Abert's squirrel or the tassel-eared squirrel (Sciurus aberti) is a tree squirrel in the genus Sciurus native to the southern Rocky Mountains from the United States to the northern Sierra Madre Occidental of Mexico, with concentrations found in Arizona, New Mexico, and southwestern Colorado. It is closely associated with, and largely confined to, mature ponderosa pine forests. It is named in honor of the American naturalist John James Abert; nine subspecies are recognised. It is recognizable by its tufted ears, gray color, pale underparts and rufous patch on the lower back. The squirrel feeds on the seeds and cones of the Mexican pinyon and the ponderosa pine when they are available, but will also take fungi, buds, bark, and carrion. Breeding normally occurs in summer, with a spherical nest being built high in the canopy.
| Abert's squirrel[1] | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Sciuridae |
| Genus: | Sciurus |
| Subgenus: | Otosciurus Nelson, 1899 |
| Species: | S. aberti
|
| Binomial name | |
| Sciurus aberti Woodhouse, 1853
| |
| Subspecies | |
| |
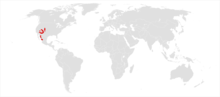
| |
| Range of Abert's squirrel | |
Etymology
editAbert's squirrel is named after Colonel John James Abert, an American naturalist and military officer who headed the Corps of Topographical Engineers and organized the effort to map the American West in the 19th century.
Taxonomy
editThe currently accepted scientific name for Abert's squirrel is Sciurus aberti Woodhouse, 1853.[4] Woodhouse had initially described the species as Sciurus dorsalis in 1852, but this name turned out to be preoccupied by Sciurus dorsalis Gray, 1849 (now a subspecies of variegated squirrel S. variegatoides), and thus the present species was renamed.
There are nine recognized subspecies, including the Kaibab squirrel (S. a. kaibabensis), formerly recognized as a separate species (S. kaibabensis). The nine subspecies are listed in the Distribution section.[5][6]
Physical characteristics
editAbert's squirrels are 46–58 cm long with a tail of 19–25 cm. They are easily recognized by their long ear tufts, which extend up from each ear 2–3 cm. This gives this species a striking similarity to the Eurasian red squirrel, aside from its differing dark coloration.
Abert's squirrels vary in color across their range. Most populations have a gray coat with a reddish stripe down the back, a dark stripe along the side, and a white underbelly. Some populations lack the reddish back stripe, instead having fully gray upperparts. A fully black color morph is present in the foothills of the Rocky Mountains in Colorado. Abert's squirrels on Arizona's Kaibab Plateau, commonly known as Kaibab squirrels, have black underparts and a striking white tail.
Distribution
editAbert's squirrel is confined to the Colorado Plateau and the southern Rocky Mountains of Colorado, Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico; its range extends south in the Sierra Madre Occidental to Chihuahua and Durango in Mexico.[5] Abert's squirrel also extends into Wyoming where ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa) is present.[7] Abert's squirrels transplanted to the Graham and Santa Catalina Mountains of Arizona have established stable populations.[8] Mellott and Choate reported Abert's squirrels present in the Spanish Peaks State Wildlife Area, 43 miles (69 km) southeast of the previously known Abert's squirrel range.[9]
The distribution of Abert's squirrel subspecies in the Southwest is coincident with the disjunct ponderosa pine forests.[10] Subspecies distributions are as follows:[5][11]
- S. a. aberti Woodhouse, 1853 – northern Arizona
- S. a. barberi Allen, 1904 – northwestern Chihuahua
- S. a. chuscensis Goldman, 1931 – New Mexico-Arizona border area
- S. a. durangi Thomas, 1893 – Durango
- S. a. ferreus True, 1900 – Rocky Mountains, central Colorado
- S. a. kaibabensis Merriam, 1904 – Kaibab Plateau, northern Arizona
- S. a. mimus Merriam, 1904 – New Mexico-Colorado border area
- S. a. navajo Durrant and Kelson, 1947 – southeastern Utah
- S. a. phaeurus Allen, 1904 – northwestern and southwestern Durango and southwesternmost Chihuahua
Habitat
