 2009-10-08 at the Wayback Machine. Medicalnewstoday.com
- ^ "A/H1N1 Swine Flu (Influenza) Timeline | September 24: Portugal (PT): First death confirmed". Archived from the original on 2010-06-16. Retrieved 2009-09-24.
- ^ "Schweinegrippe: Erster H1N1-Todesfall ins Gelsenkirchen Deutschland - News - Bild.de". 25 September 2009. Archived from the original on 2009-09-28.
- ^ a b Stein, Rob (2009-09-27). "Swine Flu Surge Closes Schools, Tests Hospitals - washingtonpost.com". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 2012-11-08.
- ^ a b CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 68. Who.int
- ^ "VOA News - H1N1 Swine Flu Keeps Hospitals in Northern Hemisphere Busy". Archived from the original on 2009-09-28. Retrieved 2009-09-28.
- ^ a b "Cambodia records first swine flu death: PM". Archived from the original on March 4, 2012. Retrieved September 29, 2009. Officials confirm flu death
- ^ a b Norfolk pigs catch swine flu - Norfolk News. EDP24
- ^ Wong, Fayen (2009-09-30). "Australia rolls out nationwide swine flu vaccination". Reuters. Retrieved 22 October 2010.
- ^ "UPDATE 1-China's Sinovac gets additional order for H1N1 vaccine". Reuters. 2009-09-30. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ H1N1 Vaccine Orders Top 1B, WHO Says Archived 2009-08-21 at the Wayback Machine. Medicalnewstoday.com
- ^ "Orders for Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine". Archived from the original on October 3, 2009. Retrieved October 5, 2009.
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ a b WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 69. Who.int
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - 2009-10 Influenza (Flu) Season. Cdc.gov
- ^ News - Science: UN calls for sharing of flu vaccines Archived 2009-04-30 at the Wayback Machine. Iol.co.za
- ^ China reports 1st swine flu death - CTV News. Ctv.ca
- ^ Yahoo! News. Asia.news.yahoo.com [permanent dead link]
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 70. Who.int
- ^ Swine flu found in Norwegian pigs / News / The Foreigner — Norwegian News in English Archived 2011-07-24 at the Wayback Machine. Theforeigner.no
- ^ a b Disease Prevention & Control Cluster (DPC) - WHO|Regional Office for Africa Archived 2009-10-12 at the Wayback Machine. Afro.who.int
- ^ "Yahoo | Mail, Weather, Search, Politics, News, Finance, Sports & Videos". Yahoo | Mail, Weather, Search, Politics, News, Finance, Sports & Videos.
- ^ "Vietnam detects 3 cases of drug-resistant swine flu". Reuters. 2009-10-12. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Mongolian Views: Breaking news: Swine flu outbreak in Mongolia. Mongolianviews.blogspot.com (2009-10-13)
- ^ "Consolidated Status of Influenza A H1N1 - 15th October 2009". PIB Press Release. 2009-10-15. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ T&T has first swine flu deaths|The Trinidad Guardian. Guardian.co.tt (2009-10-15)
- ^ "UK Swine Flu Cases Rise, Vaccines Available From Next Week - 15th October 2009". Wall Street Journal. 2009-10-15. Archived from the original on 6 January 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ a b CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ "US swine flu vaccines 'delayed'". BBC News. 2009-10-17. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu. Cdc.gov (2010-07-15)
- ^ Grady, Denise (2009-10-17). "Officials See a Shortage in Vaccine for Swine Flu". The New York Times. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 71. Who.int
- ^ News - World: China reports second H1N1 death Archived 2009-04-30 at the Wayback Machine. Iol.co.za
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ U.S. Department of Agriculture Home Page. Home Page. Usda.gov (2010-07-21)
- ^ Johnson, Andrea. (2009-10-20) Minnesota State Fair study provides new glimpses of H1N1 Farm and Ranch Guide: Livestock News. Farmandranchguide.com [permanent dead link]
- ^ https://news.yahoo.com/s/nm/20091019/ts_nm/us_flu_usda[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Consolidated Status of Influenza A H1N1 - 19th October 2009". PIB Press Release. 2009-10-19. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ https://news.yahoo.com/s/afp/20091019/wl_asia_afp/healthflujapan_20091019041838 [permanent dead link]
- ^ "Ont. turkeys with H1N1 pose 'minimal' risk". CBC News. 2009-10-20. Archived from the original on 22 October 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ First swine flu death in Iceland - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2009-10-23 at the Wayback Machine. Javno.com (2009-10-19)
