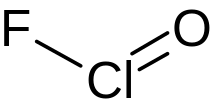
Chlorosyl fluoride is an inorganic compound of chlorine, fluorine, and oxygen with the chemical formula OClF.[1][2][3]
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| ClFO | |
| Molar mass | 70.45 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Synthesis
edit- Partial hydrolysis of chlorine trifluoride in diluted gas phase at low temperatures.[4]
- Reaction of chlorine trifluoride with nitric acid.[4]
Chemical properties
editChlorosyl fluoride is thermolabile and disproportionates to ClF and ClO
2F.:[4]
- 2FClO → ClF + FClO2
- 2FClO → 2ClF +O2
References
edit- ^ Müller, Holger S. P (10 December 1999). "Infrared spectroscopy and molecular properties of chlorosyl fluoride, FClO". Chemical Physics Letters. 314 (5): 396–402. Bibcode:1999CPL...314..396M. doi:10.1016/S0009-2614(99)01197-5. ISSN 0009-2614.
- ^ Müller, Holger S. P.; Cohen, Edward A. (8 February 2002). "The molecular properties of chlorosyl fluoride, FClO, as determined from the ground-state rotational spectrum". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 116 (6): 2407–2416. Bibcode:2002JChPh.116.2407M. doi:10.1063/1.1433002. ISSN 0021-9606.
- ^ Vogt, J. (2011). "755 ClFO Chlorosyl fluoride". Asymmetric Top Molecules. Part 3. Landolt-Börnstein - Group II Molecules and Radicals. 29D3. Springer Berlin Heidelberg: 296–298. Bibcode:2011LanB.29D3..296V. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-14145-4_177. ISBN 978-3-642-14144-7.
- ^ a b c Haupt, Axel (22 March 2021). Organic and Inorganic Fluorine Chemistry: Methods and Applications. Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG. p. 139. ISBN 978-3-11-065933-7. Retrieved 27 March 2023.