editAbert's squirrels in the U.S. make almost exclusive use of ponderosa pine for cover, nesting, and food.[5] In Mexico where ponderosa pines are absent, the species is found in stands of the closely related Pinus arizonica.[12][13] Optimum Abert's squirrel habitat is composed of all-aged ponderosa pine stands with trees in even-aged groups, densities of 168 to 250 trees per acre (496–618/ha), and 150 to 200 square feet per acre (34.4–45.3 sq m/ha) basal area. In optimum habitat average diameter of ponderosa pines is 11 to 13 inches (28 to 33 centimetres), with Gambel oaks in the 11.8- to 14-inch (30–36 cm) diameter at breast height (d.b.h.) range.[14] Optimum habitat has some ponderosa pine over 20 inches (51 cm) d.b.h., which are the best cone producers.[15] Larson and Schubert report that ponderosa pine 36 to 40 inches (91 to 102 centimetres) d.b.h. produced an average of 446 cones per tree per crop. Trees less than 24 inches (61 cm) d.b.h. produced fewer than 100 cones per crop.[16]
In central Arizona, Abert's squirrel summer home ranges averaged 18 acres (7.3 hectares) and ranged from 10 to 24 acres (4.0 to 9.7 ha). Ranges were somewhat smaller in winter.[5] Ramey reports that the mean Abert's squirrel home range for spring and summer was 20 acres (8.1 hectares) in Black Forest, Colorado. Subadult males had spring home ranges of about 27 acres (11 hectares), and adult females had somewhat larger summer home ranges than adult males.[17] Patton reported the ranges of three squirrels as 10, 30, and 60 acres (4.0, 12.2, and 24.4 ha) in Arizona.[18] Hall reported the home range of an adult female as 29 acres (12 hectares).[19]
In Colorado, Ramey found a density of 83 squirrels per square mile (30/km2) in spring 1970 but only 33 squirrels per square mile (12/km2) in spring 1971.[17] In another Colorado study, Farentinos estimated 227 squirrels per square mile (82/km2) in fall 1970 and 317 per square mile (114/km2) in fall 1971.[20]
Plant communities
editAbert's squirrel is closely associated with, and nearly confined to cool, dry interior ponderosa pine forests.[5] In Arizona, ponderosa pine forests are most extensive between 5,500 and 8,500 feet (1,700 and 2,600 metres) elevation.[21] Abert's squirrels occur in pure ponderosa pine stands or stands with associated Gambel oak (Quercus gambelii), Colorado pinyon (Pinus edulis), junipers (Juniperus spp.), quaking aspen (Populus tremuloides), and Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii).[5] Findley and others mention that Abert's squirrels are common in mixed conifer canyons in New Mexico.[22]
In Durango and Chihuahua the squirrels are said to inhabit high altitude ponderosa pine stands.[12] However, the ponderosa pines of Mexico have relatively recently (since at least 1997) been reclassified as a separate species Pinus arizonica (syn. P. ponderosa var. arizonica), and some regard much of that population as yet another species Pinus cooperi (P. arizonica var. cooperi).[13]
Conservation
editThis is a common species with a wide range and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being of "least concern".[2] Nonetheless, in Mexico, where much of its habitat has been logged, this species is considered 'vulnerable' by the Mexican environmental protection agency SEMARNAT and is protected.[12][23]
Ecology and behavior
editAbert's squirrels are diurnal. They are often active for a short time before sunrise and active for periods throughout the day, and they usually return to shelter before sunset.[5] Abert's squirrel does not store food, as other North American squirrels do.[24]
The most apparent causes of Abert's squirrel mortality are food shortage and injuries (such as broken teeth) that lead to mortality.[5]
Reproduction
editIn central Arizona, breeding occurs from May 1 to June 1 and there are young in the nest from June 10 to July 27.[5] Farantinos reported a 46-day gestation period.[25] Eight litters were composed of two to five young each.[5][25] Three or four young per litter is typical.[26] Young Abert's squirrels are born naked, with ears and eyes closed. At 2 weeks thin short hair is noticeable and the ears are slightly open. By 6 weeks the pelage has developed and the eyes are open. By 7 weeks the tail has broadened and is held over the back, ears are held erect. Mushrooms and bark have been added to the diet at this time. Captive young first venture from the nest at about 7 weeks, but do not venture to the ground until about 9 weeks. By 10 weeks Abert's squirrels are weaned. Mature size is reached by 15 to 16 weeks.[5] Female Abert's squirrels usually bear only one litter per year.[5] Hall and Kelson, however, report that two litters are often borne per year in the southern parts of Abert's squirrel range.[26]
Nesting
