The buccal nerve (long buccal nerve) is a sensory nerve of the face arising from the mandibular nerve (CN V3) (which is itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve). It conveys sensory information from the skin of the cheek, and parts of the oral mucosa, periodontium, and gingiva.
| Buccal nerve | |
|---|---|
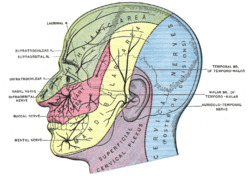 Sensory areas of the head, showing the general distribution of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (buccal nerve labeled at center left) | |
 | |
| Details | |
| From | Mandibular nerve |
| Innervates | Lateral pterygoid muscle and cheek |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus buccalis |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.073 |
| TA2 | 6258 |
| FMA | 53066 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Structure
editOrigin
editThe buccal nerve is a branch of the anterior division of the mandibular nerve (CN V3). It is the only sensory branch of the anterior division.[1]
Course and relations
editAfter branching from the anterior trunk of the mandibular nerve (CN V3), the buccal nerve passes between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle,[2][3] underneath the tendon of the temporalis muscle.[3] It then passes anterior to the ramus of the mandible to first course deep to the masseter muscle, and finally[2] anteroinferiorly[1] upon surface of the buccinator muscle[2][1] before piercing this muscle.[1]
Communications
editIt connects with the buccal branches of the facial nerve on the surface of the buccinator muscle. It gives off many significant branches.[4]
Distribution
editThe buccal nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin of the cheek, the buccal mucosa, buccal periodontium, and gingiva of mandibular/lower molar[2] and second premolar teeth (until the mental foramen). It also issues proprioceptive fibres into the buccinator muscle.[1]
Clinical significance
editAnesthesia
editBuccal nerve block (long buccal nerve block) is indicated for procedures involving the mucosa adjacent to the posterior molar teeth, such as the placement of a rubber dam clamp. The injection site is distal and buccal to the third molar, with the needle penetrating 1-2mm as the nerve lies directly below the mucosa.[5] A buccal nerve block is carried out after an inferior alveolar nerve block for specific procedures, such as extraction of mandibular molar teeth.
Surgical damage
editThe buccal nerve may be damaged by surgical incisions near the external oblique ridge of the mandible.[3][4]
Additional images
edit-
The nerves of the scalp, face, and side of neck.
-
Infaorbital and buccal nerve. Superficial dissection. Lateral view.
References
edit- "Nerve, buccal." Stedman's Medical Dictionary, 27th ed. (2000). ISBN 0-683-40007-X
- Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. (2005). ISBN 0-443-07168-3
- Specific
- ^ a b c d e Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). pp. 364–365. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ a b c d Fehrenbach, Margaret J.; Herring, Susan W. (2017). Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck (5th ed.). St. Louis: Elsevier. pp. 188–189. ISBN 978-0-323-39634-9.
- ^ a b c Hendy, C. W.; Robinson, P. P. (1994-12-01). "The sensory distribution of the buccal nerve". British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 32 (6): 384–386. doi:10.1016/0266-4356(94)90030-2. ISSN 0266-4356. PMID 7848999.
- ^ a b Hendy, C. W; Smith, K. G; Robinson, P. P (1996-10-01). "Surgical anatomy of the buccal nerve". British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 34 (5): 457–460. doi:10.1016/S0266-4356(96)90108-4. ISSN 0266-4356. PMID 8909743.
- ^ Malamed, Stanley (2012). Handbook of Local Anesthesia. Elsevier. p. 234. ISBN 9780323074131.
External links
edit- Anatomy figure: 27:03-03 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb3.htm
- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (mandibularnerve)
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)