This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (December 2020) |
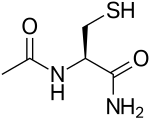
N-Acetylcysteine amide (abbrev. NACA, AD4 and also known as acetylcysteinamide) is an amide derivative of N-acetylcysteine that appears to have better blood–brain barrier permeability and bioavailability and a similar antioxidant capability.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.211.696 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C5H10N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 162.21 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.227 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 308 °C (586 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 22[citation needed] mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |