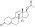
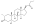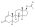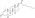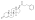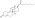An androgen or anabolic steroid ester is an ester of an androgen/anabolic steroid (AAS) such as the natural testosterone or dihydrotestosterone (DHT) or the synthetic nandrolone (19-nortestosterone). Esterification renders AAS into metabolism-resistant prohormones of themselves, improving oral bioavailability, increasing lipophilicity, and extending the elimination half-life (which necessitates less frequent administration). In addition, with intramuscular injection, AAS esters are absorbed more slowly into the body, further improving the elimination half-life. Aside from differences in pharmacokinetics (e.g., duration), these esters essentially have the same effects as the parent drugs.[1] They are used in androgen replacement therapy (ART), among other indications. Examples of androgen esters include testosterone esters such as testosterone cypionate, testosterone enanthate, testosterone propionate, and testosterone undecanoate and nandrolone esters such as nandrolone decanoate and nandrolone phenylpropionate.

| Medication | Form | Major brand names | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone | Aqueous suspension | Andronaq, Sterotate, Virosterone | 2–3 days |
| Testosterone propionate | Oil solution | Androteston, Perandren, Testoviron | 3–4 days |
| Testosterone phenylpropionate | Oil solution | Testolent | 8 days |
| Testosterone isobutyrate | Aqueous suspension | Agovirin Depot, Perandren M | 14 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersa | Oil solution | Triolandren | 10–20 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersb | Oil solution | Testosid Depot | 14–20 days |
| Testosterone enanthate | Oil solution | Delatestryl | 14–28 days |
| Testosterone cypionate | Oil solution | Depovirin | 14–28 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersc | Oil solution | Sustanon 250 | 28 days |
| Testosterone undecanoate | Oil solution | Aveed, Nebido | 100 days |
| Testosterone buciclated | Aqueous suspension | 20 Aet-1, CDB-1781e | 90–120 days |
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | Oil solution | Durabolin | 10 days |
| Nandrolone decanoate | Oil solution | Deca Durabolin | 21–28 days |
| Methandriol | Aqueous suspension | Notandron, Protandren | 8 days |
| Methandriol bisenanthoyl acetate | Oil solution | Notandron Depot | 16 days |
| Metenolone acetate | Oil solution | Primobolan | 3 days |
| Metenolone enanthate | Oil solution | Primobolan Depot | 14 days |
| Note: All are via i.m. injection. Footnotes: a = TP, TV, and TUe. b = TP and TKL. c = TP, TPP, TiCa, and TD. d = Studied but never marketed. e = Developmental code names. Sources: See template. | |||
| Testosterone ester | Form | Route | Tmax | t1/2 | MRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone undecanoate | Oil-filled capsules | Oral | ? | 1.6 hours | 3.7 hours |
| Testosterone propionate | Oil solution | Intramuscular injection | ? | 0.8 days | 1.5 days |
| Testosterone enanthate | Castor oil solution | Intramuscular injection | 10 days | 4.5 days | 8.5 days |
| Testosterone undecanoate | Tea seed oil solution | Intramuscular injection | 13.0 days | 20.9 days | 34.9 days |
| Testosterone undecanoate | Castor oil solution | Intramuscular injection | 11.4 days | 33.9 days | 36.0 days |
| Testosterone buciclatea | Aqueous suspension | Intramuscular injection | 25.8 days | 29.5 days | 60.0 days |
| Notes: Testosterone cypionate has similar pharmacokinetics to Testosterone enanthate. Footnotes: a = Never marketed. Sources: See template. | |||||
| Androgen | Structure | Ester | Relative mol. weight |
Relative T contentb |
logPc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position(s) | Moiet(ies) | Type | Lengtha | ||||||
| Testosterone | – | – | – | – | 1.00 | 1.00 | 3.0–3.4 | ||
| Testosterone propionate | C17β | Propanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 3 | 1.19 | 0.84 | 3.7–4.9 | ||
| Testosterone isobutyrate | C17β | Isobutyric acid | Branched-chain fatty acid | – (~3) | 1.24 | 0.80 | 4.9–5.3 | ||
| Testosterone isocaproate | C17β | Isohexanoic acid | Branched-chain fatty acid | – (~5) | 1.34 | 0.75 | 4.4–6.3 | ||
| Testosterone caproate | C17β | Hexanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 6 | 1.35 | 0.75 | 5.8–6.5 | ||
| Testosterone phenylpropionate | C17β | Phenylpropanoic acid | Aromatic fatty acid | – (~6) | 1.46 | 0.69 | 5.8–6.5 | ||
| Testosterone cypionate | C17β | Cyclopentylpropanoic acid | Cyclic carboxylic acid | – (~6) | 1.43 | 0.70 | 5.1–7.0 | ||
| Testosterone enanthate | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.39 | 0.72 | 3.6–7.0 | ||
| Testosterone decanoate | C17β | Decanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 10 | 1.53 | 0.65 | 6.3–8.6 | ||
| Testosterone undecanoate | C17β | Undecanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 11 | 1.58 | 0.63 | 6.7–9.2 | ||
| Testosterone buciclated | C17β | Bucyclic acide | Cyclic carboxylic acid | – (~9) | 1.58 | 0.63 | 7.9–8.5 | ||
| Footnotes: a = Length of ester in carbon atoms for straight-chain fatty acids or approximate length of ester in carbon atoms for aromatic or cyclic fatty acids. b = Relative testosterone content by weight (i.e., relative androgenic/anabolic potency). c = Experimental or predicted octanol/water partition coefficient (i.e., lipophilicity/hydrophobicity). Retrieved from PubChem, ChemSpider, and DrugBank. d = Never marketed. e = Bucyclic acid = trans-4-Butylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid. Sources: See individual articles. | |||||||||
| Anabolic steroid | Structure | Ester | Relative mol. weight |
Relative AAS contentb |
Durationc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Moiety | Type | Lengtha | ||||||
| Boldenone undecylenate | C17β | Undecylenic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 11 | 1.58 | 0.63 | Long | ||
| Drostanolone propionate | C17β | Propanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 3 | 1.18 | 0.84 | Short | ||
| Metenolone acetate | C17β | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.14 | 0.88 | Short | ||
| Metenolone enanthate | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.37 | 0.73 | Long | ||
| Nandrolone decanoate | C17β | Decanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 10 | 1.56 | 0.64 | Long | ||
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | C17β | Phenylpropanoic acid | Aromatic fatty acid | – (~6–7) | 1.48 | 0.67 | Long | ||
| Trenbolone acetate | C17β | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.16 | 0.87 | Short | ||
| Trenbolone enanthated | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.41 | 0.71 | Long | ||
| Footnotes: a = Length of ester in carbon atoms for straight-chain fatty acids or approximate length of ester in carbon atoms for aromatic fatty acids. b = Relative androgen/anabolic steroid content by weight (i.e., relative androgenic/anabolic potency). c = Duration by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection in oil solution. d = Never marketed. Sources: See individual articles. | |||||||||
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Richard Lawrence Miller (2002). The Encyclopedia of Addictive Drugs. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 416–. ISBN 978-0-313-31807-8.
Further reading
edit- Vermeulen A (1975). "Longacting steroid preparations". Acta Clin Belg. 30 (1): 48–55. doi:10.1080/17843286.1975.11716973. PMID 1231448.