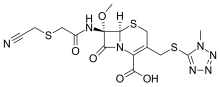
Cefmetazole is a cephamycin antibiotic, usually grouped with the second-generation cephalosporins.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a601206 |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.877 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H17N7O5S3 |
| Molar mass | 471.53 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Adverse effects
editThe chemical structure of cefmetazole, like that of several other cephalosporins, contains an N-methylthiotetrazole (NMTT or 1-MTT) side chain. As the antibiotic is broken down in the body, it releases free NMTT, which can cause hypoprothrombinemia (likely due to inhibition of the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase) and a reaction with ethanol similar to that produced by disulfiram, due to inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase.[1]
Spectrum of bacterial susceptibility
editCefmetazole is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antimicrobial and has been effective in treating bacteria responsible for causing urinary tract and skin infections. [citation needed]The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant microorganisms.
- Bacteroides fragilis: 0.06 - >256 μg/ml
- Clostridioides difficile: 8 - >128 μg/ml
- Staphylococcus aureus: 0.5 - 256 μg/ml (includes MRSA)[2]
References
edit- ^ Stork CM (2006). "Antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals". In Nelson LH, Flomenbaum N, Goldfrank LR, Hoffman RL, Howland MD, Lewin NA (eds.). Goldfrank's toxicologic emergencies. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 847. ISBN 0-07-143763-0. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
- ^ "Cefmetazole, free acid Susceptibility and Concentration Range (μg/ml) Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Data" (PDF). The Antimicrobial Index. TOKU-E. 6 January 2020.