This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2010) |
The cavernous nerve plexus (also called the Walther plexus[1]) is situated below and medial to that part of the internal carotid artery which is placed by the side of the sella turcica in the cavernous sinus, and is formed chiefly by the medial division of the internal carotid nerve.
| Cavernous nerve plexus | |
|---|---|
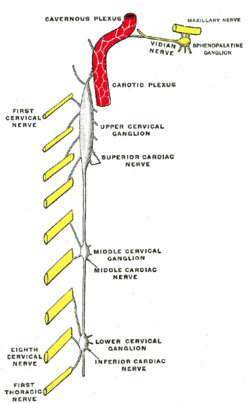 Diagram of the cervical sympathetic. (Cavernous nerve plexus labeled at top.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plexus cavernosus |
| TA98 | A14.3.03.006 |
| TA2 | 6650 |
| FMA | 67563 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
It communicates with the oculomotor, the trochlear, the ophthalmic and the abducent nerves, and with the ciliary ganglion, and distributes filaments to the wall of the internal carotid artery.
The branch of communication with the oculomotor nerve joins that nerve at its point of division; the branch to the trochlear nerve joins it as it lies on the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus; other filaments are connected with the under surface of the ophthalmic nerve; and a second filament joins the abducent nerve.
Additional images
edit-
Plan of oculomotor nerve.
References
edit- ^ Burdan, F.; Dworzański, W.; Cendrowska-Pinkosz, M.; Burdan, M.; Dworzańska, A. (2016). "Anatomical eponyms — unloved names in medical terminology". Folia Morphol. 75 (4): 413–438. doi:10.5603/FM.a2016.0012. PMID 27830870.
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 978 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)