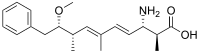
ADDA ((all-S,all-E)-3-amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyldeca-4,6-dienoic acid) is a non-proteinogenic amino acid found in toxins made by cyanobacteria. Toxins which include this amino acid include microcystins[1] and nodularins.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4E,6E,8S,9S)-3-Amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyldeca-4,6-dienoic acid | |
| Other names
(all-S,all-E)-3-Amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyldeca-4,6-dienoic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H29NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 331.456 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Along with leucine and arginine, it is found in microcystin-LR, an extremely toxic compound produced by cyanobacteria. In order to treat a water supply contaminated with microcystin-LR, chlorination can be used to oxidize the double bonds of ADDA in order to initiate the chemical breakdown of this compound.[2]
References
edit- ^ Rudolph-Böhner, Sabine; Mierke, Dale F.; Moroder, Luis (1994). "Molecular structure of the cyanobacterial tumor-promoting microcystins". FEBS Letters. 349 (3): 319–323. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)00680-6. PMID 8050589. S2CID 23312111.
- ^ "ADDA". American Chemical Society. Retrieved 5 February 2023.