- ^ On Parenting - Health (usnews.com). Health.usnews.com
- ^ A/H1N1 flu confirmed in turkey flock in Canada _English_Xinhua. News.xinhuanet.com (2009-10-21)
- ^ Kyodo News - Story[permanent dead link]. Home.kyodo.co.jp
- ^ News: H1N1 also notified in Japanese swine herd Archived 2012-04-18 at the Wayback Machine. Pig Progress
- ^ Triggle, Nick (2009-10-21). "Swine flu vaccination under way". BBC News. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "H1N1 vaccinations rolled out in UK". CNN. 2009-10-21. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ First swine flu death in Serbia - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2013-01-26 at archive.today. Javno.com (2009-10-21)
- ^ First H1N1 flu death in Czech Republic - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2013-01-26 at archive.today. Javno.com (2009-10-22)
- ^ Leland, John (2009-10-23). "Fear Over Swine Flu Closes Schools in Iraq". The New York Times. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Schweinegrippe: Dritter Todesfall in Deutschland - News. Bild.de
- ^ Mongolian Views: First death due to swine flu in Mongolia. Mongolianviews.blogspot.com (2009-10-23)
- ^ "Obama declares H1N1 emergency". CNN. 2009-10-26. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Treasure Valley residents line up for H1N1 protection|Health & Fitness Top. Idaho Statesman (2009-10-25)
- ^ "Frustration looms as H1N1 vaccines run out". CNN. 2009-10-26. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Calmes, Jackie (2009-10-25). "H1N1 Widespread in 46 States as Vaccines Lag". The New York Times. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 72. Who.int
- ^ Chinese mainland reports new death case of A/H1N1 flu_English_Xinhua. News.xinhuanet.com (2009-10-26)
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Eastern Mediterranean Region Countries which have already started vaccination campaign against Pandemic (H1N1) influenza" (PDF). www.emro.who.int. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 17, 2009.
- ^ "H1N1 vaccine clinics hit by 'pent-up demand'". CBC News. 2009-10-28. Archived from the original on 30 October 2009. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Russia registers first A/H1N1 flu deaths, 2009-10-27
- ^ Iceland Review Online: Daily News from Iceland, Current Affairs, Business, Politics, Sports, Culture Archived 2012-02-29 at the Wayback Machine. Icelandreview.com
- ^ Morreu hoje a primeira criança com Gripe A em Portugal - Portugal Archived 2009-10-31 at the Wayback Machine. DN
- ^ Mcneil, Donald G. (April 27, 2009). "Flu Outbreak Raises a Set of Questions". The New York Times. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Swine flu arrives in Turkey: 6 tourists in quarantine". eturbonews.com. 2009-05-17. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ a b "Son durum: 12 bin 316 vaka, 458 ölüm" (in Turkish). ntvmsnbc. 2009-12-22. Archived from the original on 2013-04-18. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Afghanistan reports first swine flu death". Archived from the original on October 28, 2009. Retrieved November 2, 2009.
- ^ Adelaja, Abiose. (2009-10-29) Swine flu detected in Nigeria Archived 2009-11-01 at the Wayback Machine. 234next.com
- ^ News - Africa: Congo students diagnosed with swine flu Archived 2009-04-30 at the Wayback Machine. Iol.co.za
- ^ 2009 influenza A (H1N1) pandemic site Archived 2009-10-29 at the Wayback Machine. Ecdc.europa.eu
- ^ Ukraine confirms first swine flu death, quarantine ordered Archived 2020-02-20 at the Wayback Machine. Monsters and Critics (2009-10-30)
- ^ Croatia records first death linked to swine flu - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2009-11-06 at the Wayback Machine. Javno.com (2009-10-31)
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ Afghanistan shuts schools over swine flu - Asia - World - Dalje.com Archived 2012-09-04 at archive.today. Javno.com (2009-11-01)
- ^ Turkey starts swine flu vaccinations - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2012-09-04 at archive.today. Javno.com (2009-11-02)
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 73. Who.int
- ^ First swine flu death in Austria - General News - Austrian Times Online News - English Newspaper. Austriantimes.at
- ^ "Earth Times: news/293058,belarus-registers-first-swine-flu-death.html". www.earthtimes.org. Archived from the original on 2017-09-07. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ "First Person Dies of Swine Flu in Slovenia". Slovenian Press Agency. Ljubljana. 3 November 2009. Retrieved 26 March 2016.
