Carmotetraviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses. There is only one genus in this family, Alphacarmotetravirus, which has one species: Providence virus. Lepidopteran insects serve as natural hosts.[1][2]
| Carmotetraviridae | |
|---|---|
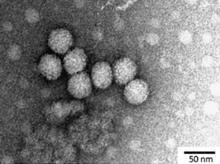
| |
| Transmission electron micrograph of providence virus (PrV) virion | |

| |
| Genome of providence virus (PrV). | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Kitrinoviricota |
| Class: | Tolucaviricetes |
| Order: | Tolivirales |
| Family: | Carmotetraviridae |
| Genus: | Alphacarmotetravirus |
Structure
editViruses in Carmotetraviridae are non-enveloped, with icosahedral geometries, and T = 4 symmetry. The virion diameter is around 40 nm.[1]
Genome
editGenomes are linear, around 6.1kb in length. The genome codes for two proteins, and has three open reading frames.[1]
Life cycle
editViral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by penetration into the host cell. Replication follows the positive stranded RNA virus replication model. Positive stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. Translation takes place by suppression of termination. Lepidopteran insects serve as the natural host. Transmission routes are oral and tissue tropism is the midgut.[1]
References
edit- ^ a b c d "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ^ "Virus Taxonomy: 2020 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). March 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2021.