editNests are built by the female Abert's squirrel out of pine twigs 0.5 inches (1.3 cm) or less in diameter and 6 to 24 inches (15 to 61 centimetres) long. Nests are lined with a variety of materials.[5] Summer nests are built by Abert's squirrels on ponderosa pine branches, in Gambel oak cavities, and sometimes in cottonwood (Populus spp.) branches. Ponderosa pine seldom have cavities big enough for Abert's squirrels. In central Arizona nest trees ranged from 12 to 41 inches d.b.h. and were 20 to 110 feet (6.1 to 33.5 m) tall.[5] In another Arizona study, nest trees ranged from 11.6 to 36.6 inches (29 to 93 centimetres) d.b.h. Most nests are placed in the upper third of the tree crown.[27] Nests are placed from 16 to 90 feet (4.9–27) above the ground, usually on a large limb against the bole, or in the forks of smaller branches. Nests were most often built on the southern to southeastern side of the tree.[5] Patton reports that nest trees in Arizona had crowns that were 35% to 55% of the total tree height, and most often were 14 to 16 inches (36 to 41 centimetres) d.b.h.[10] Nests are built in trees occurring as part of a grouping of trees with interlocking crowns.[10][15] Dwarf mistletoe (Arceuthobium vaginatum) infestations that cause the formation of "witches brooms" are often incorporated into or support Abert's squirrel nests.[28]
Nests are roughly spherical and a small platform often extends beyond the bowl edge on one side.[29]
The nests are used year-round by most Abert's squirrels for nightly shelter,[27] although females often move the litter to a larger nest when the young are 3 to 6 weeks old.[5] In winter, pairs of Abert's squirrels, usually an adult female and one subadult (presumed) offspring, use the same nest for shelter.[5]
Food habits
editAbert's squirrels consume ponderosa pine year-round. Parts eaten include seeds, which are the most highly preferred item, inner bark (particularly of young twigs), terminal buds, staminate buds, and pollen cones. Other foods include fleshy fungi (particularly hypogeous fungi), carrion, bones, and antlers. Severe weather is not always a deterrent to feeding activity.[5] Where Mexican pinyon (Pinus cembroides) seeds are available, Abert's squirrels consume them in preference to ponderosa pine seeds.[19] Gambel oak acorns may also provide substantial food for Abert's squirrels.[30]
Ponderosa pines produce large cone crops every 3 to 4 years; cones are virtually absent about 1 year out of 4. Abert's squirrels begin eating immature seed shortly after cone development begins in late May. Seeds are eaten through the summer as the cones mature. Seeds from up to 75 cones may be eaten per day per squirrel during the months when seeds form the squirrels' major food. Seeds are disseminated from cones in October and November. Abert's squirrels continue to consume seed from late maturing cones and collect single seeds from the ground. The succulent inner bark of twigs is eaten all year, but most heavily in winter. Needle clusters are clipped from the twigs, the outer bark is removed, the inner bark is consumed, and then the twig is discarded. In winter a single squirrel consumes about 45 twigs per day.[5] Most feed trees range from 11 to 30 inches (28 to 76 centimetres) d.b.h.[21] After seeds have been disseminated Abert's squirrels are dependent on inner bark, which forms the bulk of the diet from November to April. The soft inner tissue of small apical buds is also a preferred item. In May, staminate buds and cones and immature ovules are consumed as available. New staminate cones are entirely consumed; only the pollen is eaten from dried cones. The bark of areas infected with dwarf mistletoe also appears to be preferred.[5]
Fleshy fungi consumed include members of the following genera: Agaricus, Amanita, Boletus, Hypholoma, Lepiota, Lycopedon, Russula and Tuber. Mushrooms poisonous to humans are consumed by Abert's squirrels without difficulty, including destroying angels (A. bisporigera and A. ocreata) and a species of Russula.[5]
Water is obtained mostly from food, but Abert's squirrels sometimes drink at stock ponds or other standing water (i.e., rain puddles).[5]
Predators
editReynolds [31] suggested that northern goshawks (Accipiter gentilis) may take enough Abert's squirrels to regulate Abert's squirrel populations. Hawks (Accipitridae and Falconidae) prey on Abert's squirrels in central Arizona, but even though other potential predators are present, i.e., gray fox (Urocyon cinereoargenteus), bobcat (Lynx rufus), coyote (Canis latrans), there is no evidence that they prey on Abert's squirrels.[5]
References
editThis article incorporates public domain material from Sciurus aberti. United States Department of Agriculture. Archived from the original on 2012-10-17.