- ^ "USDA finds pandemic H1N1 in Indiana commercial swine". Reuters. 2009-11-02. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Illinois vet: H1N1 found in Indiana hogs no surprise, Nov 04, 2009
- ^ Netherlands reports first drug-resistant flu case - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2012-09-12 at archive.today. Javno.com (2009-11-04)
- ^ Knox, Richard. (2009-11-04) Sick Iowa Kitty Had Swine Flu Archived 2013-07-31 at the Wayback Machine. NPR
- ^ Radio e Televisione della Repubblica di San Marino - Cronaca e Attualità Archived 2011-05-28 at the Wayback Machine. Sanmarinortv.sm
- ^ a b c Bulgaria declares nationwide swine flu epidemic - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2013-01-26 at archive.today. Javno.com (2009-11-06)
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ Swine flu claims first life in Pakistan. Thenews.com.pk (2009-11-08) [permanent dead link]
- ^ https://news.yahoo.com/s/afp/20091108/wl_sthasia_afp/healthflusrilanka_20091108114131 [permanent dead link]
- ^ Latvia reports first swine flu death - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2010-01-29 at the Wayback Machine. Javno.com (2009-11-09)
- ^ FOCUS Information Agency Archived 2013-05-09 at the Wayback Machine. Focus-fen.net
- ^ "International Health Insurance for Leisure, Business, and Student Travelers -- H1N1 (Swine) Flu". Travel Health Insurance. 2009-11-12. Retrieved 2024-07-15.
- ^ France begins mass swine-flu vaccinations|Visit Bulgaria Archived 2009-11-15 at the Wayback Machine. Visitbulgaria.info
- ^ WHO|Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 74. Who.int
- ^ FOCUS Information Agency. Focus-fen.net
- ^ Turkish Cyprus reports first death from swine flu - Hurriyet Daily News and Economic Review Archived 2011-07-23 at the Wayback Machine. Hurriyetdailynews.com (2009-11-13)
- ^ Kosovo reports country's 1st death from swine flu|khou.com|Khou.com - News - World. Khou.com (2009-11-14)
- ^ Poland reports first swine flu death - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2009-11-17 at the Wayback Machine. Javno.com (2009-11-14)
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ "Earth Times: news/294941,tunisia-reports-first-two-swine-flu-deaths--summary.html". www.earthtimes.org. Archived from the original on 2017-09-07. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ IRIN Africa|SOMALIA: WHO confirms first cases of H1N1|Horn of Africa|Somalia|Flu Health & Nutrition|News Item. Irinnews.org
- ^ First flu victim in Bosnia-Herzegovina|Radio Netherlands Worldwide Archived 2011-06-08 at the Wayback Machine. Rnw.nl (2009-11-17)
- ^ H5N1: North Korea's first H1N1 case is a South Korean. Crofsblogs.typepad.com (2009-11-16)
- ^ Hungary declares swine flu epidemic - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2010-02-12 at the Wayback Machine. Javno.com (2009-11-18)
- ^ Lithuania reports first swine flu death. Baltictimes.com (2009-11-19)
- ^ First swine flu death in Macedonia - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2013-01-26 at archive.today. Javno.com (2009-11-18)
- ^ Oregon cat died of H1N1, first such fatality in nation. OregonLive.com
- ^ [2][permanent dead link]
- ^ Denmark reports two first swine flu deaths - Europe - World - Dalje.com Archived 2009-11-24 at the Wayback Machine. Javno.com (2009-11-20)
- ^ https://news.yahoo.com/s/afp/20091120/hl_afp/healthfluwhomutation_20091120183022[permanent dead link]
- ^ H1N1 mutation found in some flu fatalities - Health - Cold and flu - Swine flu - msnbc.com. MSNBC (2009-11-20)
- ^ Walsh, Fergus (2009-11-20). "Drug-resistant swine flu hits UK". BBC News. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Tamiflu-resistant swine flu cluster reported in NC". Archived from the original on November 22, 2009. Retrieved November 22, 2009.
