Crotylsarin (CRS) is an extremely toxic organophosphate nerve agent of the G-series.[1] Like other nerve agents, CRS irreversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase. However, since the inhibited enzyme ages so rapidly, it can't be reactivated by cholinesterase reactivators.[2][3]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
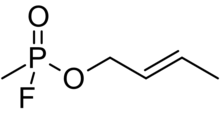
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-But-2-en-1-yl methylphosphonofluoridate | |
| Other names
CRS
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10FO2P | |
| Molar mass | 152.105 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Worek, Franz; Wille, Timo; Koller, Marianne; Thiermann, Horst (27 June 2016). "Toxicology of organophosphorus compounds in view of an increasing terrorist threat". Archives of Toxicology. 90 (9): 2131–2145. doi:10.1007/s00204-016-1772-1. PMID 27349770. S2CID 15724842.
- ^ Busker, R.W.; Zijlstra, J.J.; van der Wiel, H.J.; Melchers, B.P.C.; van Helden, H.P.M. (January 1991). "Organophosphate poisoning: a method to test therapeutic effects of oxamines other than acetylcholinesterase activation in the rat". Toxicology. 69 (3): 331–344. doi:10.1016/0300-483x(91)90191-3. PMID 1658986.
- ^ Soukup, O.; Jun, D.; Tobin, G.; Kuca, K. (21 November 2012). "The summary on non-reactivation cholinergic properties of oxime reactivators: the interaction with muscarinic and nicotinic receptors". Archives of Toxicology. 87 (4): 711–719. doi:10.1007/s00204-012-0977-1. PMID 23179755. S2CID 18252681.