- ^ Thorington, R.W. Jr.; Hoffmann, R.S. (2005). "Sciurus (Otosciurus) aberti". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: a taxonomic and geographic reference (3rd ed.). The Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 754–818. ISBN 0-8018-8221-4. OCLC 26158608.
- ^ a b Cassola, F. (2017). "Sciurus aberti". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T42461A22245623. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T42461A22245623.en. Retrieved 6 September 2021.
- ^ "Sciurus aberti". NatureServe Explorer. Retrieved 17 April 2024.
- ^ Hall, E. Raymond. 1981. The mammals of North America. 2nd ed. Vol. 2. New York: John Wiley and Sons
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x Keith, James O. (1965). "The Abert Squirrel and Its Dependence on Ponderosa Pine". Ecology. 46 (1/2): 150–163. Bibcode:1965Ecol...46..150K. doi:10.2307/1935266. JSTOR 1935266.
- ^ Nash, Donald J.; Seaman, Richard N. (1977). "Sciurus aberti" (PDF). Mammalian Species (80): 1–5. doi:10.2307/3503958. JSTOR 3503958. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-10-16. Retrieved 2017-01-07.
- ^ Davis, R; Brown, DE (1989). "Role of post-Pleistocene dispersal in determining the modern distribution of Abert's squirrel". Great Basin Naturalist. 49 (3). Article 13.
- ^ Davis, R; Brown, DE (1988). "Documentation of the transplanting of Abert's squirrels". Southwestern Naturalist. 33 (4): 490–492. doi:10.2307/3672222. JSTOR 3672222.
- ^ Mellott, Ron S.; Choate, Jerry R. (1984). "Sciurus aberti and Microtus montanus on Foothills of the Culebra Range in Southern Colorado". The Southwestern Naturalist. 29 (1): 135–137. doi:10.2307/3670779. JSTOR 3670779.
- ^ a b c Patton, David R. (1975). Abert squirrel cover requirements in Southwestern ponderosa pine. Res. Pap. RM-145. Fort Collins, Colorado: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station
- ^ Ceballos, Gerardo; Arroyo-Cabrales, Joaquin (December 2012). "Lista Actualizada de los Mamíferos de Mexico 2012". Revista Mexicana de Mastozoología Nueva Época (in Spanish). 2 (1): 27–80. ISSN 2007-4484. Retrieved 9 August 2018.
- ^ a b c Valdés Alarcón, Manuel (November 2003). "Las Ardillas de México" (PDF). Biodiversitas (in Spanish). No. 51. Mexico City: Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad. Retrieved 9 August 2018.
- ^ a b Earle, Christopher J. (29 December 2017). "Pinus arizonica (Arizona pine, pino de Arizona) description - The Gymnosperm Database". The Gymnosperm Database. Retrieved 9 August 2018.
"P. arizonica has often been treated under [P. ponderosa] as a variety, but more recent treatments recognize it as a distinct species, with possible introgression in Arizona and New Mexico" (Farjon & Styles 1997)
- ^ Flyger, Vagn; Gates, J. Edward. 1982. Pine squirrels: Tamiasciurus hudsonicus and T. douglasii. In: Chapman, Joseph A.; Feldhamer, George A., eds. Wild mammals of North America: Biology, management, and economics. Baltimore, Maryland: The Johns Hopkins University Press: 230–238.
