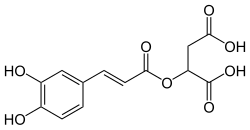
Caffeoylmalic acid is an ester of caffeic acid and malic acid found in the leaves and flowers of Parietaria officinalis.[1] It is also found in Chelidonium majus[2] and Urtica dioica.[3]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-[(E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxybutanedioic acid
| |
| Other names
(+)-(E)-caffeoyl-L-malic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H12O8 | |
| Molar mass | 296.231 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ Budzianowski J (January 1990). "Caffeoylmalic and two pyrrole acids from Parietaria officinalis". Phytochemistry. 29 (10): 3299–301. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(90)80203-S.
- ^ Hahn R, Nahrstedt A (February 1993). "Hydroxycinnamic Acid Derivatives, Caffeoylmalic and New Caffeoylaldonic Acid Esters, from Chelidonium majus". Planta Medica. 59 (1): 71–5. doi:10.1055/s-2006-959608. PMID 17230338.
- ^ Farahpour, MR (January 2015). "Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of hydroethanolic extract of Urtica dioica" (PDF). Int. J. Biol. Pharm. Allied Sci. 4 (1): 165–167 – via Google Scholar.