Abequose is a hexose and a 3,6-dideoxysugar. It is a constituent of the in O-specific chains in lipopolysaccharides that occur in certain serotypes of Salmonella[1][2] and Citrobacter bacteria.[3] It is the enantiomer of colitose.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
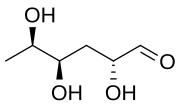
| IUPAC name
(2R,4R,5R)-2,4,5-Trihydroxyhexanal
| |
| Other names
3,6-Dideoxy-D-xylo-hexose
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O4 | |
| Molar mass | 148.158 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ "Abequose". Oxford Reference. Retrieved May 24, 2022.
- ^ Osborn, M. J.; Weiner, I. M. (1968). "Biosynthesis of a Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 243 (10): 2631–2639. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)93419-8.
- ^ Katzenellenbogen, Ewa; Kocharova, Nina A.; Toukach, Philip V.; Górska, Sabina; Korzeniowska-Kowal, Agnieszka; Bogulska, Maria; Gamian, Andrzej; Knirel, Yuriy A. (2009). "Structure of an abequose-containing O-polysaccharide from Citrobacter freundii O22 strain PCM 1555". Carbohydrate Research. 344 (13): 1724–1728. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2009.06.005. PMID 19576576.
External links
editMedia related to Abequose at Wikimedia Commons