Caramiphen is an anticholinergic drug used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.[1] In combination with phenylpropanolamine it is used as a cough suppressant and nasal decongestant to treat symptoms associated with respiratory illnesses such as cold, allergies, hay fever, and sinusitis.[2] It was added to the British National Formulary in 1963, with a dosage of 10 to 20 mg. Side effects include nausea, dizziness, and drowsiness.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Carafen |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.922 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
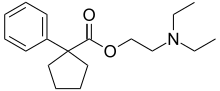
| Formula | C18H27NO2 |
| Molar mass | 289.419 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
It binds to the sigma-1 receptor with an IC50 value of 25 nM.[4]
References
edit- ^ "Caramiphen". drugs.com. Retrieved 26 September 2012.
- ^ "Caramiphen with phenylpropanolamine-oral, Ordrine AT, Rescaps-D, Tuss Vernade, Tusso-Gest". medicine.net. Archived from the original on 29 October 2012. Retrieved 26 September 2012.
- ^ Beirn SF, Lavelle S (May 1964). "To-day's drugs: Cough suppressants". British Medical Journal. 1 (5391): 1165–1167. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.5391.1165. PMC 1813498. PMID 14120813.
- ^ Musacchio JM, Klein M (June 1988). "Dextromethorphan binding sites in the guinea pig brain". Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology. 8 (2): 149–156. doi:10.1007/BF00711241. PMID 3044591. S2CID 33844132.