Castilla (sometimes incorrectly spelled Castilloa) is a genus of 3 species of large trees in the family Moraceae, native to Central and South America.[2]
| Castilla | |
|---|---|
| |
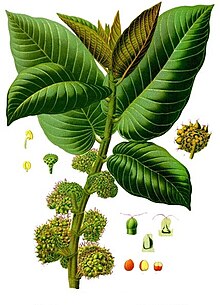
| Castilla elastica | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Moraceae |
| Tribe: | Castilleae |
| Genus: | Castilla Cerv. (1794) |
| Species | |
|
3; see text | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Castilloa Endl. (1837), orth. var. | |
Etymology
editThis genus is named after Juan Diego del Castillo (d. 1793), a Spanish botanist who was a friend of Vicente Cervantes, who chose the name in his friend's honor.[3][4]
Description
editCastilla species are monoecious or dioecious trees up to 40 meters tall, with buttressed trunks and abundant white latex of commercial value.[2] The branchlets have scars left by the fallen stipules. The leaves are oblong to elliptic, with entire margins.[2][5] The inflorescences are surrounded by bracts and have small flowers. The male flowers are borne in lengthwise-folded kidney-shaped inflorescences and female flowers in globose inflorescences.[2][5] The infrutescence varies in shape and has orange or red fruits.[2]
Ecology
editCastilla species exhibit a phenomenon known as cladoptosis, the regular shedding of branches. This may be an adaptation to prevent the growth of climbing plants.[6]
Castilla elastica is a weedy tree which has become invasive in areas where it has been introduced, such as in Tanzania and the South Pacific.[5][7]
Uses
editThe main species is Castilla elastica, one of several plants from which rubber has been extracted. The vernacular name is Panama rubber tree or castilloa rubber. The pre-Columbian MesoAmericans used the latex of this plant to make a ball used in a ceremonial game.
The Miskitu and Mayangna peoples of the Mosquito Coast, stretching from the Honduras to Nicaragua, traditionally made fabric from the bark of the Tunu rubber tree (Castilla tunu).[8]
Species
edit| Image | Common Name | Scientific name | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Panama rubber tree, Castilloa rubber, palo de hule, olicuáhuitl | Castilla elastica Sessé | Mexico, Central America, and northern South America | |
| Castilla tunu Hemsl. | Ecuador, Colombia, Panama, Belize | ||
| Caucho rubber, Caucho Negro | Castilla ulei Warb. | Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador and Colombia |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Castilla Cerv. Plants of the World Online. Retrieved 22 April 2024.
- ^ a b c d e Cardona–Peña, Victor; Fuentes, Alfredo; Cayola, Leslie (2005). "Las moráceas de la región de Madidi, Bolivia" (PDF). Ecología en Bolivia (in Spanish). Retrieved 23 May 2016.
- ^ González, J. "Explicación Etimológica de las Plantas de La Selva" (PDF). Flórula Digital de la Estación Biológica La Selva (in Spanish). Retrieved 23 May 2016.
- ^ Loadman, John (2005). Tears of the Tree: The Story of Rubber –a Modern Marvel. Oxford University Press. pp. 25. ISBN 9780198568407.
- ^ a b c "Castilla elastica (PIER species info)". www.hear.org. Retrieved 2016-05-23.
- ^ Berg, C.C. (1977). "Castilleae, a tribe of the Moraceae, renamed and redefined due to the exclusion of the type genus Olmedia from the Olmedieae". Acta Botanica Neerlandica: 75. Retrieved 23 May 2016.
- ^ "Castilla elastica (Panama Rubber Tree)". BioNET-EAFRINET Keys and Fact Sheets. BioNET-EAFRINET. Retrieved 23 May 2016.
- ^ Chavez Helm, Jasmine. "Tunu: A cloth of necessity, spirituality & resistance". The Critical Pulse SDU.