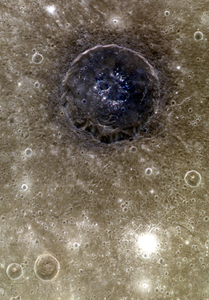
Atget crater is distinctive on the planet Mercury's surface due to its dark color. Atget crater is located within Caloris basin, near Apollodorus crater and Pantheon Fossae. The dark color of the floor of Atget is in contrast to other craters within Caloris basin that exhibit bright materials on their floors, such as the craters Kertész and Sander. Other craters on Mercury, such as Bashō and Neruda, have halos of dark material but the dark material does not cover the crater floors.
 Atget is the dark crater in the lower middle of this MESSENGER photograph, from the first flyby in January 2008 | |
| Feature type | Impact crater |
|---|---|
| Location | Raditladi quadrangle, Mercury |
| Coordinates | 25°39′N 193°56′W / 25.65°N 193.93°W |
| Diameter | 100 km (62 mi) |
| Eponym | Eugène Atget |
A confirmed dark spot is present in Atget.[1]
The crater's name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 2008, shortly after its discovery on the first flyby of MESSENGER. It is named for the French photographer Eugène Atget.[2]
-
Closeup of Atget also from MESSENGER
-
Atget crater in exaggerated color
References
edit- ^ Zhiyong Xiao, Robert G. Strom, David T. Blewett, Paul K. Byrne, Sean C. Solomon, Scott L. Murchie, Ann L. Sprague, Deborah L. Domingue, Jörn Helbert, 2013. Dark spots on Mercury: A distinctive low-reflectance material and its relation to hollows. Journal of Geophysical Research Planets. doi.org/10.1002/jgre.20115
- ^ "Atget". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. NASA. Retrieved 10 February 2020.