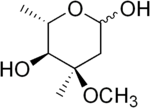
Cladinose is a hexose deoxy sugar that in several antibiotics (such as erythromycin) is attached to the macrolide ring.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4R,5S,6S)-4-Methoxy-4,6-dimethyl-tetrahydropyran-2,5-diol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H16O4 | |
| Molar mass | 176.21 g/mol |
| Density | 1.156 g/mL |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
In ketolides, a relatively new class of antibiotics, the cladinose is replaced with a keto group.
External links
edit- Cladinose at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- PubChem
- Diagrams