- ^ a b Clary, Warren P. 1987. Overview of ponderosa pine bunchgrass ecology and wildlife habitat enhancement with emphasis on southwestern United States. In: Fisser, Herbert G., ed. Wyoming shrublands: Proceedings, 16th Wyoming shrub ecology workshop; 1987 May 26–27; Sundance, Wyoming. Laramie, Wyoming: University of Wyoming, Department of Range Management, Wyoming Shrub Ecology Workshop: 11–21
- ^ Larson, M. M.; Schubert, Gilbert H. (1970). Cone crops of ponderosa pine in central Arizona, including the influence of Abert squirrels. Res. Pap. RM-58. Fort Collins, Colorado: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station
- ^ a b Ramey, Craig Anthony. (1973). The movement patterns and coat color polymorphism of Abert's squirrel, Sciurus aberti ferreus. Fort Collins, Colorado: Colorado State University. Dissertation
- ^ Patton, David R. (1975). Nest use and home range of three Abert squirrels as determined by radio tracking. Res. Note RM-281. Fort Collins, Colorado: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station
- ^ a b Hall, Joseph G. (1973). "The Kiabab squirrel". In: Symposium on rare and endangered wildlife of the southwestern United States: Proceedings; 1972 September 22–23; Albuquerque, New Mexico. Santa Fe, New Mexico: New Mexico Department of Game and Fish: 18–21
- ^ Farentinos, R (1972). "Social dominance and mating activity in the tassel-eared squirrel (Sciurus aberti ferreus)". Animal Behaviour. 20 (2): 316–26. doi:10.1016/S0003-3472(72)80053-8. PMID 4674670.
- ^ a b Patton, David R.; Green, Win. (1970). Abert's squirrels prefer mature ponderosa pine. Res. Note RM-169. Fort Collins, Colorado: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station
- ^ Findley, James S.; Harris, Arthur H.; Wilson, Don E.; Jones, Clyde. (1975). Mammals of New Mexico. Albuquerque, New Mexico: University of New Mexico Press. ISBN 0826303692.
- ^ Ceballos, Gerardo; Arroyo-Cabrales, Joaquin; Medellín, Rodrigo A. (18 December 2002). "The Mammals of Mexico: Composition, Distribution and Conservation Status" (PDF). Occasional Papers of the Museum of Texas Tech University (218): 1–27. Retrieved 9 August 2018.
- ^ Edelman, A.J., and J.L. Koprowski. 2009. Introduced Abert’s squirrels in the Pinaleño Mountains: a review of their natural history and potential impacts on the red squirrel. The Last Refuge of the Mt. Graham Red Squirrel: Ecology of Endangerment (H.R. Sanderson and J.L. Koprowski, eds.). University of Arizona Press, Tucson. Pp 370-388.
- ^ a b Farentinos, R. C. (1972). "Observations on the Ecology of the Tassel-Eared Squirrel". The Journal of Wildlife Management. 36 (4): 1234–1239. doi:10.2307/3799253. JSTOR 3799253.
- ^ a b Hall, E. Raymond; Kelson, Keith R. (1959). The mammals of North America, Volume II. New York: The Ronald Press Company
- ^ a b Snyder, M. A.; Linhart, Y. B. (1994). "Nest-Site Selection by Abert's Squirrel: Chemical Characteristics of Nest Trees". Journal of Mammalogy. 75 (1): 136–141. doi:10.2307/1382245. JSTOR 1382245.
- ^ Farentinos, R. C. (1972). "Nests of the Tassel-Eared Squirrel". Journal of Mammalogy. 53 (4): 900–903. doi:10.2307/1379231. JSTOR 1379231.
- ^ Skinner, T. H.; Klemmedson, J. O. (1978). Abert squirrels influence nutrient transfer through litterfall in a ponderosa pine forest. Res. Note RM-353. Fort Collins, Colorado: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station
- ^ Reynolds, Hudson G.; Clary, Warren P.; Ffolliott, Peter F. (1970). "Gambel oak for Southwestern wildlife". Journal of Forestry. 68 (9): 545–547.
- ^ Reynolds, H. G. (1963). "Western goshawk take abert squirrel in Arizona". Journal of Forestry. 61: 839.