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ Romania has 1st H1N1 death Archived 2009-11-26 at the Wayback Machine. Straitstimes.com (2009-11-23)
- ^ "Montserrat reports first H1N1 flu case". 2009-11-24. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Mcneil Jr., Donald G. (2009-11-28). "Experts Say Swine Flu Mutations Do Not Warrant New Alarm". The New York Times. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ The D225G change in 2009 H1N1 influenza virus is not a concern. Virology.ws (2009-11-24)
- ^ VB - The D225G change in 2009 H1N1 influenza virus is not a concern. FluTrackers
- ^ lefigaro.fr (2009-11-27). "Mutation du H1N1 : 2 morts en France". Lefigaro.
- ^ "Jump in global swine flu deaths". BBC News. 2009-11-27. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Two die from mutated H1N1 virus in France Archived 2017-09-06 at the Wayback Machine. Thaindian.com (2009-11-27)
- ^ The Chosun Ilbo (English Edition): Daily News from Korea - Korea, U.S. Report Double H1N1 Infection Cases. English.chosun.com (2009-11-27)
- ^ China urges intensified supervision on A/H1N1 flu in animals_English_Xinhua. News.xinhuanet.com (2009-11-28)
- ^ Jurnal Nasional. Jurnal Nasional (2009-11-28) Archived December 27, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ CDC H1N1 Flu|Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ Libya Reports First Swine Flu Death Archived 2017-03-19 at the Wayback Machine. Tripolipost.com
- ^ Kasolowsky, Raissa (2009-12-01). "Muslim pilgrimage ends with handful of flu cases". Reuters. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ name="edp24.co.uk"/
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ "H1N1 virus finally reaches blockaded Gaza Strip". Reuters. 2009-12-06. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Kajimoto, Tetsushi (2009-12-06). "H1N1 deaths hit 100 in Japan: report". Reuters. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Swine flu has killed 10,000 Americans since April". Reuters. 2009-12-10. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ North Korea Today - Good Friends: North Korea Today No. 311/No.311-1 Hot Topics December 2009. Goodfriendsusa.blogspot.com (2009-12-08)
- ^ https://news.yahoo.com/s/ap/20091208/ap_on_re_as/as_koreas_swine_flu;_ylt=Ano4rtHUnNuIVB6qnxVoPoYBxg8F;_ylu=X3oDMTJxcnZudTlqBGFzc2V0A2FwLzIwMDkxMjA4L2FzX2tvcmVhc19zd2luZV9mbHUEcG9zAzMyBHNlYwN5bl9wYWdpbmF0ZV9zdW1tYXJ5X2xpc3QEc2xrA3Nrb3JlYW5wcmVzaQ-- [permanent dead link]
- ^ The Severity of Pandemic H1N1 Influenza in the United States, from April to July 2009: A Bayesian Analysis. PLoS Medicine
- ^ "Swine flu may be mildest pandemic ever, researchers say". Los Angeles Times. 2009-12-08. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Stein, Rob (2009-12-08). "Flu pandemic could be mildest on record". The Washington Post. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ A/H1N1 kills 17 in Afghanistan _English_Xinhua. News.xinhuanet.com (2009-12-12)
- ^ Palestinian child dies of A/H1N1 flu in Gaza _English_Xinhua. News.xinhuanet.com (2009-12-12)
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ Qatar- Mass H1N1 vaccination begins today Archived 2011-06-11 at the Wayback Machine. Menafn.com (2009-12-13)
- ^ Mcneil Jr., Donald G. (2009-12-18). "Assessment and Thanks as Flu Wave Ebbs in U.S." The New York Times. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "Walgreen leads U.S. drugstores with H1N1 vaccine". Reuters. 2009-12-16. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "2nd UPDATE: Walgreen To Offer H1N1 Vaccine Nationwide By Year End". Archived from the original on 2009-12-17. Retrieved 12 May 2013.
- ^ Thailand's pig infected with A/H1N1 but recovers: health official _English_Xinhua. News.xinhuanet.com (2009-12-17)
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu|2009 H1N1 U.S. Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ Dog in New York Diagnosed with Swine Flu Archived 2017-03-19 at the Wayback Machine. PetMD (2009-12-22)
- ^ H1N1 found at pig farms - Health/Science Archived 2017-03-19 at the Wayback Machine. NewsObserver.com
- ^ Pediatric Hospitalizations Associated with 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) in Argentina|H1N1 Influenza Center. H1n1.nejm.org (2009-12-23)
- ^ "Swine flu deadlier in children than seasonal flu". Reuters. 2009-12-23. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Libster, R; Bugna, J; Coviello, S; Hijano, DR; Dunaiewsky, M; Reynoso, N; Cavalieri, ML; Guglielmo, MC; Areso, MS (2010). "Pediatric hospitalizations associated with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in Argentina". The New England Journal of Medicine. 362 (1): 45–55. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0907673. PMID 20032320. S2CID 23375582.
