Bullacephalus is an extinct genus of biarmosuchian therapsids belonging to the family Burnetiidae. The type species B. jacksoni was named in 2003. It is known from a relatively complete skull and lower jaw, discovered in the Late Permian Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group of South Africa.[1] This genus of therapsida lived during the Late Permian period, approximately 250 million years ago.
| Bullacephalus Temporal range: Late Permian
| |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Suborder: | †Biarmosuchia |
| Family: | †Burnetiidae |
| Genus: | †Bullacephalus Rubidge and Kitching, 2003 |
| Species: | †B. jacksoni
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Bullacephalus jacksoni Rubidge and Kitching, 2003
| |
The name Bullacephalus comes from the Latin words "bullatus," meaning "bossed" or "knobbed," and "cephalus," meaning "head." This name refers to the distinctive bony knob on the top of the therapsid's skull, which contributes to the history of this genus. This stem based taxon includes Ictidorhinus or Hippasaurs. Bullacephalus can even be characterized as having "skull moderately to greatly pachyostotic; swollen boss present above the postorbital bar formed by the postfrontal and postorbital; deep linear sculpturing of the snout; exclusion of the jugal from the lateral temporal fenestra".[2] [3][4] Further research into the morphology, phylogenetics, and ecology of Bullacephalus and other Burnetiamorpha will likely continue to yield insights into the evolution of therapsids and the complex history of life on Earth.
Taxonomy
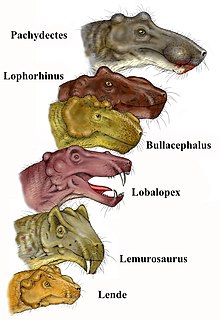
editDespite the limited amount of fossil material available, Bullacephalus has generated considerable interest among paleontologists due to its unique morphology and uncertain taxonomic classification. It is a part of the Burnetiamorpha suborder. Currently, the Burnetiamorpha comprise nine genera: Bullacephalus, Burnetia, Lemurosaurus, Lobalopex, Lophorhinus, Paraburnetia, and Pachydectes from South Africa. (Kruger et al., 2015).[5] Some researchers have suggested that Bullacephalus are a type of Therapsida: Biarmoschia, related to the successful tetrapod Anomadontia helping researchers understand the basic morphology. This specific therapsid could be distinguished by the short snout, septomaxilla, and has a short facial exposure between nasal and maxilla, along with many other skull characteristics. Its unique morphology, particularly its short snout and septomaxilla, have led researchers to speculate about its feeding habits and ecological niche.
References
edit[6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15]
- ^ Rubidge, Bruce S.; Kitching, James W. (2003-11-24). "A new burnetiamorph (Therapsida: Biarmosuchia) from the Lower Beaufort Group of South Africa". Palaeontology. 46 (1): 199–210. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00294. ISSN 0031-0239.
- ^ Day, Michael; Rubidge, Bruce; Abdala, Fernando (2016). "A new mid-Permian burnetiamorph therapsid from the Main Karoo Basin of South Africa and a phylogenetic review of Burnetiamorpha". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 61. doi:10.4202/app.00296.2016. ISSN 0567-7920.
- ^ Rubidge, Bruce S.; Kitching, James W. (January 2003). "A new burnetiamorph (Therapsida: Biarmosuchia) from the Lower Beaufort Group of South Africa". Palaeontology. 46 (1): 199–210. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00294. ISSN 0031-0239.
- ^ Liu, Jun; Rubidge, Bruce; Li, Jinling (2009-07-29). "A new specimen of Biseridens qilianicus indicates its phylogenetic position as the most basal anomodont". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 277 (1679): 285–292. doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.0883. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 2842672. PMID 19640887.
- ^ Kruger, Ashley; Rubidge, Bruce S.; Abdala, Fernando; Chindebvu, Elizabeth Gomani; Jacobs, Louis L. (2015-10-29). "Lende chiweta, a new therapsid from Malawi, and its influence on burnetiamorph phylogeny and biogeography". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (6): e1008698. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.1008698. ISSN 0272-4634.
- ^ Day, Michael O.; Smith, Roger M. H.; Benoit, Julien; Fernandez, Vincent; Rubidge, Bruce S. (2018-04-29). Angielczyk, Kenneth (ed.). "A new species of burnetiid (Therapsida, Burnetiamorpha) from the early Wuchiapingian of South Africa and implications for the evolutionary ecology of the family Burnetiidae". Papers in Palaeontology. 4 (3): 453–475. doi:10.1002/spp2.1114. ISSN 2056-2799.
- ^ Day, Michael; Rubidge, Bruce; Abdala, Fernando (2016). "A new mid-Permian burnetiamorph therapsid from the Main Karoo Basin of South Africa and a phylogenetic review of Burnetiamorpha". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 61. doi:10.4202/app.00296.2016. ISSN 0567-7920.
- ^ Kruger, Ashley; Rubidge, Bruce S.; Abdala, Fernando; Chindebvu, Elizabeth Gomani; Jacobs, Louis L. (2015-11-02). "Lende chiweta , a new therapsid from Malawi, and its influence on burnetiamorph phylogeny and biogeography". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (6): e1008698. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.1008698. ISSN 0272-4634.
- ^ Sidor, C. A.; Welman, J. (2003-09-12). "A second specimen of Lemurosaurus pricei (Therapsida: Burnetiamorpha)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 23 (3): 631–642. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2003)023[0631:ASSOLP]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634.
- ^ Sidor, Christian A.; Hopson, James A.; Keyser, André W. (2004-12-10). "A new burnetiamorph therapsid from the Teekloof Formation, Permian, of South Africa". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 24 (4): 938–950. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2004)024[0938:ANBTFT]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634.
- ^ Kammerer, Christian F.; Sidor, Christian A. (2021-01-13). Angielczyk, Kenneth (ed.). "A new burnetiid from the middle Permian of Zambia and a reanalysis of burnetiamorph relationships". Papers in Palaeontology. 7 (3): 1261–1295. doi:10.1002/spp2.1341. ISSN 2056-2799.
- ^ Liu, Jun; Rubidge, Bruce; Li, Jinling (2010-01-22). "A new specimen of Biseridens qilianicus indicates its phylogenetic position as the most basal anomodont". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 277 (1679): 285–292. doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.0883. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 2842672. PMID 19640887.
- ^ Sidor, Christian A. (2003). "The naris and palate of Lycaenodon longiceps (Therapsida: Biarmosuchia), by comments on their early evolution in the Therapsida". Journal of Paleontology. 77 (5): 977–984. doi:10.1666/0022-3360(2003)077<0977:TNAPOL>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0022-3360.
- ^ Smith, Roger M. H.; Rubidge, Bruce S.; Sidor, Christian A. (2006-06-12). "A new burnetiid (Therapsida: Biarmosuchia) from the Upper Permian of South Africa and its biogeographic implications". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 26 (2): 331–343. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2006)26[331:ANBTBF]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634.
- ^ Rubidge, Bruce S.; Kitching, James W. (January 2003). "A new burnetiamorph (Therapsida: Biarmosuchia) from the Lower Beaufort Group of South Africa". Palaeontology. 46 (1): 199–210. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00294. ISSN 0031-0239.