- ^ CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ "At least 12,220 dead from H1N1 around world: WHO". Reuters. 2009-12-30. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Nepals 1st H1N1 death Archived 2010-01-17 at the Wayback Machine. Straitstimes.com (2009-12-28)
- ^ "Swine flu pandemic 'not yet over'". BBC News. 2009-12-29. Archived from the original on 5 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ Household Transmission of 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) Virus in the United States|H1N1 Influenza Center. H1n1.nejm.org (2009-12-30)
- ^ Cauchemez, S; Donnelly, CA; Reed, C; Ghani, AC; Fraser, C; Kent, CK; Finelli, L; Ferguson, NM (2009). "Household transmission of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus in the United States". The New England Journal of Medicine. 361 (27): 2619–27. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0905498. PMC 3840270. PMID 20042753.
- ^ "Swine flu 'more likely in young'". BBC News. 2009-12-31. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "CDC - Seasonal Influenza (Flu) - Weekly Report: Influenza Summary Update". www.cdc.gov.
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu|2009 H1N1 U.S. Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ IRIN Africa|MALI: Lab confirms H1N1|West Africa|Mali|Flu Health & Nutrition|News Item. Irinnews.org
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu|2009 H1N1 U.S. Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ The Royal Gazette. The Royal Gazette (2010-01-20)
- ^ Union-Tribune, San Diego (2010-01-19). "Nigeria reports first swine flu-related death". San Diego Union-Tribune. Retrieved 2024-07-15.
- ^ a b "WHO African Region situation updates". Archived from the original on February 25, 2010. Retrieved March 2, 2010.
- ^ CDC H1N1 Flu|Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ Agence de Presse Africaine - Article Archived 2012-01-21 at the Wayback Machine. Apanews.net
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu|2009 H1N1 U.S. Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu|2009 H1N1 U.S. Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu|2009 H1N1 U.S. Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu|2009 H1N1 U.S. Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu|2009 H1N1 U.S. Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ In policy reversal, Cubans to get H1N1 vaccinations|The Columbus Dispatch.|(2010-03-27)
- ^ CDC reports states' H1N1 flu inoculation rates vary widely Archived 2010-04-21 at the Wayback Machine. Vaccine News Daily (2010-03-31)
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu|2009 H1N1 U.S. Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ "300,000 H1N1 Vaccinations Underway". Voice of America. 2010-04-02. Retrieved 2024-07-15.
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu|2009 H1N1 U.S. Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ Lejourguinee-Medium Guinéen de l'actualité instantanée. Lejourguinee.com Archived April 15, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ First Meeting Of WHO H1N1 Response Probe Concludes - Kaiser Global Health. Globalhealth.kff.org (2010-04-15)
- ^ CDC 2009 H1N1 Flu|2009 H1N1 U.S. Situation Update. Cdc.gov
- ^ WHO warns H1N1 to continue through 2011 Archived 2010-04-27 at the Wayback Machine. Vaccine News Daily (2010-04-20)
- ^ DOH: 1st recipient to get shot of A(H1N1)vaccine Monday - Nation - GMANews.TV - Official Website of GMA News and Public Affairs - Latest Philippine News. GMANews.TV
- ^ "WHO chief says world "lucky" to have mild pandemic influenza". Xinhuanet. Xinhua News Agency. 18 May 2010. Archived from the original on May 22, 2010. Retrieved 27 June 2013.
- ^ "Gene mutation caused 2009 H1N1 virus spread". Medical Daily. 6 August 2010. Archived from the original on 25 February 2012. Retrieved 27 June 2013.
- ^ Devitt, Terry (2011). "H1N1 Flu Virus Used New Biochemical Trick to Cause Pandemic". School of Veterinary Medicine. University of Wisconsin–Madison. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011. Retrieved 27 June 2013.
- ^ Neale, Todd (10 August 2010). "WHO Declares End to H1N1 Pandemic". www.medpagetoday.com.
- ^ a b Jordans, Frank (10 August 2012). "WHO says swine flu pandemic is over". Yahoo! News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 15 August 2010. Retrieved 27 June 2013.